Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Jun 18, 2025; 16(6): 104853
Published online Jun 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i6.104853
Published online Jun 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i6.104853
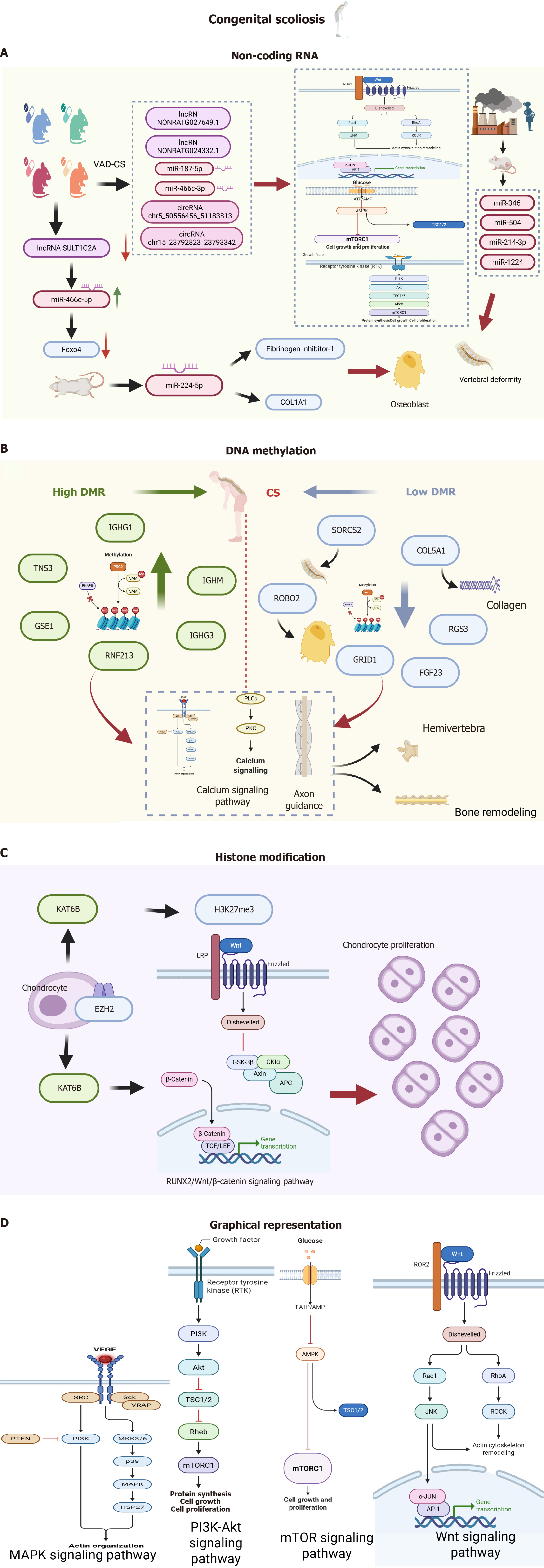
Figure 2 Schematic representation of epigenetic modification mechanisms in congenital scoliosis.
A: Mechanism of non-coding RNA-mediated vitamin A deficiency-induced congenital scoliosis through the regulation of genes such as Forkhead box subclass O protein 4 and collagen type I alpha 1 in a murine model. This process involves various non-coding RNAs, including long-chain non-coding RNA SULT1C2A, as well as microRNAs such as miR-466c-5p and miR-224-5p; B: Alterations in DNA methylation in patients with congenital scoliosis, specifically highlighting the distinctions between hypermethylated genes (e.g., immunoglobulin heavy constant chain gamma 1, tensin-3, and genetic suppressor element 1) and hypomethylated genes (e.g., SORCS2, ROBO2, and collagen type V alpha 1), which play integral roles in several signaling pathways, including the mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, and axonal guidance; C: The influence of histone modifications on chondrocyte proliferation, incorporating key regulatory factors such as lysine acetyltransferase 6B, enhancer of zeste homolog 2, and histone H3 at lysine 27, alongside the associated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway; D: A legend for figures A, B, and C, offering essential clarifications and contexts for the data presented. VAD-CS: Vitamin A deficiency-induced congenital scoliosis; lncRNA: Long noncoding RNA; Foxo4: Forkhead box subclass O protein 4; COL1A1: Collagen type I alpha 1; DMR: Differentially methylated region; CS: Congenital scoliosis; IGHG1: Immunoglobulin heavy constant chain gamma 1; TNS3: Tensin-3; GSE1: Genetic suppressor element 1; RNF213: Ring finger protein 213; IGHM: Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu; COL5A1: Collagen type V alpha 1; GRID1: Glutamate receptor delta 1; FGF23: Fibroblast growth factor 23; RGS3: Regulators of G-protein signaling 3; KAT6B: Lysine acetyltransferase 6B; EZH2: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; H3K27me3: Histone H3 at lysine 27; LRP: Low-density lipoprotein-related protein; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; CKIα: Casein kinase I alpha; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; TCF: T cell factor; LEF: Lymphoid enhancer factor; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; RUNX2: Runt-related transcription factor 2; PLC: Phospholipase C; PKC: Protein kinase C.
- Citation: Zhao R, Zhao JR, Xue X, Ma D. Deciphering the etiology of congenital scoliosis: A genetic and epigenetic perspective. World J Orthop 2025; 16(6): 104853
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i6/104853.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i6.104853