Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
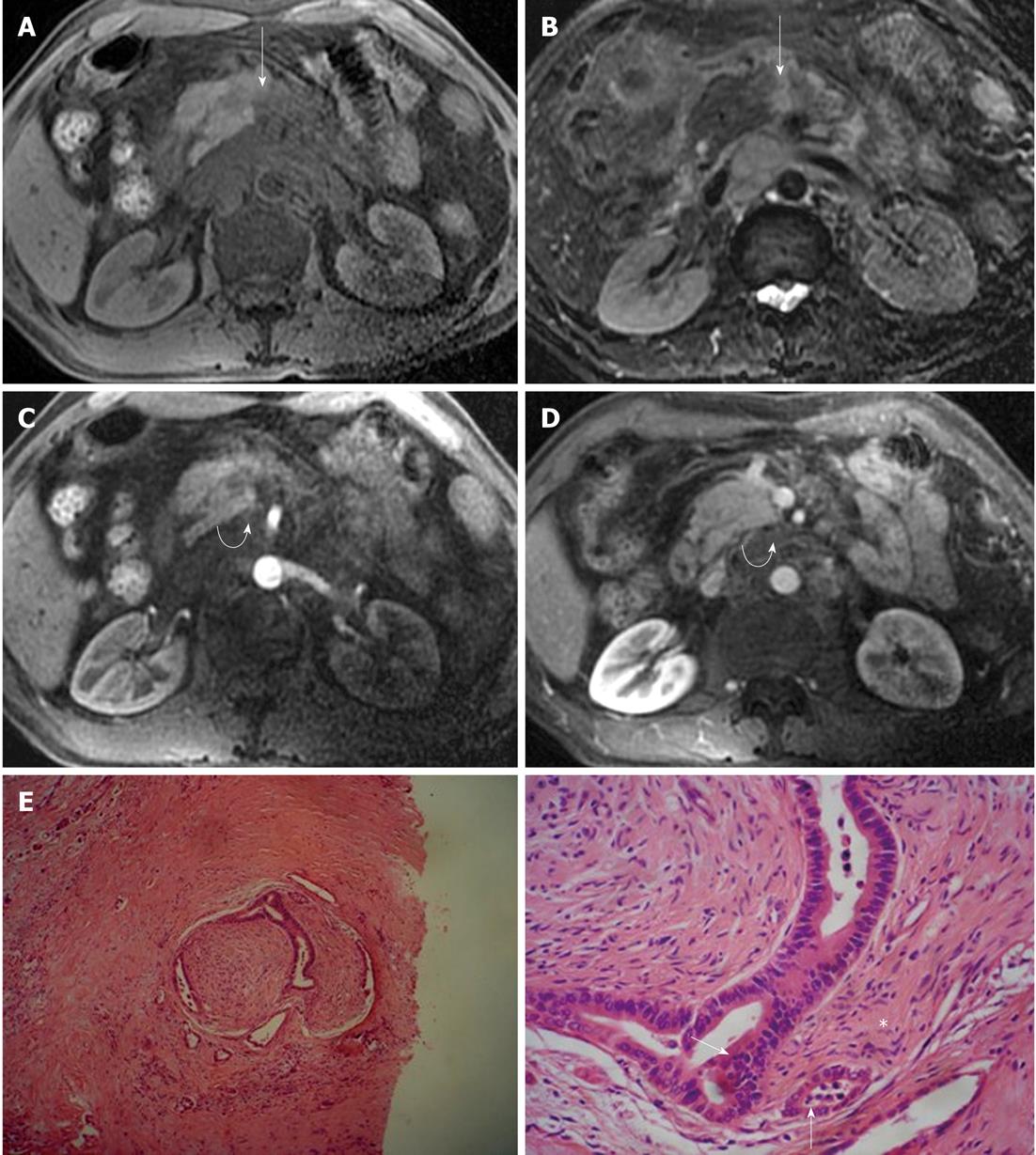
Figure 9 Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of extrapancreatic neural invasion by pancreatic carcinoma in a 48-year-old male.
The tumor (arrows) was located at the body of the pancreas and invaded the extrapancreatic neural plexus, forming a mass (curved arrows), and the adjacent celiac trunk. A: 3D gradient-echo (GRE) T1-weighted non-enhanced image; B: Fat-saturated fast recovery fast spin-echo T2-weighted image; C and D: 3D GRE T1-weighted Gd-enhanced arterial and venous phases. Histopathological images showed extrapancreatic neural (asterisk) invasion by pancreatic carcinoma (arrows); E: HE, 40 ×; F: HE, 200 ×.
- Citation: Zuo HD, Tang W, Zhang XM, Zhao QH, Xiao B. CT and MR imaging patterns for pancreatic carcinoma invading the extrapancreatic neural plexus (Part II): Imaging of pancreatic carcinoma nerve invasion. World J Radiol 2012; 4(1): 13-20
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i1/13.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i1.13