Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2025; 17(6): 107776
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776
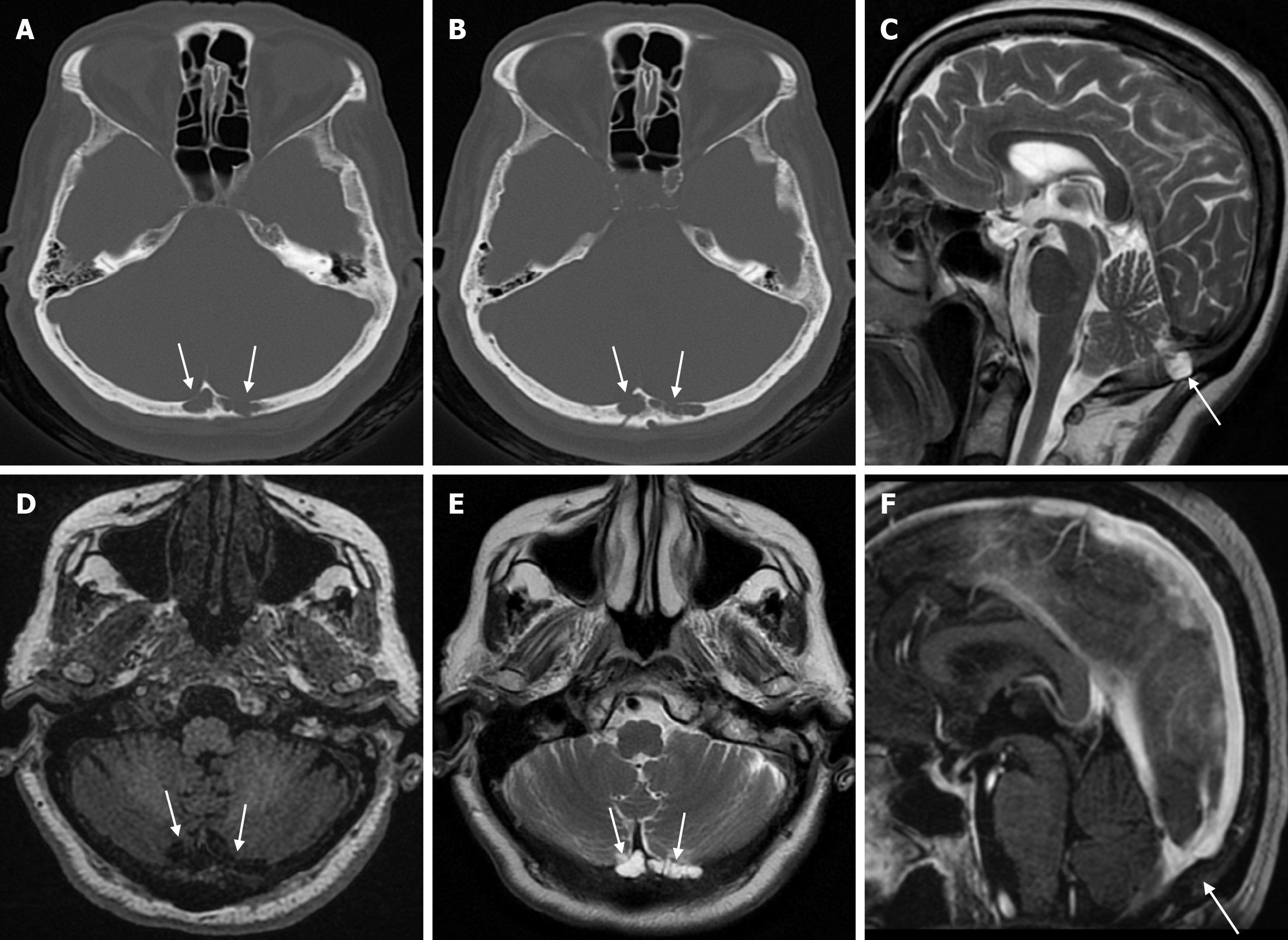
Figure 1 Arachnoid granulations in seventy-eight years old female patient who underwent imaging for headache.
A and B: Axial computed tomography on the bone window show adjacent hypoattenuating structures (arrows) accompanied by cortical destruction in places in the inner table at the level of the internal occipital protuberance of the occipital bone; C: On sagittal T2-weighted image; D: On axial T1-weighted image; E: On axial T2-weighted image; F: On sagittal contrast enhanced T1-weighted image, signal intensities of non-contrast enhanced arachnoid granulation (arrows) are seen, more prominent to the left of the midline in the occipital bone, isointense with cerebrospinal fluid.
- Citation: Gökçe E, Beyhan M. Review of imaging modalities and radiological findings of calvarial lesions. World J Radiol 2025; 17(6): 107776
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i6/107776.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.107776