Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2025; 17(8): 106663
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.106663
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.106663
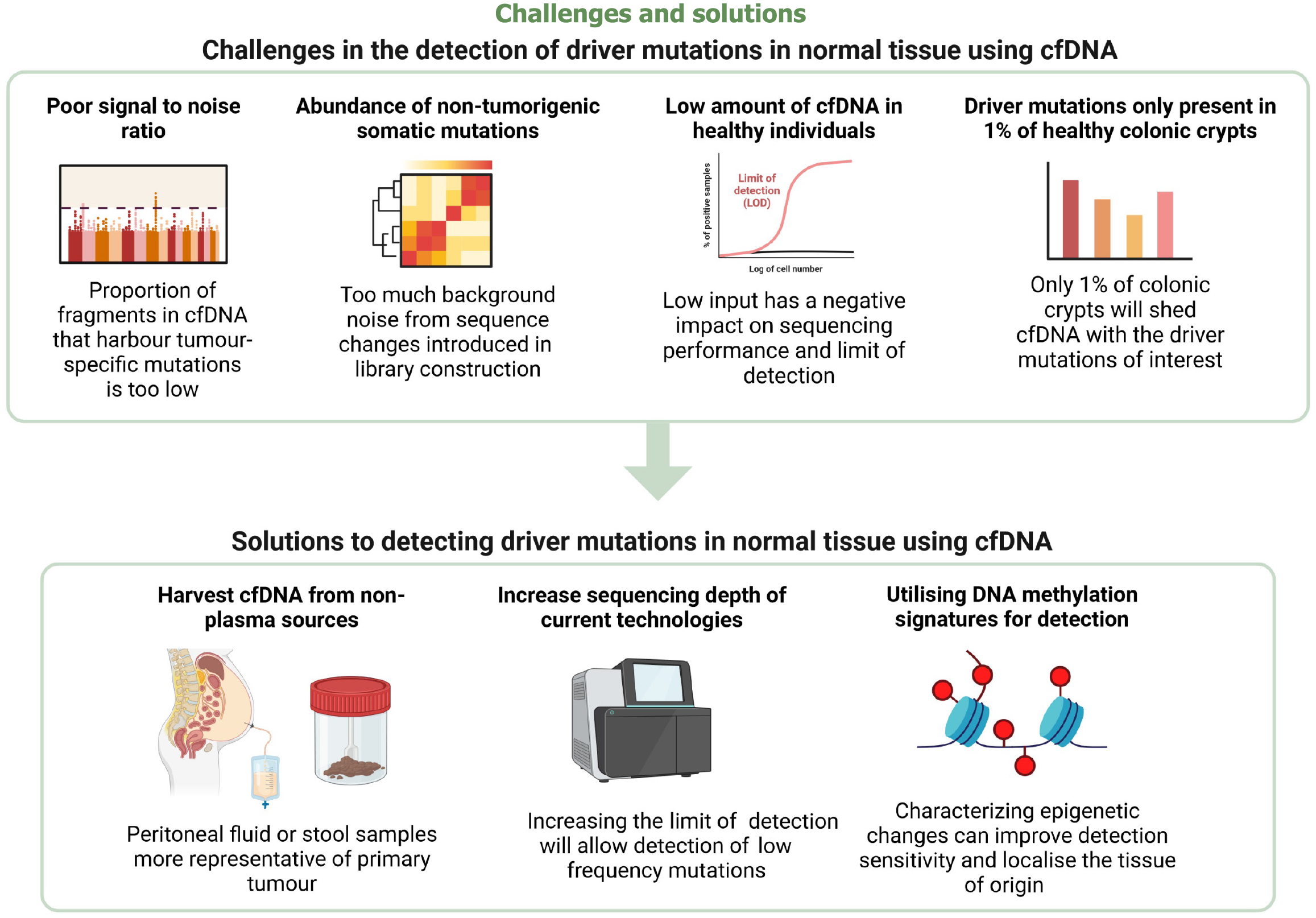
Figure 2 The challenges of using cell free DNA for the detection of driver mutations in normal tissue and proposed solutions.
Figure was created with Biorender.com. Challenges preventing the adoption of cell free DNA (cfDNA) for individuals with normal colonic epithelium include poor signal-to-noise ratio, the abundance of non-tumorigenic background mutations, the low amount of cfDNA found in healthy individuals, and that only 1% of healthy colonic crypts possess the driver mutations of interest. Potential solutions that can be explored are to harvest cfDNA from non-plasma sources like the stool and peritoneal fluid, increase the sequencing depth of current technologies or to analyze epigenetic changes instead. cfDNA: Cell free DNA.
- Citation: Chua MWE, Chan DKH. Challenges and proposed solutions to the adoption of cell free DNA in screening, detecting and prognosticating colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(8): 106663
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i8/106663.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.106663