Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 15, 2004; 10(14): 2045-2049
Published online Jul 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2045
Published online Jul 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2045
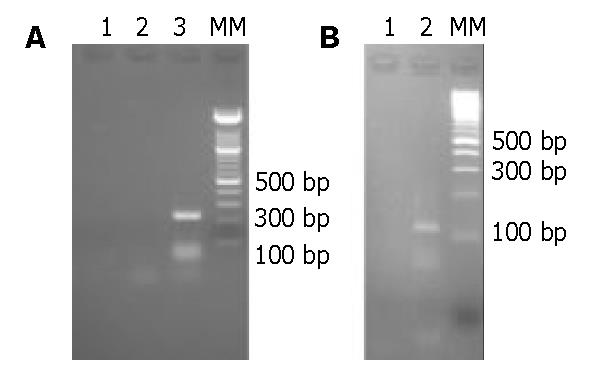
Figure 1 RT-PCR products of 5’ and 3’ RNA of HEV Morocco strain.
A: Products of 5’ RLM-RACE; Lane 1: negative control without template RNA; Lane 2: RNA template without CIP/TAP treated; Lane 3: RNA template treated with CIP and TAP. B: Products of 3’ RACE; Lane 1: negative control without template RNA; Lane 2: products of 3’ RACE; MM: 100 bp ladder.
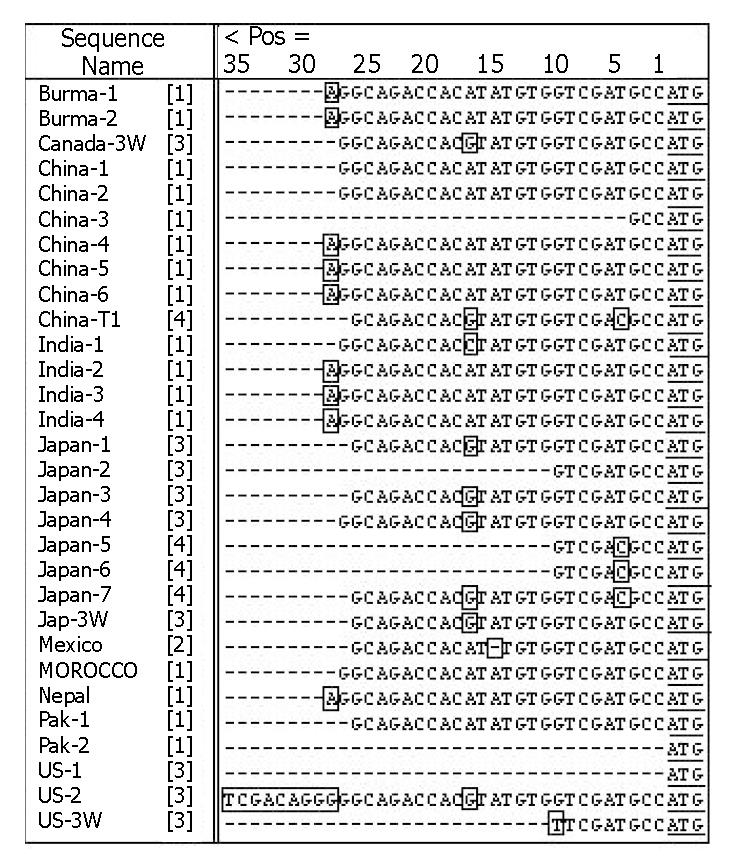
Figure 2 Comparison of sequence in the 5’ UTR of different HEV strains.
The translation initiation codon is underlined. The number in brackets following the strain name is the genotype designation. Changes from the consensus sequence are boxed.
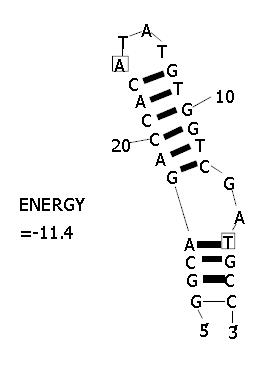
Figure 3 RNA secondary structure of HEV 5’ terminal sequence.
Changes among HEV strains are boxed.
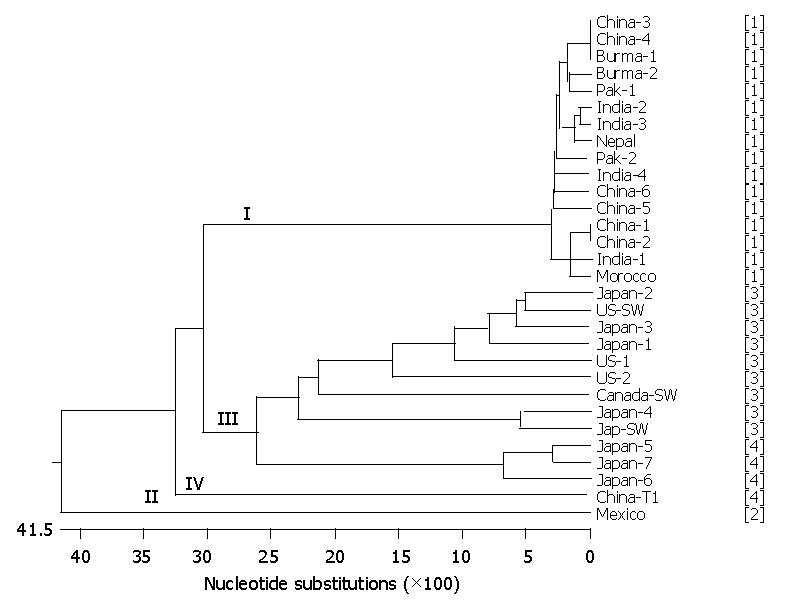
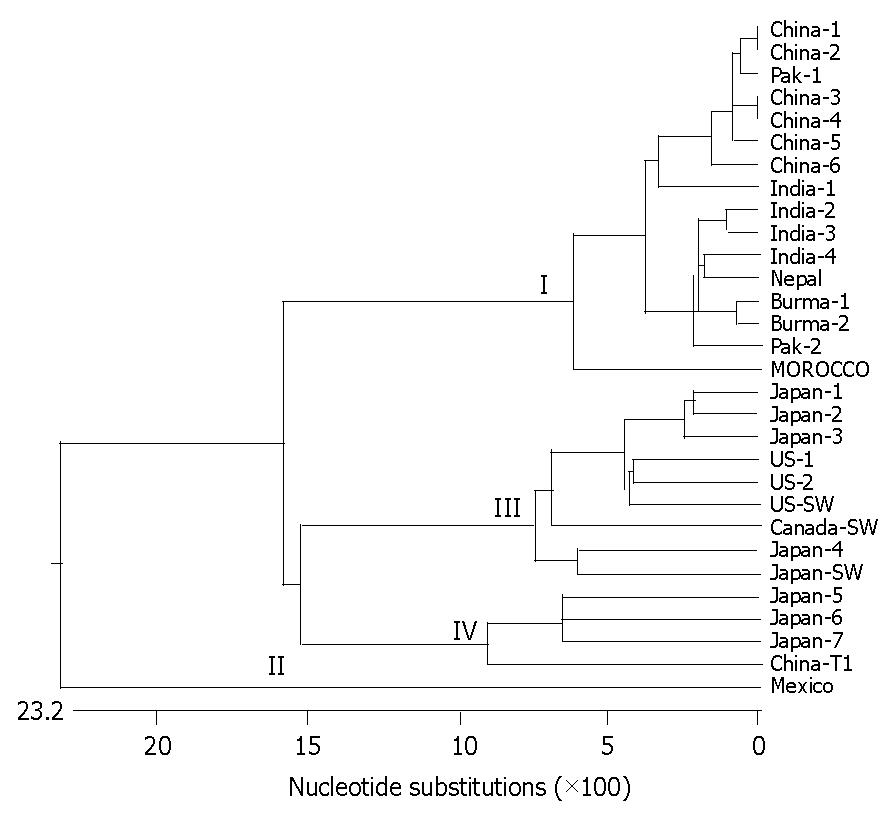
Figure 4 Proposed phylogenetic trees using 3’ UTR sequences of Morocco and other 29 HEV strains.
The Roman number in the tree represents the genotype designation based on the 3’ UTR sequence. The number in brackets following the strain name repre-sents the genotype designation based on the full genome sequence.
Figure 5 Proposed phylogenetic trees using full sequences of 30 HEV strains.
The Roman number in the tree represents the genotype designation.
- Citation: Chen GB, Meng JH. Identification of 5’ capped structure and 3’ terminal sequence of hepatitis E virus isolated from Morocco. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(14): 2045-2049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i14/2045.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2045