Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2025; 17(5): 105311
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.105311
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.105311
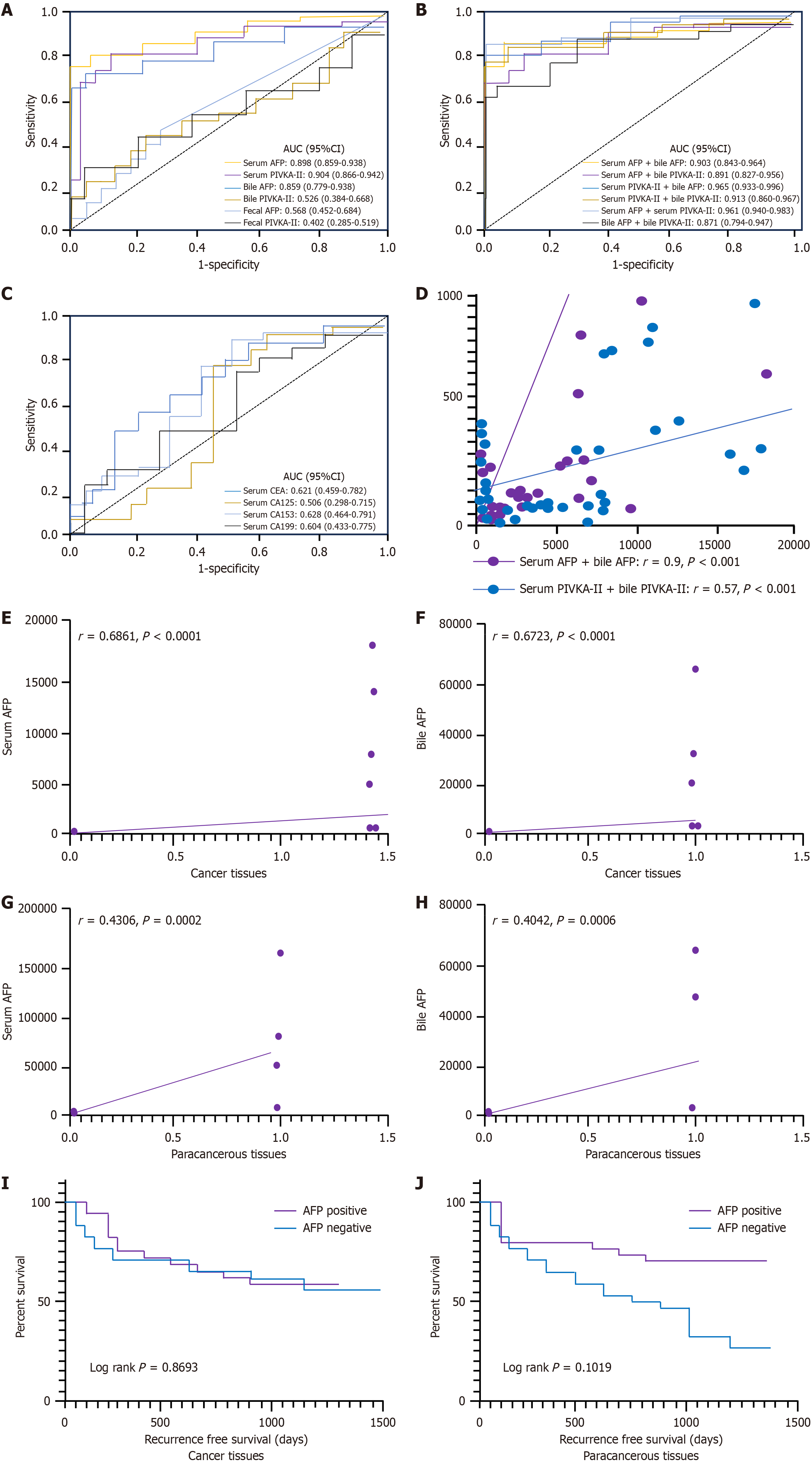
Figure 2 Diagnostic efficacy, correlation coefficients of tumor markers, immunohistochemical analysis, and recurrence-free survival analysis.
A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) diagnosis using alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) or prothrombin induced by vitamin K absence-II (PIVKA-II) in serum, bile, and feces; B: ROC curve for HCC diagnosis using the combination of AFP and PIVKA-II in serum and bile; C: ROC curve for the HCC diagnosis using carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA125), CA153, and CA19-9 in serum; D: Correlation coefficient between serum AFP, PIVKA-II, and bile AFP; E: Correlation analysis of AFP expression in tumor tissues and serum AFP levels; F: Correlation analysis between AFP expression in tumor tissues and bile AFP levels; G: Correlation analysis between AFP expression in paracancerous tissue and serum AFP levels; H: Correlation analysis between AFP expression in paracancerous tissue and bile AFP levels; I: Recurrence-free survival analysis using AFP immunohistochemistry in tumor tissue for serum in patients with AFP-positive HCC; J: Recurrence-free survival analysis using AFP immunohistochemistry in paracancerous tissue for serum in patients with AFP-positive HCC. AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Chen ZJ, Wang XK, Han CY, He YF, Liang TY, Mo ST, Zhu GZ, Yang CK, Ye XP, Lv ZL, Pang SF, Chen XD, Wang P, Peng T. Diagnostic value of alpha-fetoprotein and prothrombin induced by vitamin K absence-II in serum, bile, and feces in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(5): 105311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i5/105311.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.105311