Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2025; 17(6): 107776
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776
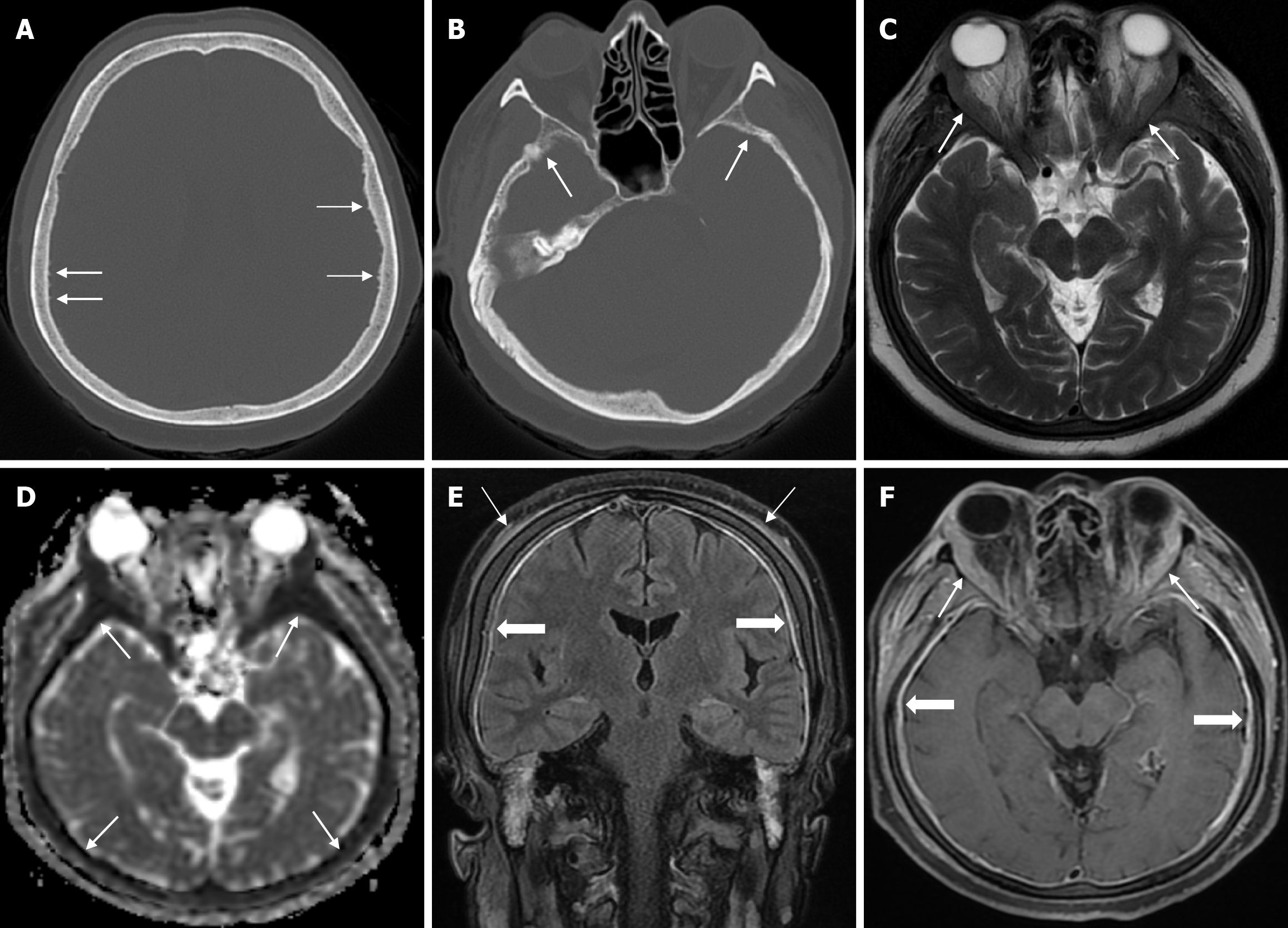
Figure 29 Calvarial involvement of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (B-cell lymphoma) in fifty-six years old female patient.
A and B: Axial computed tomography on the bone window show cortical irregularities (thin arrows) due to spiculated periosteal reactions in the inner table; C: Axial T2-weighted image shows symmetrical soft tissue and hypointense signals (thin arrows) in the vicinity of the orbital bones at the superolateral level of both orbits; D: On apparent diffusion coefficient map shows diffuse diffusion restriction at the diploe distance (thin arrows); E: Coronal contrast enhanced fluid-attenuated inversion recovery T2-weighted image shows diffuse periosteal thickening (solid periosteal reactions) and periosteal contrast enhancement (thin arrows) that may be secondary to inflammatory hyperemia and diffuse dural contrast enhancement (thick arrows); F: Axial fat-saturated contrast enhanced T1-weighted image shows lesions with contrast enhancement and diffuse dural (nodular and smooth) contrast enhancement (thick arrows) with continuity along the inner and outer table in the cranial bones, accompanied by soft tissue components surrounding the bones (thin arrows).
- Citation: Gökçe E, Beyhan M. Review of imaging modalities and radiological findings of calvarial lesions. World J Radiol 2025; 17(6): 107776
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i6/107776.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776