Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 15, 2004; 10(14): 2103-2108
Published online Jul 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2103
Published online Jul 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2103
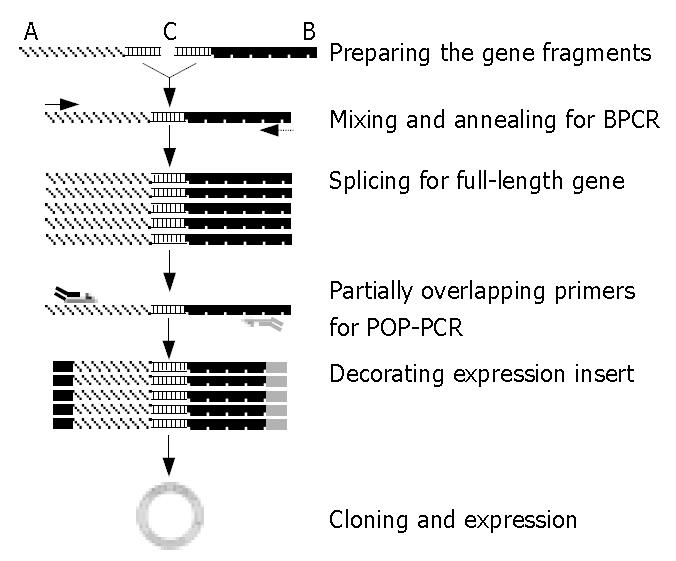
Figure 1 Experimental design and steps involved in bridging PCR (BPCR) and partially overlapping primer-based PCR (POP-PCR).
Gene fragments A and B had the junction region C. Under specific temperature conditions, the fragments would anneal together to form the template molecule, thus triggering the amplification cascade. The partially overlapping primers at each site of the template ends contained two primers pre-mixed in a certain molar ratio that had sequence identity but with different lengths. All the short primers located at the out-ward overhang region. The sequences of all primers used are shown in Table 1.
Figure 2 cDNA sequence of novel allergen gene D106 from short ragweed pollens.
The five shadowed regions represent the primer sites, Sg1p5, S5D106, S3D10, DEN3 and RAC3.
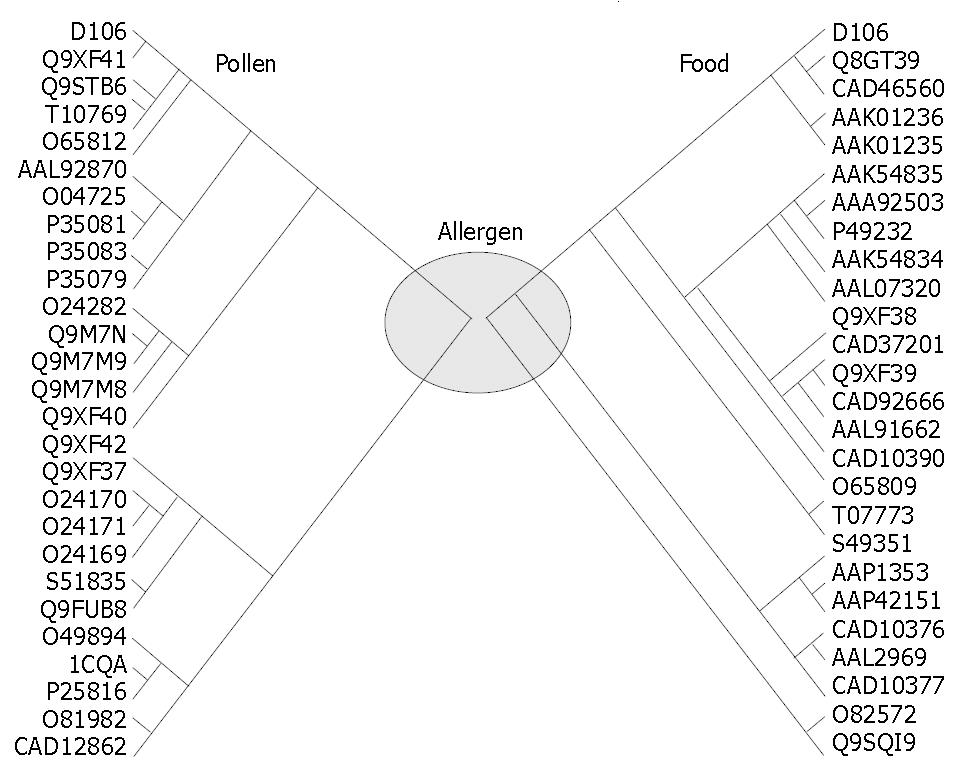
Figure 3 Phylogenetic relationships between newly obtained pollen allergen D106 (Amb a 8(D106)) and its cognates from GenBank as inferred from CLUSTAL W (1.
82) alignment of the amino acid sequences. Amb a 8(D106) shared a homology as highly as 54%-89% with different pollen allergens (from mugwort CAD12862 to apple Q9XF41) and as 79%-89% with different food allergens (from peanut Q9SQI9 to peach Q8GT39).
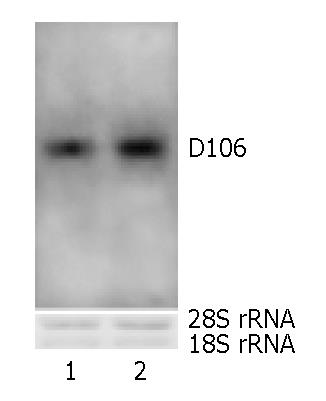
Figure 4 Northern blot profile confirming RNA derivation of cDNA of the newly obtained gene D106.
Lane 1, total RNA from calyx and pedicel; Lane 2, total RNA from pollen. Both lanes exhibit obvious bands, suggesting the real RNA derivation of D106.
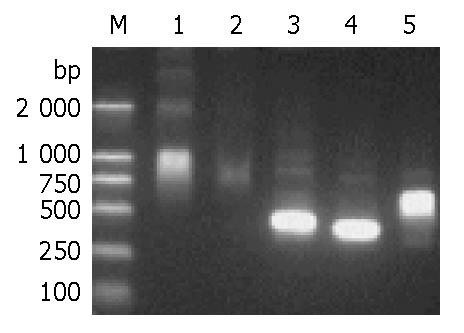
Figure 5 Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products.
The PCR steps were depicted in Figure 1. Template in lanes 1, 2 and 5 is the mixture from gene fragments A and B; while tem-plate in lanes 3 and 4 is the BPCR product (lane 5). Lane 1, primer Sg1P5/RAC3; lane 2, primer POP51/POP31; lane 3, POP-PCR with primer POP51+POP52/POP31+POP32; lane 4, general PCR of the ORF of D106 with primer pair Sg1P5/DEN3; lane 5, BPCR of full-length D106 with primer Sg1P5/RAC3; M, molecular marker.
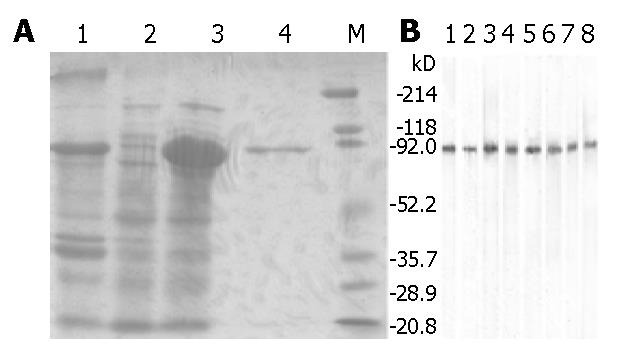
Figure 6 SDS-PAGE analysis (150 g/L) for expression (panel A) and immunoblot of fusion pollen allergen D106 (panel B).
Panel A: 1. Lysate pellet of induced cells; 2. Cells without IPTG induction; 3. Supernatant of induced cell lysate; 4. Purified fusion pollen allergen D106; M. Broad range prestained SDS-PAGE standards (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Panel B: Fusion protein D106 was blotted with 8 serum samples from pollen allergic patients. Each strip represents one serum sample.
- Citation: Tao AL, He SH. Bridging PCR and partially overlapping primers for novel allergen gene cloning and expression insert decoration. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(14): 2103-2108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i14/2103.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2103