Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Oct 26, 2014; 6(10): 1049-1059
Published online Oct 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i10.1049
Published online Oct 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i10.1049
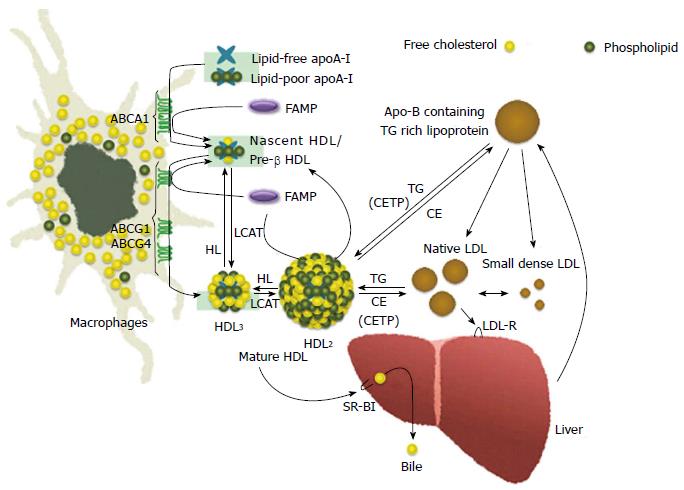
Figure 1 Illustration of high-density lipoprotein metabolism and suggested function of fukuoka university ApoA-I mimetic peptide in high-density lipoprotein metabolism.
ABC: ATP-binding cassette transporter; TG: Triglyceride; CE: Cholesteryl ester; CETP: Cholesteryl ester transfer protein; HL: Hepatic lipase; apo: Apolipoprotein; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; FAMP: Fukuoka university ApoA-I mimetic peptide; CETP: CE transfer protein; SR-BI: Scavenger receptor BI; LDL: Llow-density lipoprotein; LCAT: Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase; LDL-R: Low-density lipoprotein receptor; SR-BI: Scavenger receptor class B, type I; FAMP: Fukuoka University ApoA-I mimetic peptide.
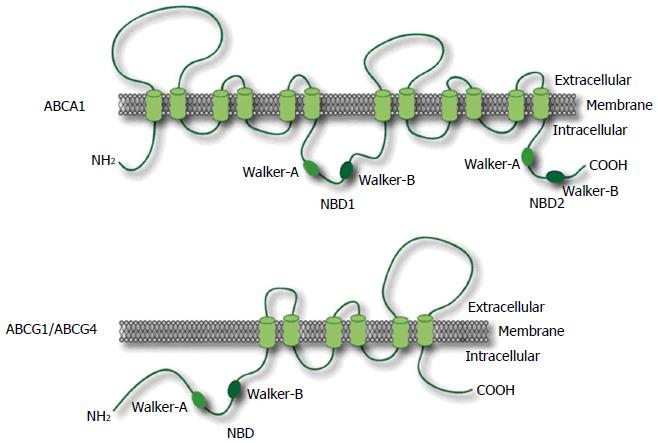
Figure 2 Secondary structures of the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1, ATP-binding cassette G1 and ATP-binding cassette G4 transporters.
The ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC)A1 transporter comprises 2201 amino acids with two transmembrane domains comprising two nucleotide binding domains (NBD-1 and -2) and six transmembrane helices, which contain two conserved peptide motifs, Walker-A and -B. ABCA1 is characterized as two large extracellular loops and N-terminus oriented towards the cytosol. Both ABCG1 and ABCG4 proteins have one transmembrane domain comprising six transmembrane helices and one NBD that contains two conserved peptide motifs, Walker-A and Walker-B.
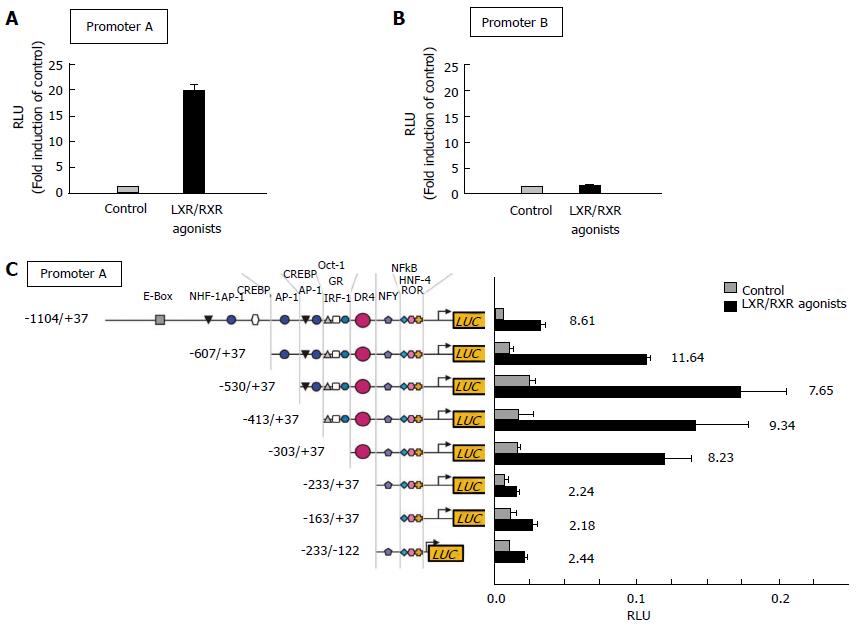
Figure 3 Response of liver X receptor and retinoid X receptor agonists to human ATP-binding G1 promoter activities in RAW264 cells.
A: Human wild-type ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 (ABCG1) promoter-A located upstream of exon 1; B: Human wild-type ABCG1 promoter-B located upstream of exon 5; C: ABCG1 promoter (promoter-A; upstream of exon 1) vectors that contain a truncated 5′-region of the ABCG1 gene. After transfection, cells were incubated with or without agonists of LXR [22(R)-hydroxycholesterol, 10 μmol/L] and RXR (9-cis-retinoic acid, 10 μmol/L). Results are expressed as mean ± SD. Graphs modified from the paper by Uehara et al[62]. LXR: Liver X receptor; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; RLU: Relative luciferase units .
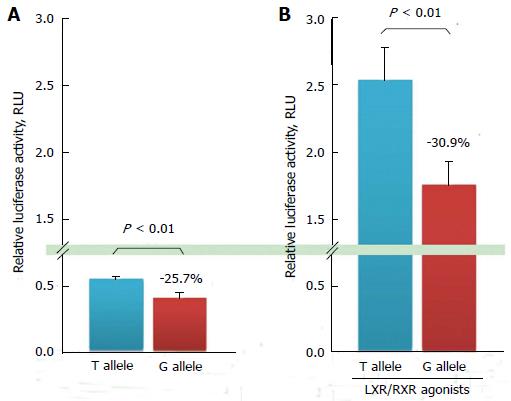
Figure 4 In vitro promoter activity assay for ATP-binding G1 promoter-A.
ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 (ABCG1) promoter construct with a −257T/G mutation, −394 T/G from the transcription start site (NM_207627.1: c.-394T > G) on ABCG1 promoter-A, which is reported to be a functional promoter with an LXR-responsive element. A: ABCG1 transcription activity on a construct that contains the T or G allelic sequence; B: ABCG1 transcription activity induced by 5 μmol/L of T0901317 (T0) and 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cisRA) on constructs that contain the T or G allelic sequence. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. Graphs are modified from the paper by Furuyama et al[67]. ABC: ATP-binding cassette; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; LXR: Liver X receptor.
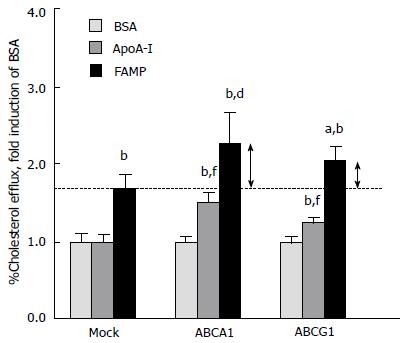
Figure 5 Fukuoka University apoA-I mimetic peptide effects on cellular cholesterol effluxes in cells that express ATP-binding A1 and ATP-binding G1.
COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with an empty vector (mock) or with human ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 (ABCG1) cDNAs. Cholesterol efflux was determined after incubation with apoA-I or FAMP. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs FAMP in mock; bP < 0.01 vs BSA; dP < 0.01 vs FAMP in mock; fP < 0.01 vs apoA-I in mock. Graph modified from the paper by Uehara et al[82]. FAMP: Fukuoka University ApoA-I mimetic peptide; BSA: bovine serum albumin; apoA-I: apolipoprotein A-I; FAMP: Fukuoka University ApoA-I Mimetic Peptide..
- Citation: Uehara Y, Saku K. High-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis: Roles of lipid transporters. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(10): 1049-1059
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i10/1049.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i10.1049