Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2025; 17(8): 108535
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108535
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108535
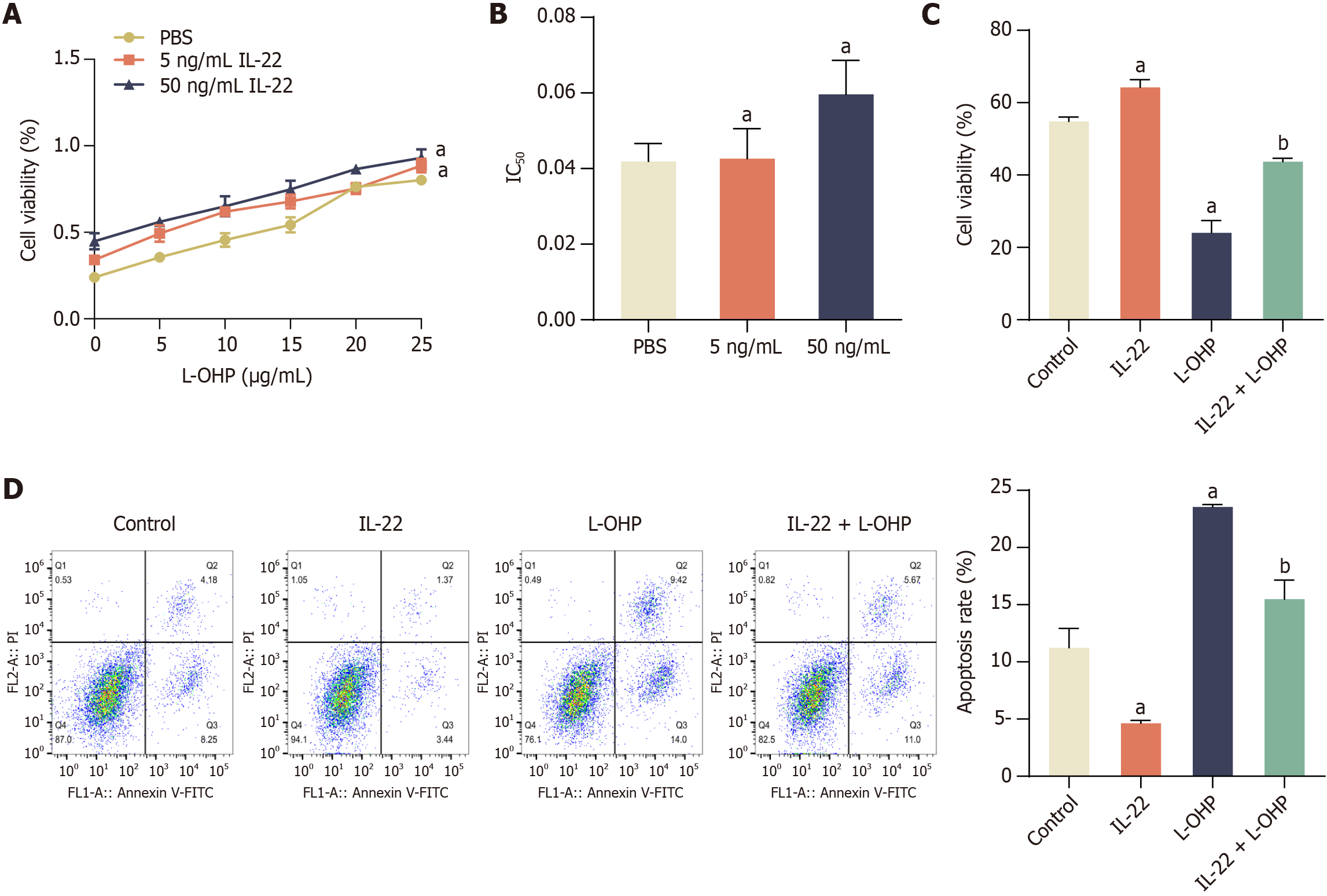
Figure 2 Interleukin-22 treatment attenuates the cytotoxic and apoptosis-inducing effects of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells.
A: Cell viability under increasing concentrations of oxaliplatin (L-OHP) (0-25 μg/mL) in the presence of interleukin-22 (IL-22) (5 ng/mL and 50 ng/mL); B: Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of L-OHP with or without IL-22 treatment; C: Cell viability in control, IL-22, L-OHP, and IL-22 + L-OHP groups assessed by MTT assay; D: Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in the same four groups. Data are represented as mean ± SE (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. aP < 0.01 vs PBS or Control group; bP < 0.01 vs L-OHP group. L-OHP: Oxaliplatin; IL-22: Interleukin-22; IC50: Half maximal inhibitory concentration.
- Citation: Ruan HX, Fang YL, Qin XN, Lin L. Interleukin-22 promotes cancer stemness and chemotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer via epidermal growth factor receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(8): 108535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i8/108535.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108535