Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2025; 17(6): 107776
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776
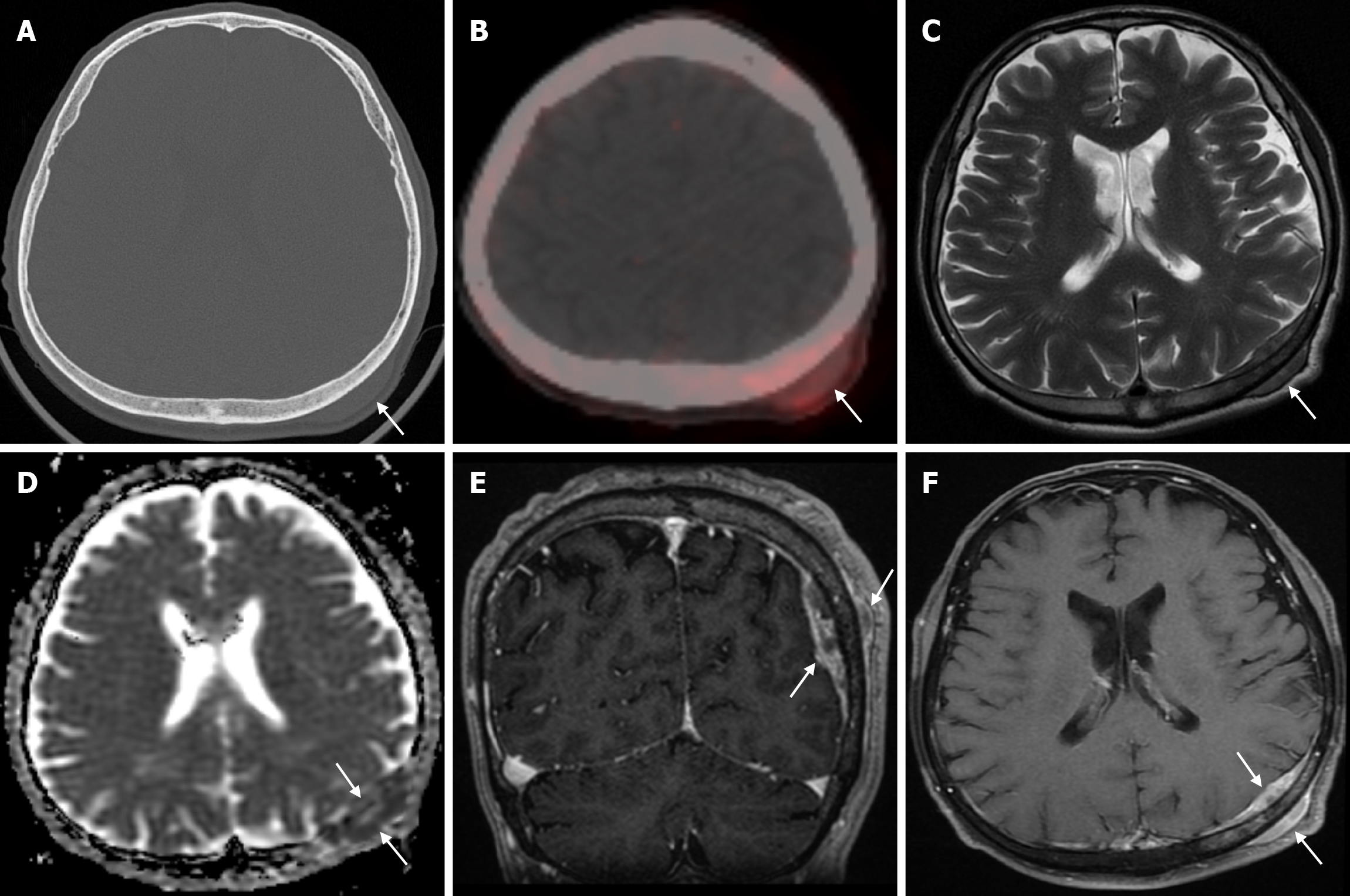
Figure 26 Calvarial solitary metastasis of a lung neuroendocrine tumor in fifty-nine years old male patient.
A: Axial computed tomography on the bone window shows a soft tissue lesion (arrow) in the extra-axial region between the scalp and the parietal bone on the left parietal side and adjacent to the inner table, without obvious deformation of the bone structure; B: Axial 68Ga-DOTATATE positron emission tomography shows heterogeneous, slightly enhanced uptake (SUVmax: 2.22) in the mass lesion in the left parietal scalp (arrow); C: Axial T2-weighted image shows heterogeneous mildly hypointense signal uptake in the left parietal bone and soft tissue components in the scalp (arrows) with extra-axial distance without significant destruction of the cortical surfaces; D: Diffusion restriction in the mass shows on apparent diffusion coefficient map (arrows); E: Coronal contrast enhanced BRAVO image shows contrast enhancement (arrows) in the parietal bone and soft tissue components; F: Axial fat-saturated contrast enhanced T1-weighted image shows intense heterogeneous contrast enhancement (arrows) in the metastatic mass.
- Citation: Gökçe E, Beyhan M. Review of imaging modalities and radiological findings of calvarial lesions. World J Radiol 2025; 17(6): 107776
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i6/107776.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776