Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2025; 17(5): 102417
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.102417
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.102417
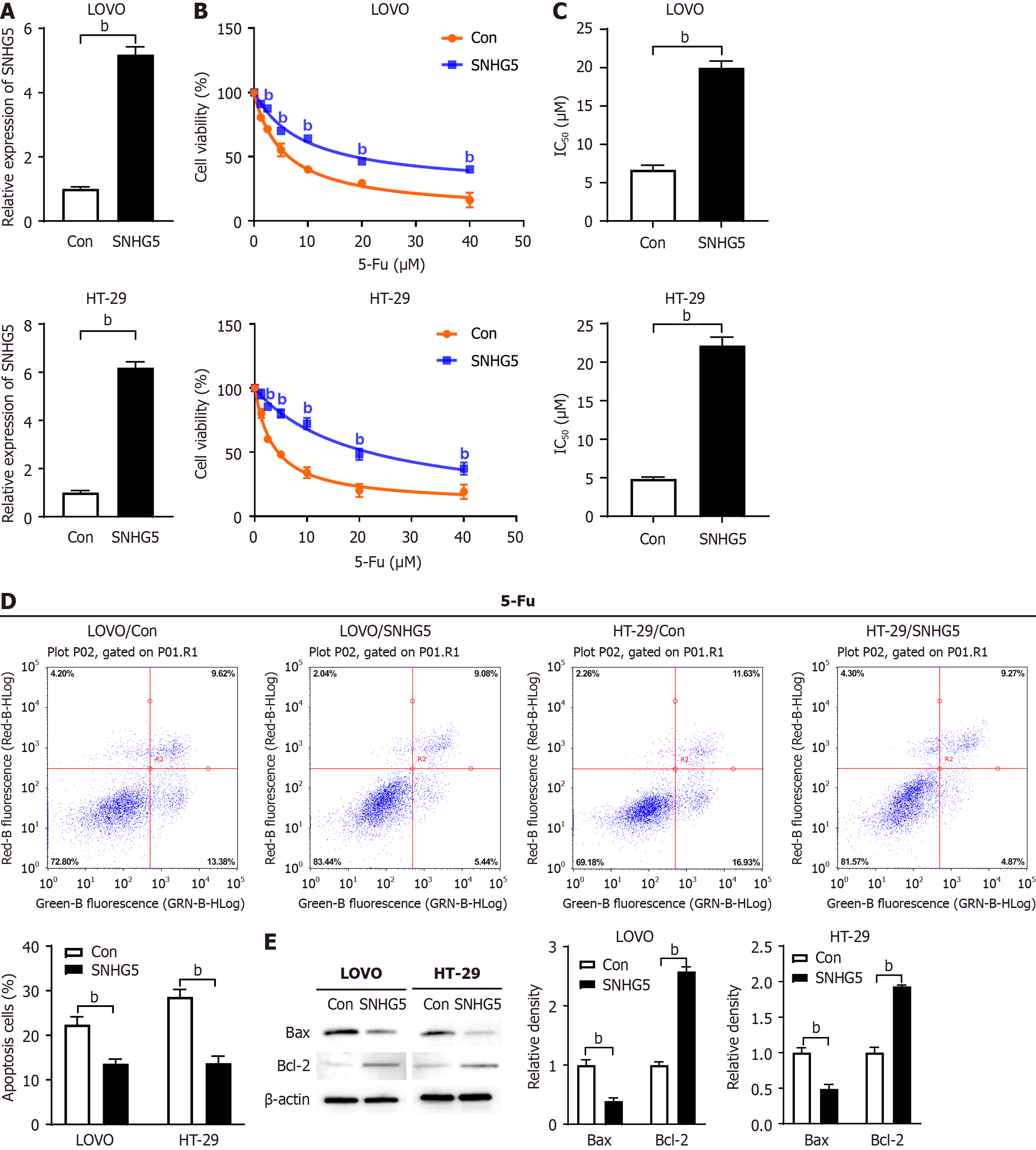
Figure 2 SNHG5 overexpression enhances 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer cells.
A: The expression of SNHG5 was assessed in LOVO and HT-29 cells which were transfected with SNHG5 and scrambled control lentivirus; B and C: The viability of LOVO and HT-29 cells treated with different concentrations of 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu) was evaluated, and the IC50 of 5-Fu in colorectal cancer cells was calculated; D: The apoptosis rate of stable cells treated with 5-Fu was analyzed via annexin-V fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate/propidium iodide staining assays (left) and quantified (right); E: Western blot analysis was performed to assess the expression of apoptosis markers (Bax and Bcl-2), with β-actin serving as an internal control (left), and densitometric analysis of the Western blot signals is shown (right). bP < 0.01. Con: Control; 5-Fu: 5-fluorouracil.
- Citation: Wang B, Zhou Q, Cheng CE, Gu YJ, Jiang TW, Qiu JM, Wei GN, Feng YD, Ren LH, Shi RH. Long noncoding RNA SNHG5 promotes 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by regulating miR-26b/p-glycoprotein axis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(5): 102417
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i5/102417.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.102417