Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
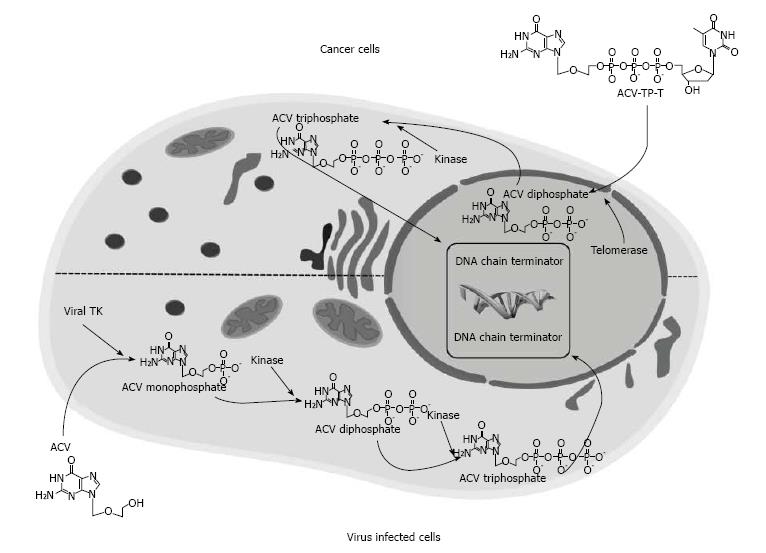
Figure 3 Structure and schematic mode of action of Acycloguanosyl 5’-thymidyltriphosphate in comparison with ACV.
For activation, ACV requires to be phosphorylated to ACV monophosphate by viral TK carried either by wildtype herpes virus or, in the suicide gene therapy, engineered adenovirus. ACV monophosphate is then further phosphorylated by cellular kinases to the triphosphated active form. Conversely, ACV-TP-T is substrate of telomerase that incorporates the thymidine in the replicating telomeres and directly release ACV diphosphate skipping the viral TK phosphorylation step. (Reproduced with permission from Ref [108]. Copyright 2011 AGA Institute). ACV-TP-T: Acycloguanosyl 5’-thymidyltriphosphate; TK: Thymidine kinase.
- Citation: Picariello L, Grappone C, Polvani S, Galli A. Telomerase activity: An attractive target for cancer therapeutics. World J Pharmacol 2014; 3(4): 86-96
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v3/i4/86.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v3.i4.86