Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2021; 13(11): 1755-1765
Published online Nov 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i11.1755
Published online Nov 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i11.1755
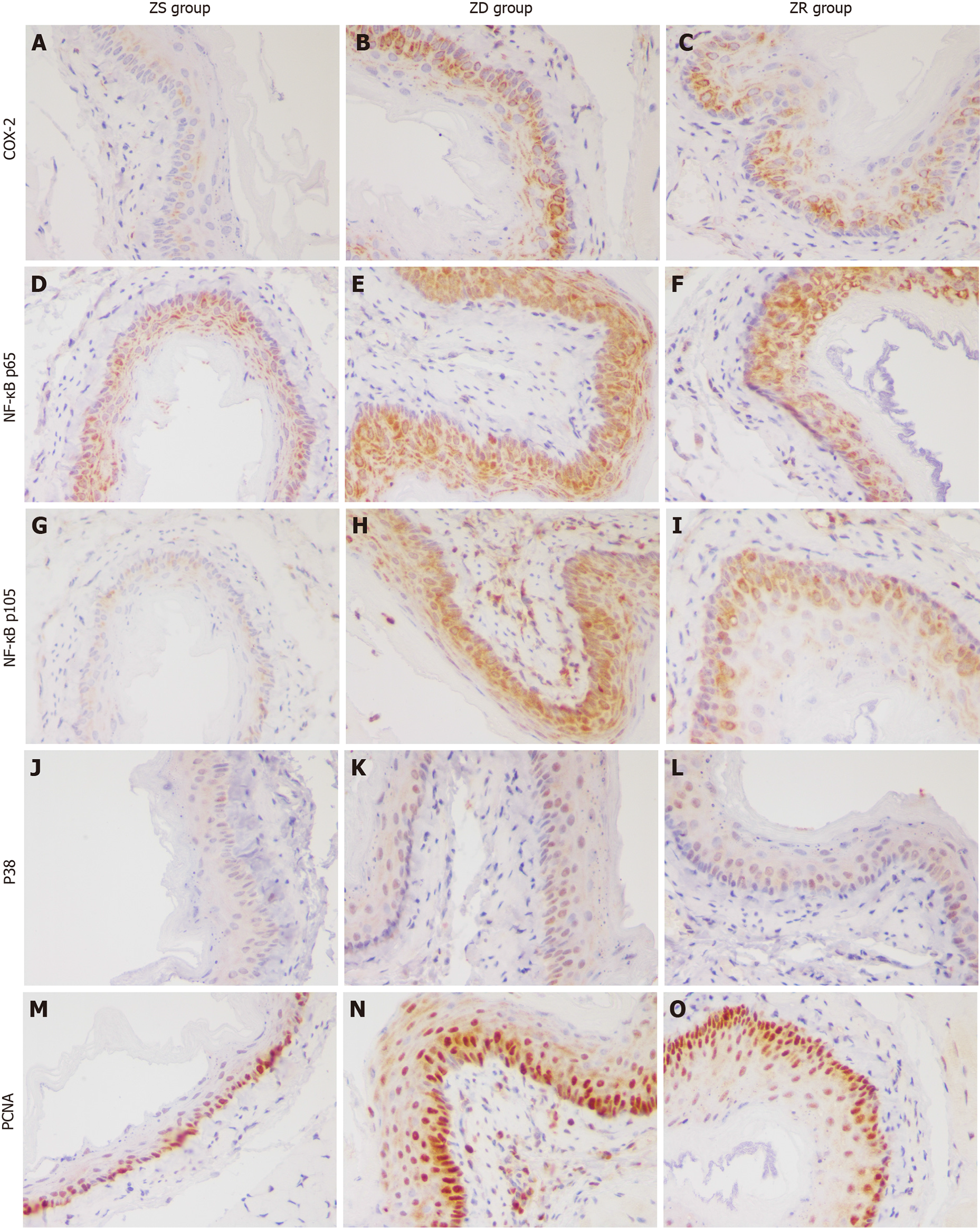
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining for cyclooxygenase-2, nuclear factor kappa B p65, nuclear factor kappa B p105, P38, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in the esophageal mucosa (200 ×).
A: Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 was not expressed or was minimally expressed in the cytoplasm of normal cells; B: COX-2 expression was significantly increased in the esophageal mucosa of mice in the zinc-deficient (ZD) group; C: Two weeks of zinc-replenished (ZR) group reduced the COX-2 expression level; D: Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) p65 showed a low expression level in the cytoplasm of normal cells; E: NF-κB p65 expression level significantly increased in the esophageal mucosa of mice in the ZD group; F: Compared with mice in the ZD group, in those in the ZR group, NF-κB p65 expression level did not change significantly in the esophageal mucosa; G: NF-κB p105 showed a low expression level in the cytoplasm of normal cells; H: NF-κB p105 expression level significantly increased in the esophageal mucosa of mice in the ZD group; I: Two weeks of ZR group reduced the NF-κB p105 expression level; J: P38 was expressed in small amounts in the cytoplasm and nucleus of normal cells; K: P38 expression was increased in the nucleus of esophageal mucosal cells in the ZD group; L: Compared with mice in the ZD group, in those in the ZR group, P38 expression level did not change significantly in the esophageal mucosa; M: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) showed a low expression level in the cytoplasm of normal cells; N: PCNA expression level significantly increased in the esophageal mucosa of mice in the ZD group; Compared with mice in the ZD group, in those in the ZR group, 2 wk of ZR reduced the PCNA expression level. ZS: Zinc-sufficient; ZD: Zinc-deficient; ZR: Zinc-replenished; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
- Citation: Chen Y, Liu FX, Liu H. Effects of dietary zinc deficiency on esophageal squamous cell proliferation and the mechanisms involved. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(11): 1755-1765
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i11/1755.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i11.1755