Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2025; 17(6): 106295
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106295
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106295
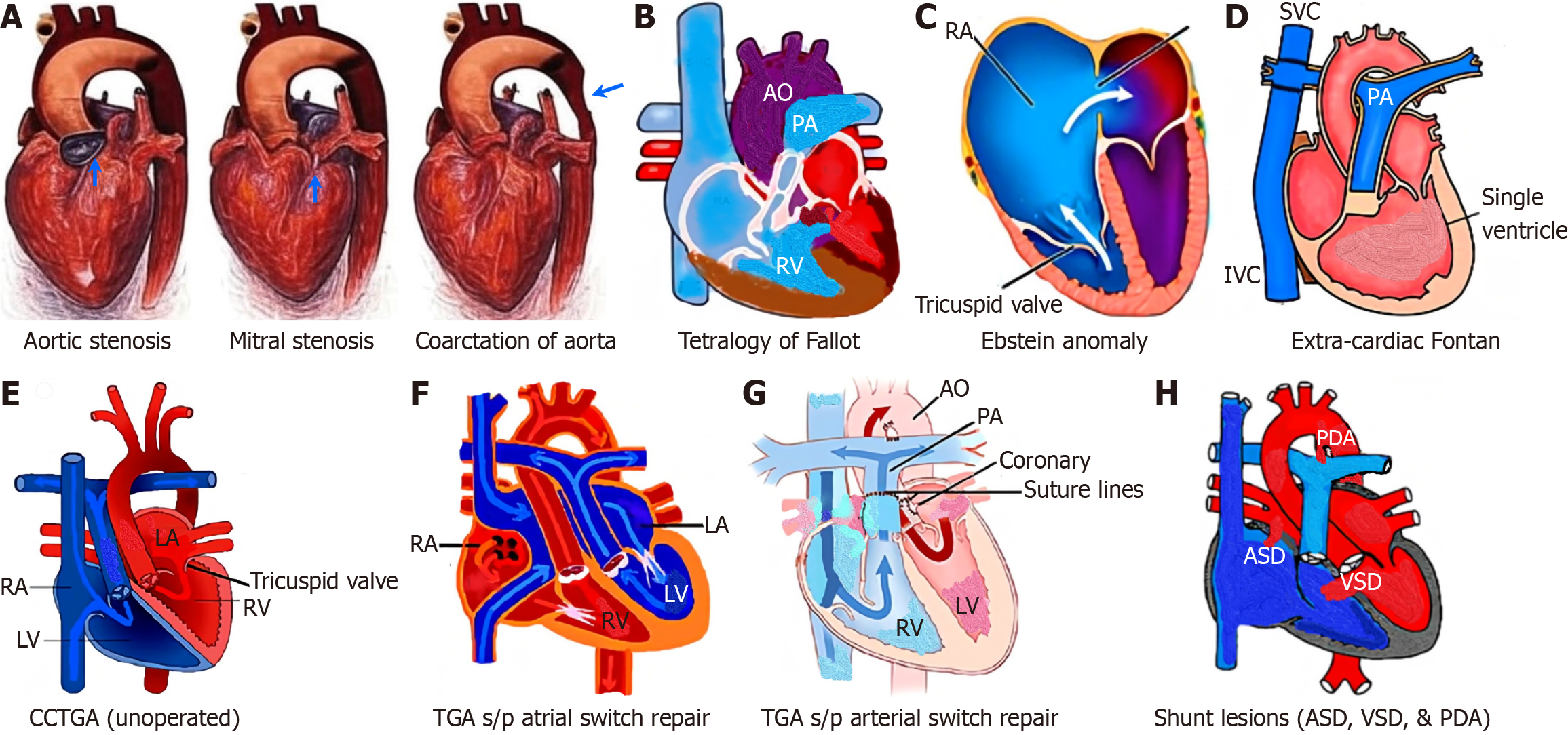
Figure 5 Adult congenital heart disease in women during pregnancy.
A: Aortic stenosis, mitral stenosis, coarctation of the aorta; B: Unrepaired tetralogy of Fallot; C: Uncomplicated Ebstein anomaly; D: Extra-cardiac Fontan; E: Congenitally corrected transpositions of great arteries; F: Transposition of great arteries after Senning/mustard; G: Transposition of great arteries after arterial switch operation; H: Left to right shunt lesions (atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, and patent ductus arteriosus). ASD: Atrial septal defect; VSD: Ventricular septal defect; PDA: Patent ductus arteriosus; AO: Aorta; PA: Pulmonary artery; RV: Right ventricle; RA: Right atrium; LV: Left ventricle; LA: Left atrium; SVC: Superior venacava; IVC: Inferior venacava; TGA: Transposition of the great arteries arteries.
- Citation: Das BB, Aggarwal V, Deshpande SR. Navigating women with congenital heart disease during pregnancy: Management strategies and future directions. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(6): 106295
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i6/106295.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106295