Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Aug 26, 2025; 17(8): 110163
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i8.110163
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i8.110163
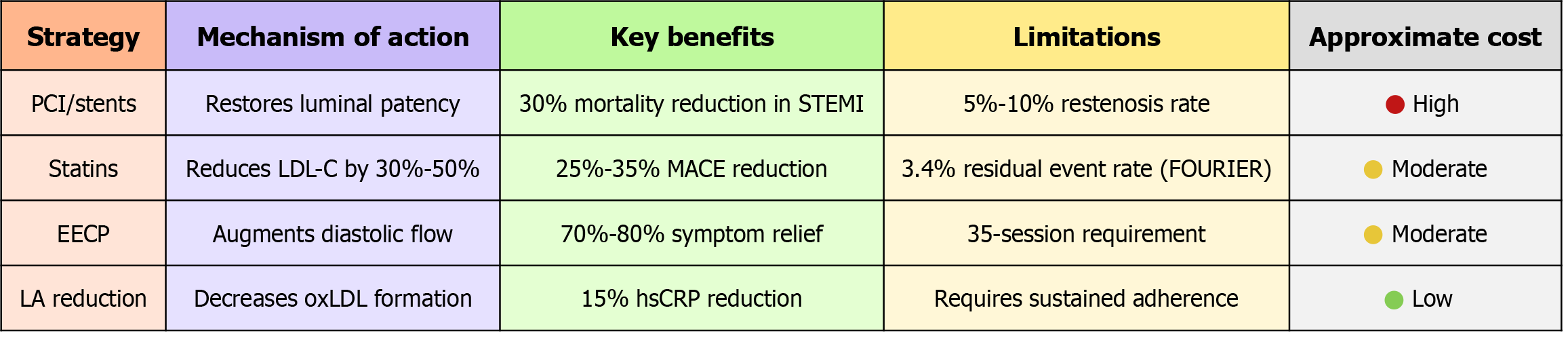
Figure 1 Comparative matrix of contemporary cardiovascular disease management modalities.
A side-by-side appraisal shows that percutaneous coronary interventions and statins yield 30% and 25%-35% reductions in their respective endpoints but carry high procedural costs or leave a 3.4% annual residual event rate. Enhanced external counter-pulsation relieves 70%-80% of anginal symptoms yet requires 35 outpatient sessions. By contrast, sustained dietary linoleic acid reduction lowers oxidized low-density lipoprotein formation and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein by approximately 15% at minimal cost, highlighting its favorable risk-benefit and economic profile within an integrative treatment framework. PCI: Percutaneous coronary interventions; EECP: Enhanced external counter pulsation; LA: Linoleic acid; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; oxLDL: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; MACE: Major adverse cardiovascular events; hsCRP: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein; FOURIER: Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research with PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Elevated Risk.
- Citation: Mercola J. Integrative cardiovascular disease therapy: Linoleic acid restriction, enhanced external counterpulsation, and emerging nanotherapies. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(8): 110163
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i8/110163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i8.110163