Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2025; 17(5): 105394
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105394
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105394
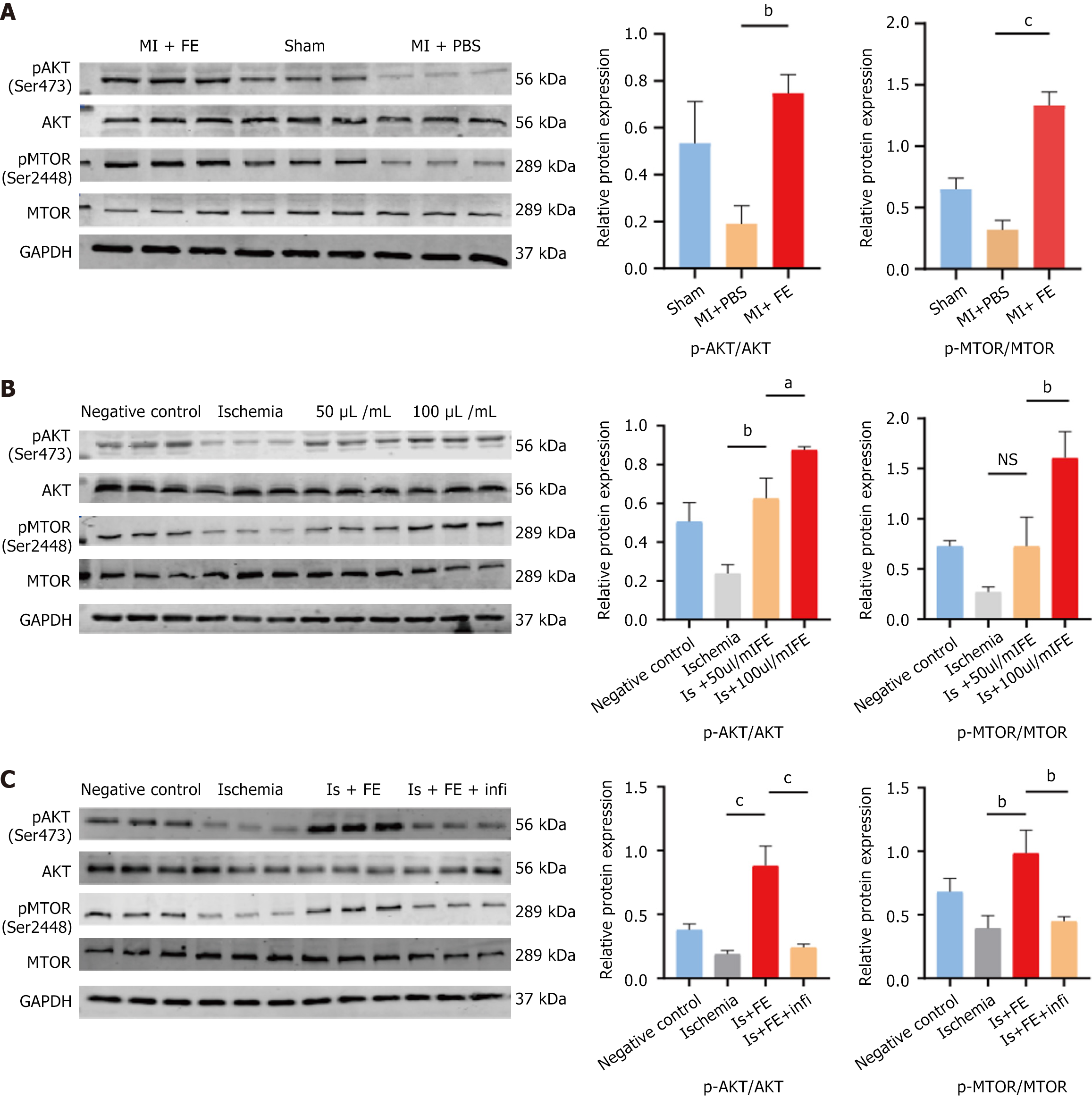
Figure 6 Activation of the basic fibroblast growth factor-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mechanistic target of rapamycin signaling pathways may be involved in the role of fat extract in myocardial ischemia injury.
The expression and phosphorylation levels of protein kinase B and mechanistic target of rapamycin were analyzed by western blot. A: C57 mice myocardial tissues; B and C: Hypoxia treated cardiomyocytes. Data were presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 per group), aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, NS: No significance. MI: Myocardial infarction; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; FE: Fat extract; Akt: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Yang TY, Sun Y, Zhang WJ, Wang CQ, Zhou J. Cell-free extracts from human fat tissue attenuate ischemic injury in cardiomyocytes in a murine model. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(5): 105394
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i5/105394.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105394