Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2025; 17(8): 107453
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.107453
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.107453
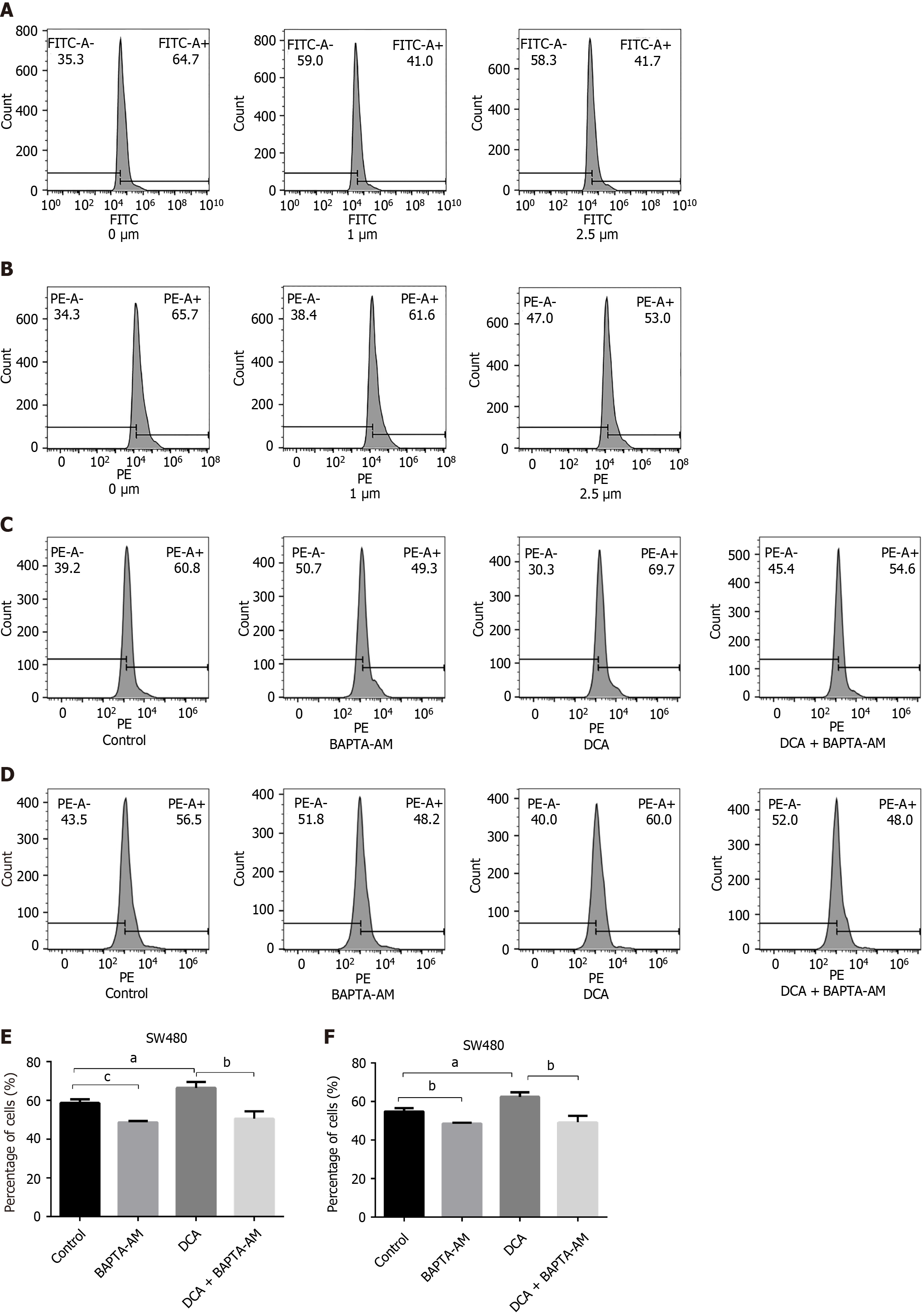
Figure 4 Effect of intracellular calcium chelator BAPTA-AM on intracellular and mitochondrial Ca2+ and reactive oxygen species.
A: Flow cytometry results of intracellular calcium content in SW480 cells; B: Flow cytometry results of intracellular calcium content in mitochondria of SW480 cells; C and D: Flow cytometry results and statistics of the calcium ion content in the mitochondria of SW480 cells; E and F: Flow cytometry results and statistical graphs of reactive oxygen species (ROS) content in mitochondria of SW480 cells. The effect of deoxycholic acid on the mitochondrial Ca2+ and ROS in SW480 cells after chelating intracellular calcium ions at 0, 1, and 2.5 μM in three replicates of BAPTA-AM treatment, respectively. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. PE: Phycoerythrin; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; DCA: Deoxycholic acid.
- Citation: Chen JY, Wen JY, Lin JL, Li Y, Wu YZ, Lou LQ, Lou YL, Zuo ZG, Li X. Deoxycholic acid induces reactive oxygen species accumulation and promotes colorectal cancer cell apoptosis through the CaMKII-Ca2+ pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(8): 107453
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i8/107453.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.107453