Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Crit Care Med. Aug 4, 2017; 6(3): 164-171
Published online Aug 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i3.164
Published online Aug 4, 2017. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i3.164
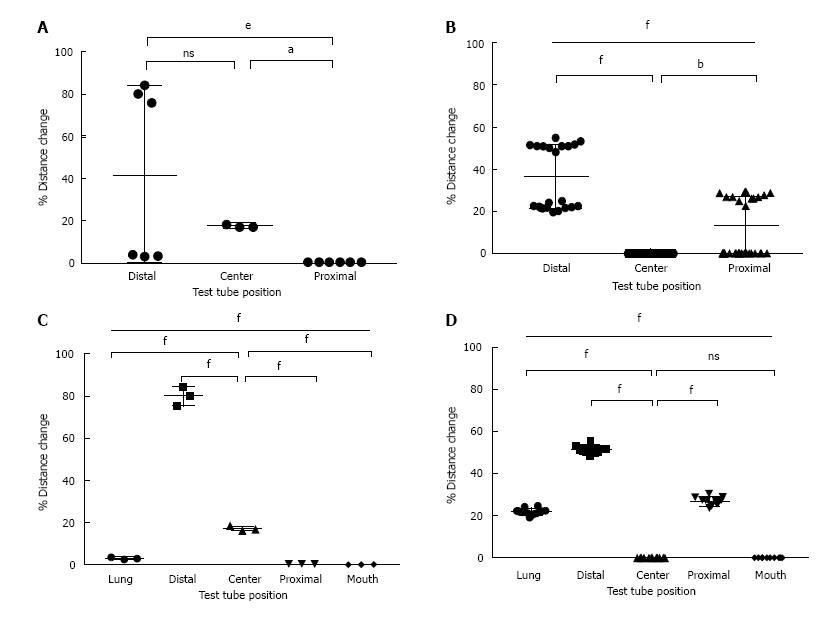
Figure 3 Percent of distance of mucus movement in the different portion of the endotracheal tube in both simulated intrapulmonary percussive ventilation models: mechanical ventilation (A and B) and spontaneous breathing (C and D).
There was an overall statistically significant amount of mucus movement proximally towards the mouth-piece in the spontaneously breathing patient. There was also an overall statistically significant amount of mucus movement distally back towards the lung in the mechanically ventilated model. Statistical significant P values: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001, fP < 0.0001. ns: No statistical significance.
- Citation: Fernandez-Restrepo L, Shaffer L, Amalakuhan B, Restrepo MI, Peters J, Restrepo R. Effects of intrapulmonary percussive ventilation on airway mucus clearance: A bench model. World J Crit Care Med 2017; 6(3): 164-171
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v6/i3/164.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v6.i3.164