Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2024; 16(2): 563-570
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i2.563
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i2.563
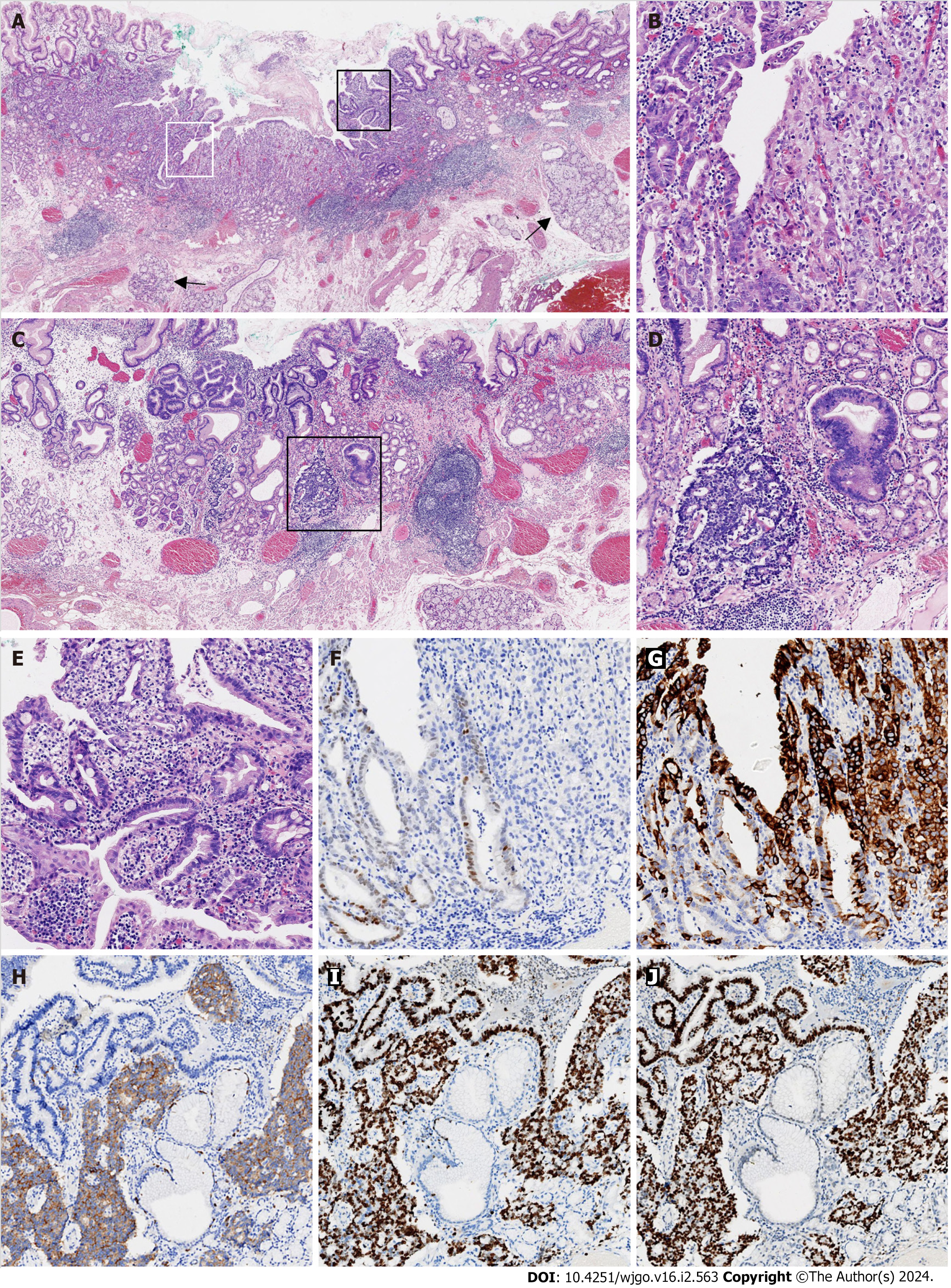
Figure 2 Histological findings of poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma mixed with a neuroendocrine carcinoma component.
A: Submucosal esophageal glands (arrow) were observed, indicating the distal esophageal location (× 20); B: The area defined by the white rectangle in Figure 2A was enlarged and showed the mixture of moderately (left) and poorly (right) differentiated adenocarcinomas (× 100); C: Adenocarcinoma with a neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC) component arose in the cardiac mucosa (× 20); D: The area in the black rectangle in Figure 2C exhibited a mixture of adenocarcinoma (right) with NEC (left; × 100); E: The area defined by the black rectangle in Figure 2A was enlarged and demonstrated glandular dysplasia with goblet cells (× 100); F: CDX2 was weakly immunoreactive in moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma and immunonegative in poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (× 100); G: Mucin 5AC was diffusely immunopositive in poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma and focally immunopositive in moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (× 100); H: Synaptophysin was diffusely immunopositive in NEC, but immunonegative in adenocarcinoma (× 100); I: The Ki-67 proliferative index was approximately 90% for both the adenocarcinoma and NEC components (× 100); J: p53 was diffusely immunopositive for the adenocarcinoma and NEC components (× 100). All controls stains were adequate.
- Citation: Cheng YQ, Wang GF, Zhou XL, Lin M, Zhang XW, Huang Q. Early adenocarcinoma mixed with a neuroendocrine carcinoma component arising in the gastroesophageal junction: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(2): 563-570
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i2/563.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i2.563