Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2020; 12(6): 642-650
Published online Jun 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i6.642
Published online Jun 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i6.642
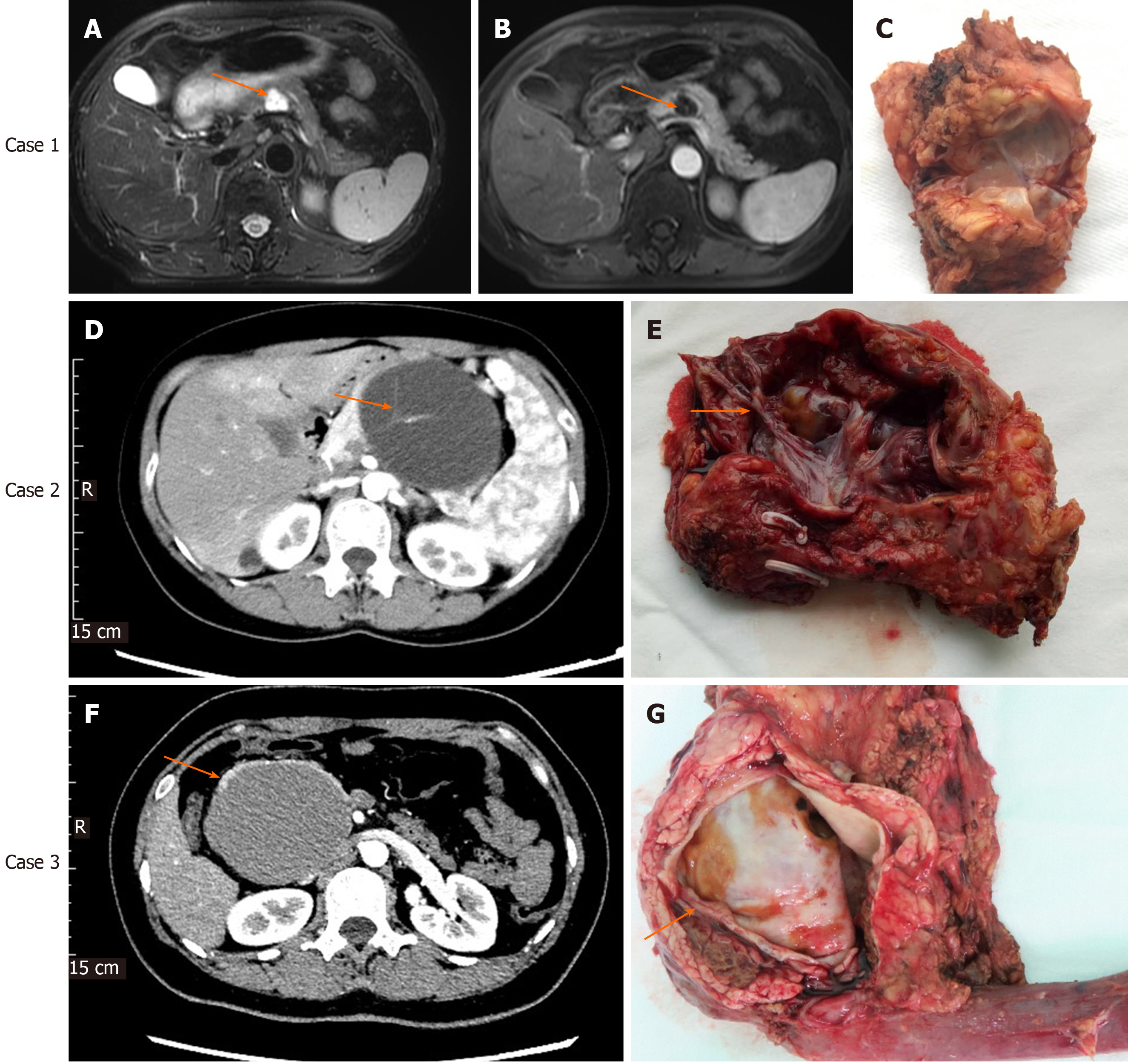
Figure 1 Imaging and histological characteristics of pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma and mucinous cystadenocarcinomas.
Case 1: Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma (MCA). A: Pronounced cystic lesion approximately 2 cm in length in the body of the pancreas (arrow) as seen on a T2W axial MRI image; B: Cyst wall and internal septations enhancement in the portal phase; C: Cut surface of the tumor with MCA pathology; Case 2: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) for pancreatic MCA. D: Cystic lesion in the body of the pancreas observed in the arterial phase of CT, with prominently enhanced internal septations (arrow); E: Cut surface of the tumor, with visible and pronounced internal septations (arrow) and MCA pathology; Case 3: Contrast-enhanced CT for pancreatic mucinous cystadenocarcinoma (MCC). F: Cystic lesion in the head of the pancreas observed in the arterial phase of CT. The cyst wall was thickened, but no internal septations were seen; G: Cut surface of the tumor. No internal septations can be seen. The thickness of the cyst wall measured approximately 3.5 mm (arrow); pathology testing showed features of MCC.
- Citation: Zhao ZM, Jiang N, Gao YX, Yin ZZ, Zhao GD, Tan XL, Xu Y, Liu R. Clinical diagnosis and management of pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma and cystadenocarcinoma: Single-center experience with 82 patients. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(6): 642-650
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i6/642.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i6.642