Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2013; 5(1): 26-33
Published online Jan 26, 2013. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v5.i1.26
Published online Jan 26, 2013. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v5.i1.26
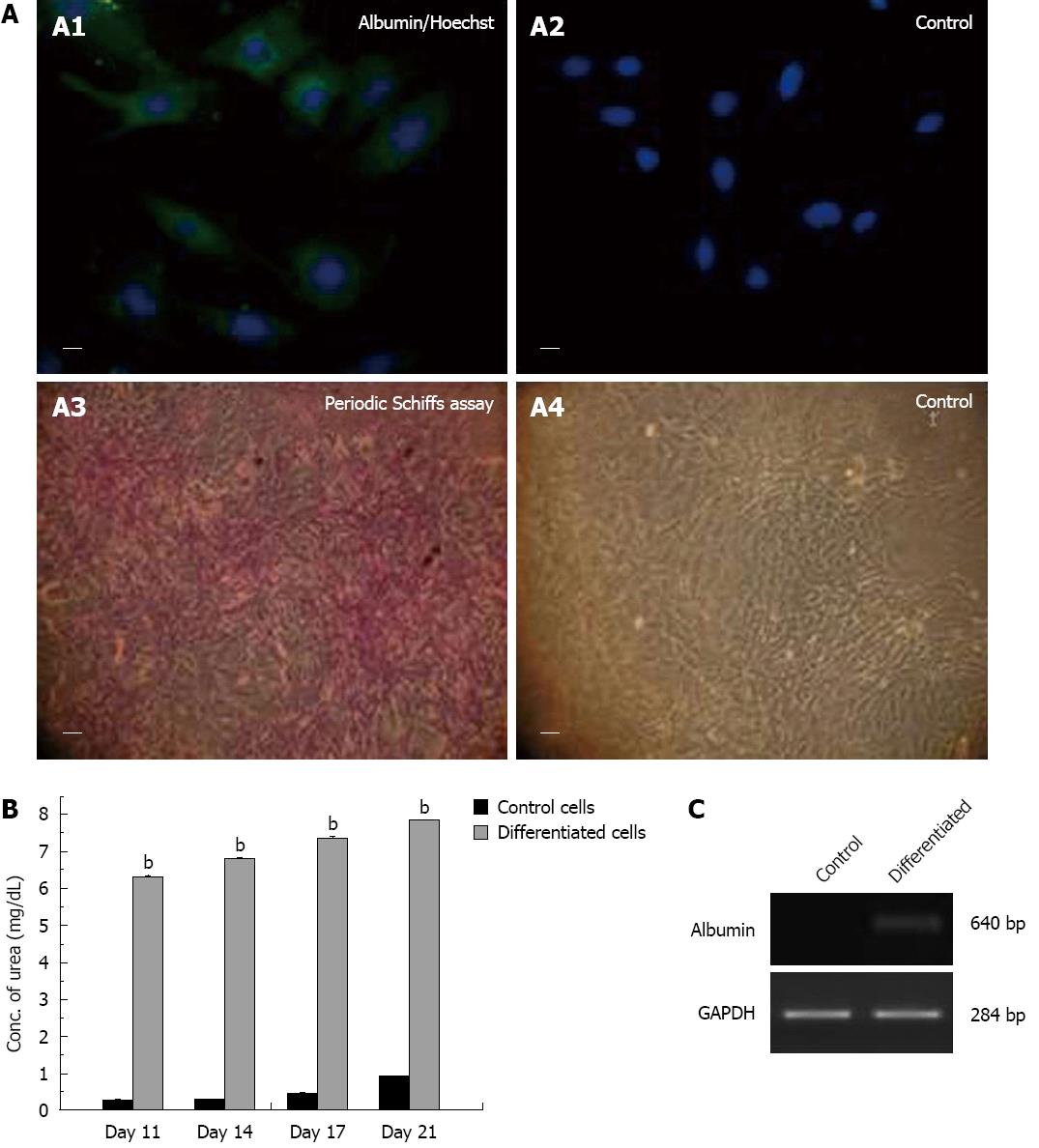
Figure 5 On treatment with hepatogenic medium, fetal cardiac mesenchymal stem cells exhibited differentiation into hepatocytic cells (endoderm), as demonstrated by expression of albumin by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and immunocytochemistry, glycogen deposits by Periodic Schiffs staining and excretion of urea in the supernatant.
A: Representative immunocytochemistry photomicrographs (40 ×, 20 μm) showing differentiation of rat fetal cardiac mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes (A1: albumin and Hoechst dye and A2: no albumin only Hoechst dye in control cells); (A3: Periodic Acid Schiff stain and A4: control cells negative for Periodic Acid Schiff stain); B: Urea levels in the supernatant of control and differentiated cells at days 11, 14, 17 and 21. Values are mean ± SE of three experiments; bP < 0.001 for control cells vs differentiated cells; C: Representative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction gel photomicrographs showing expression of albumin by hepatocytic cells induced from fetal cardiac mesenchymal stem cells. Control cells without induction medium did not show any expression of albumin.
- Citation: Srikanth GVN, Tripathy NK, Nityanand S. Fetal cardiac mesenchymal stem cells express embryonal markers and exhibit differentiation into cells of all three germ layers. World J Stem Cells 2013; 5(1): 26-33
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v5/i1/26.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v5.i1.26