Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2025; 17(6): 104073
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.104073
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.104073
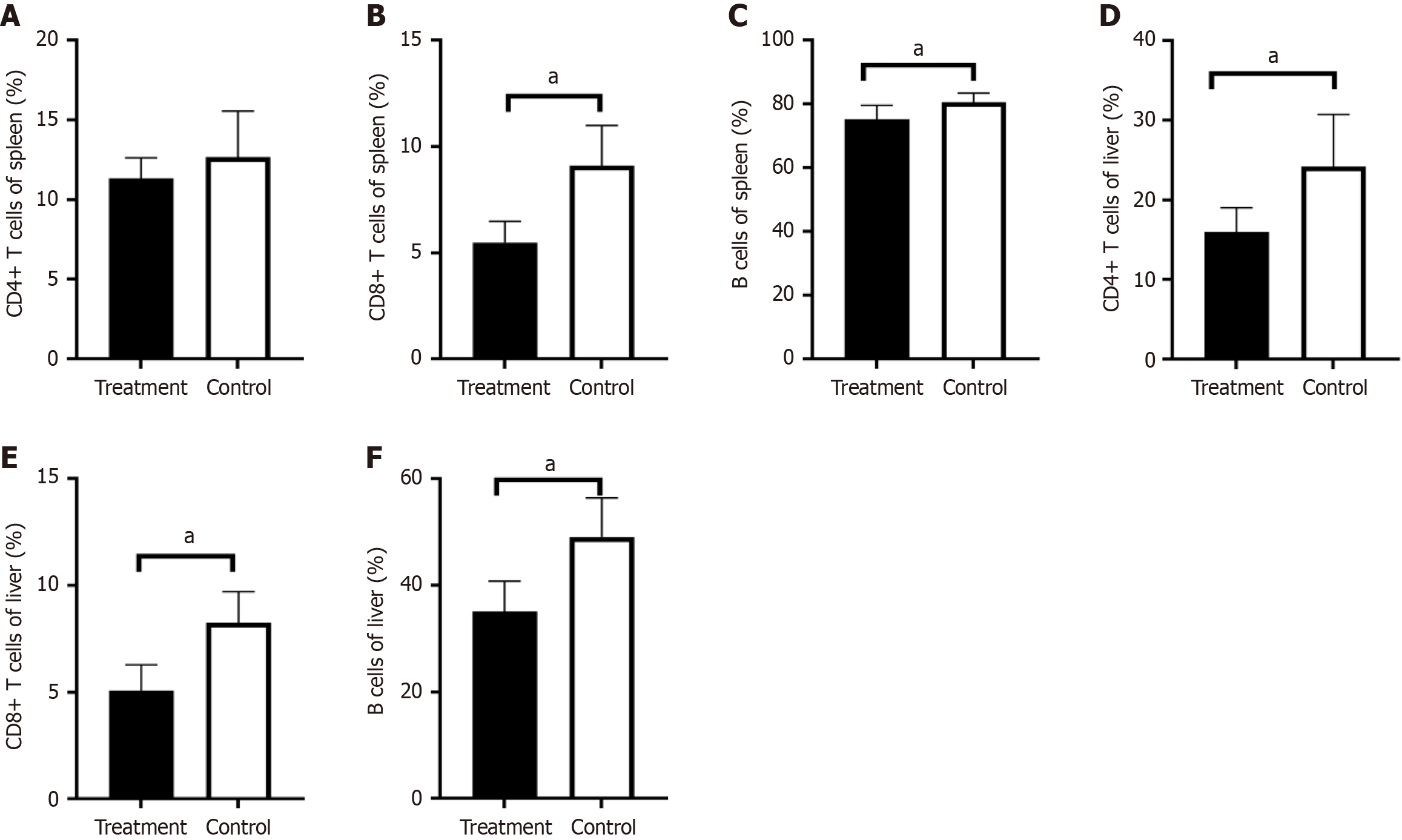
Figure 4 Nanoparticles encapsulating rapamycin treatment decreased the lymphocyte expression in the liver and spleen.
A: The percentage of CD4-positive T cells in the liver of the treatment group decreased compared with that in the control group; B: A comparison of the control and treatment groups showed that the percentage of CD8-positive T cells in the liver of the treatment group was decreased; C: The expression of B lymphocytes was decreased in the liver of the treatment group; D: There was no difference in CD4-positive T cells in the spleen between the two groups; E: The percentage of CD8-positive T lymphocytes in the spleen of the treatment group decreased compared with that in the control group; F: The expression of B lymphocytes in the spleen was decreased in the treatment group (aP < 0.05).
- Citation: Yang YS, Li XR, Wang ZM, Zheng L, Li JL, Cui XL, Song YB, Ma JJ, Guo HF, Gao LX, Zhou XH. Effect of rapamycin nanoparticles in an animal model of primary biliary cholangitis. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(6): 104073
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i6/104073.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.104073