Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2004; 10(20): 2994-2996
Published online Oct 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2994
Published online Oct 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2994
Figure 1 Inhibitory effect of SBC on H pylori GGT activity Inhibition of 85%, 92%, 94%, 95% and 96% were obtained by incubating H pylori in 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 mmol/L SBC, respectively at 37 for 30 min.
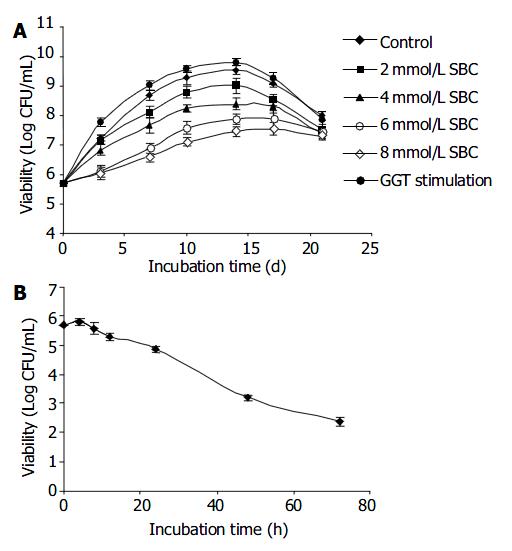
Figure 2 Effect of GGT on the growth of H pylori.
H pylori strain NCTC 11 637 was cultured microaerobically in BHI broth medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 °C nd in the presence of either different concentration of GGT inhibitor or stimulator. A: Effect of 2 mmol/L ( ■square), 4 mmol/L (▲triangle), 6 mmol/L (× ross), 8 mmol/L (* star) SBC and GGT stimulation (0.1 mol/L GSH +1 mol/L glycyl-glycine,●ircle) on NCTC 11637 over 21 d. Control (◆iamond). B: Effect of 10 mmol/L SBC on NCTC 11637 over 72 h. Viability was determined continuously at time intervals. (CFU: colony-forming units).
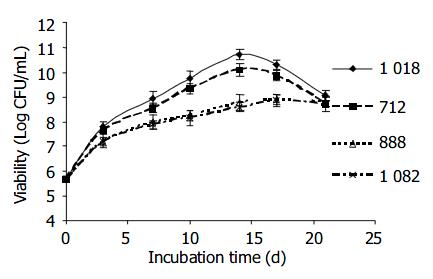
Figure 3 Growth of 4 H pylori strains with different levels of GGT activity H pylori strains 1018 and 712 expressed high GGT activity ( > 1 U/mg protein) while strains 888 and 1082 produced low GGT activity ( < 0.
4 U/mg protein). H pylori strains 1018 (diamond), 712 (■square), 888 (△triangle), and 1 082 ( × cross) were cultured in BHI medium microaerobically over 3 wk. Viability was determined continuously at time intervals.
-
Citation: Gong M, Ho B. Prominent role of γ -glutamyl-transpeptidase on the growth of
Helicobacter pylori . World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(20): 2994-2996 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i20/2994.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2994