Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. May 1, 2004; 10(9): 1310-1314
Published online May 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i9.1310
Published online May 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i9.1310
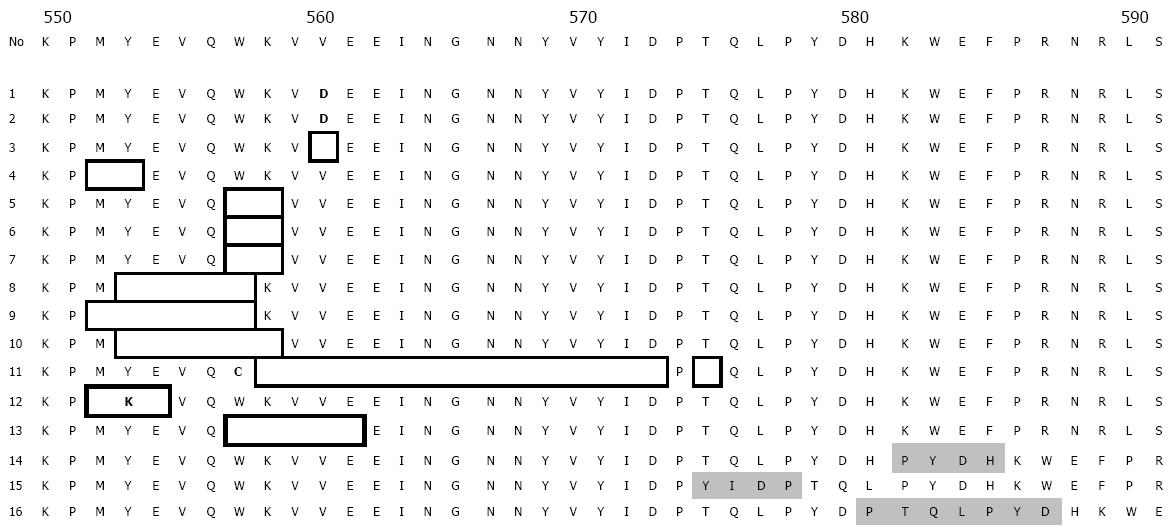
Figure 1 Exon 11 of c-kit mutations in 16 GIST samples.
The wild-type sequence of amino acids encoded by exon 11 is shown at the top. The sequence starting at codon 550 and ending at 590. The wide-type sequence is shown above, the numbers are shown at the left. Point mutation is shown in black type, deletion is shown in the thin line indicates heterozygote mutation and thick line indicates homozygote ones. the shaded areas correspond to insertion or duplication mutations.
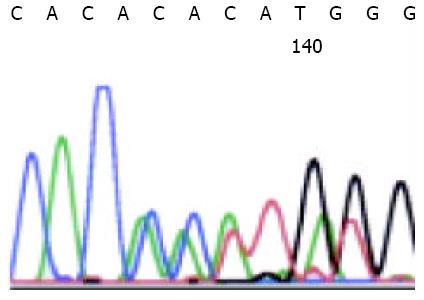
Figure 2 Duplication of codons from 581 to 584 (PYDH) in one case of GIST by direct sequencing of c-kit exon 11.
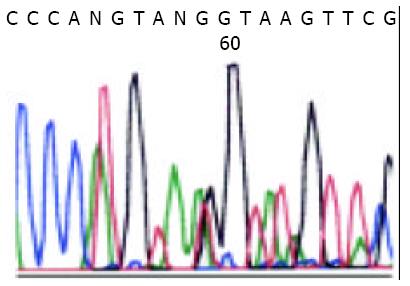
Figure 3 Deletion of codon from 553 to 557 (YEVQW) by direct sequencing of c-kit exon 11.
- Citation: Hou YY, Tan YS, Sun MH, Wei YK, Xu JF, Lu SH, A-Ke-Su SJ, Zhou YN, Gao F, Zheng AH, Zhang TM, Hou WZ, Wang J, Du X, Zhu XZ. C-kit gene mutation in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(9): 1310-1314
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i9/1310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i9.1310