Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2025; 17(8): 108887
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108887
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108887
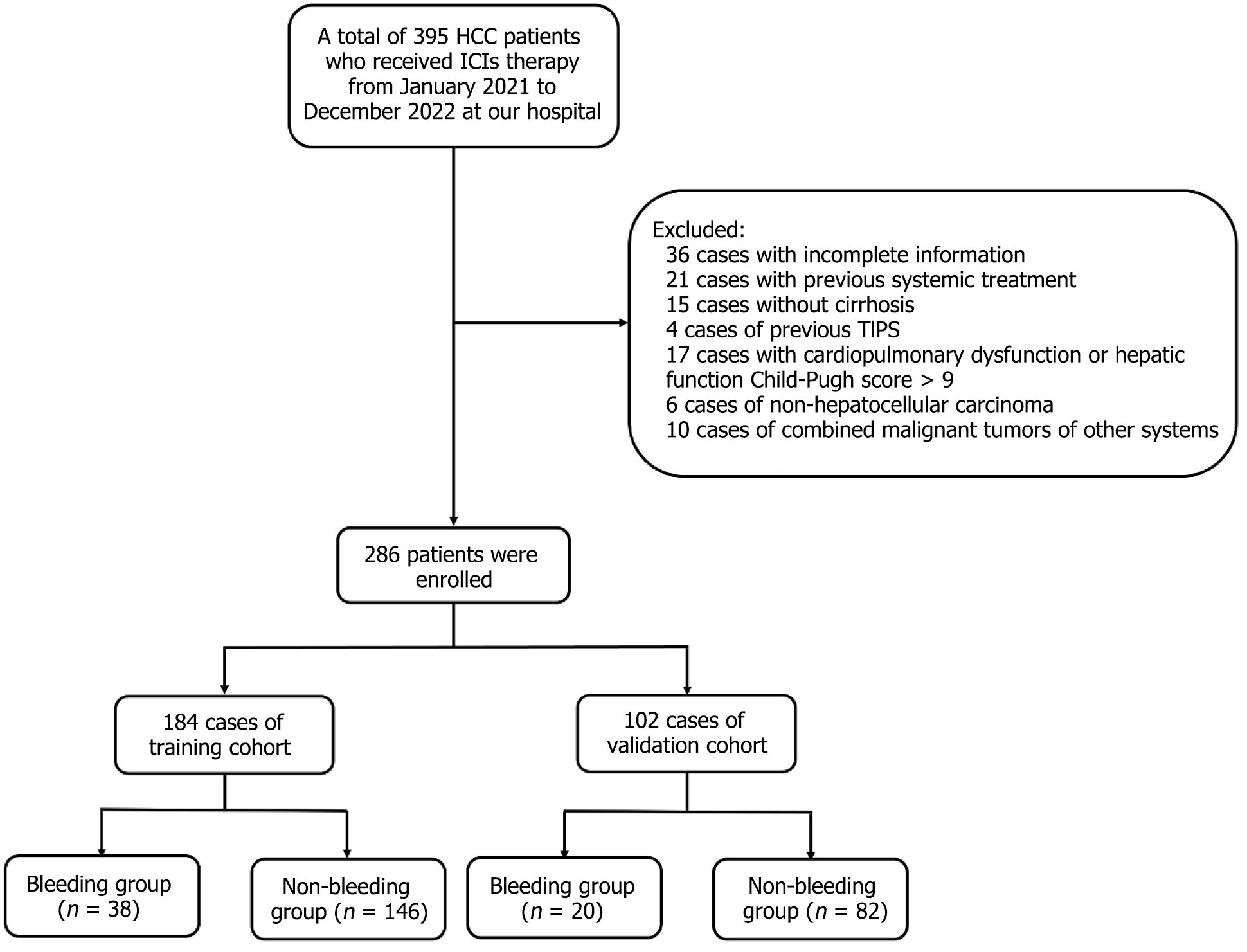
Figure 1 Retrospective selection process of patients.
A total of 395 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who received systemic therapy between January 2021 and December 2022 were initially screened. Patients were excluded due to non–HCC (n = 6), concurrent malignant tumors of other systems (n = 10), severe heart, lung, or liver disease (Child-Pugh C > 9) or kidney dysfunction (n = 17), absence of cirrhosis (n = 15), history of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (n = 4), history of previous systemic therapy (n = 21), incomplete data (n = 36). The final cohort included 286 patients for analysis. ICIs: Immune checkpoint inhibitors; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
- Citation: Zhang X, Song LM, Zheng YP, Qian BX, Liang J, Wang FM. Risk prediction of acute variceal bleeding in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing systemic therapy based on immune checkpoint inhibitors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(8): 108887
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i8/108887.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108887