Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2025; 17(6): 104073
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.104073
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.104073
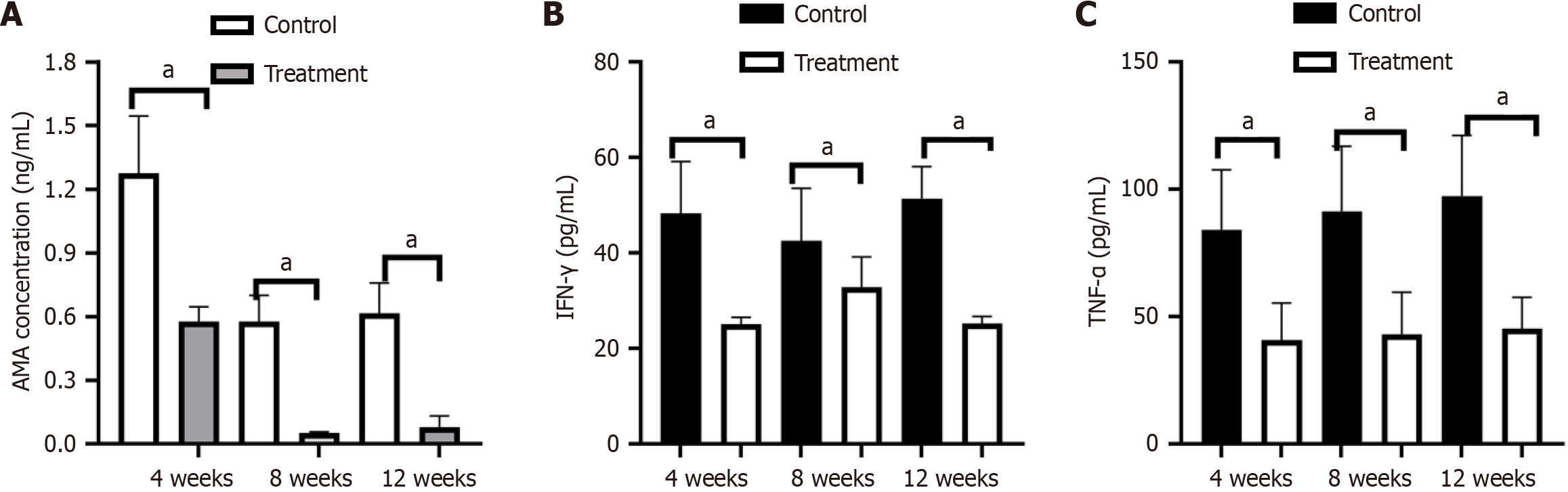
Figure 3 Nanoparticles encapsulating rapamycin treatment decreased serum anti-mitochondrial antibodies levels and inhibited the expression of cytokines.
A: Levels of anti-mitochondrial antibodies at 4 weeks, 8 weeks and 12 weeks in primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) mice treated with nanoparticles encapsulating rapamycin and in mice in the control group; B: Comparative serum profiling of interferon gamma between control and treated PBC mice; C: Comparative serum levels of tumor necrosis factor α between the control and treatment group (aP < 0.05). AMA: Anti-mitochondrial antibodies; IFN-γ: Interferon gamma; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α.
- Citation: Yang YS, Li XR, Wang ZM, Zheng L, Li JL, Cui XL, Song YB, Ma JJ, Guo HF, Gao LX, Zhou XH. Effect of rapamycin nanoparticles in an animal model of primary biliary cholangitis. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(6): 104073
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i6/104073.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.104073