Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2025; 17(6): 106520
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106520
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106520
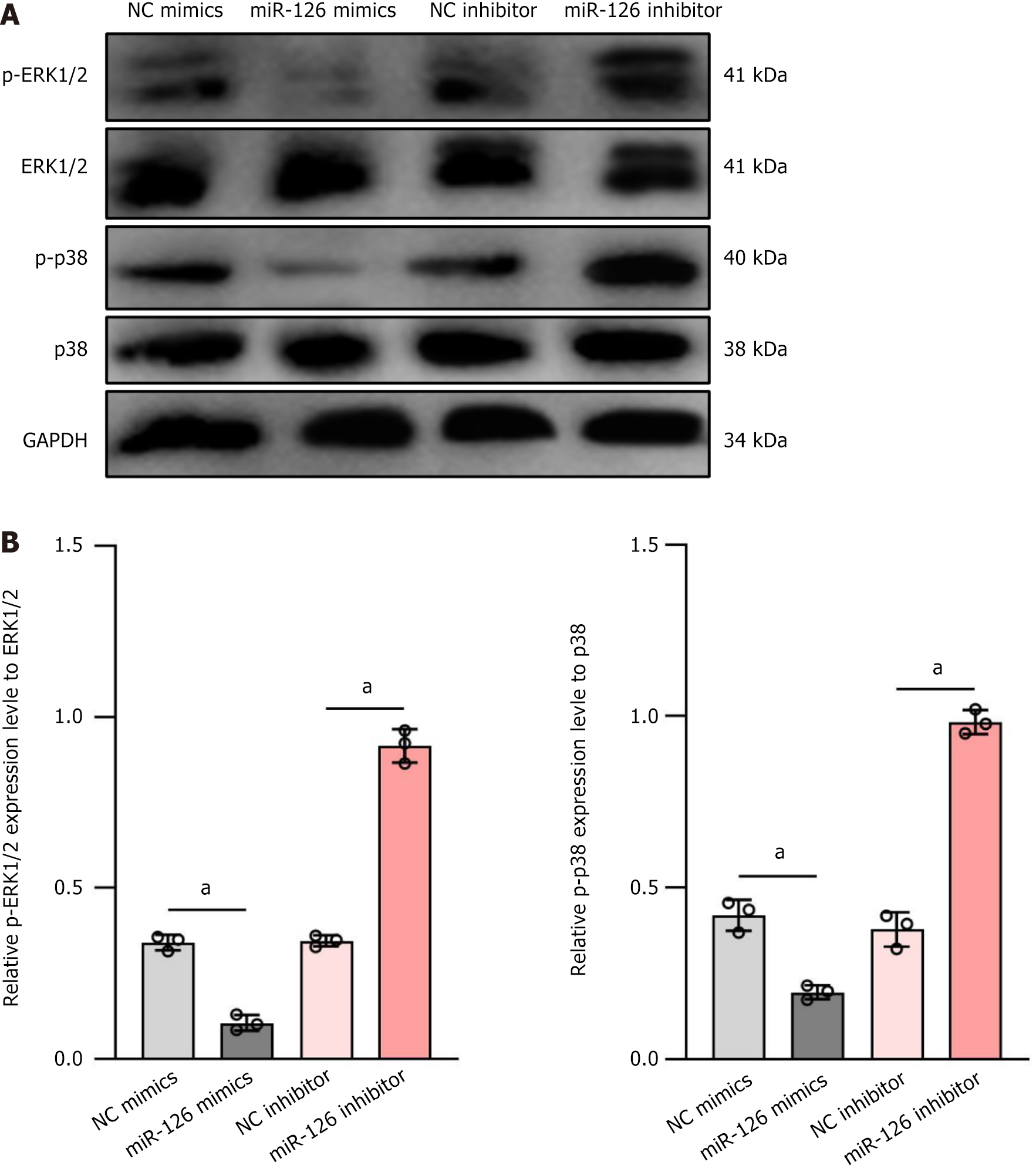
Figure 4 On the effects of miR-126 on the phosphorylation of 1 extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathways.
A: Western blot analysis was used to evaluate the expression levels of p-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2, ERK1/2, p-p38, and p38 under four conditions: Negative control mimics, miR-126 mimics, negative control inhibitor, and miR-126 inhibitor. The results showed that in the miR-126 mimics group, the expression of p-ERK1/2 and p-p38 was significantly decreased, while in the miR-126 inhibitor group, the phosphorylation levels of these proteins were markedly increased; B: The bar charts quantified the relative expression levels of p-ERK1/2 and p-p38, further supporting the above results. Thus, miR-126 may influence cell functions, particularly the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into functional endothelial cells, by modulating the ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways. Data are presented as mean ± SD, and differences between groups were calculated using one-way ANOVA. aP < 0.01. ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NC: Negative control.
- Citation: Ye ZQ, Meng XH, Fang X, Liu HY, Mwindadi HH. MiR-126 regulates the effect of mesenchymal stem cell vascular repair on carotid atherosclerosis through MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(6): 106520
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i6/106520.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106520