Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2025; 17(5): 105394
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105394
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105394
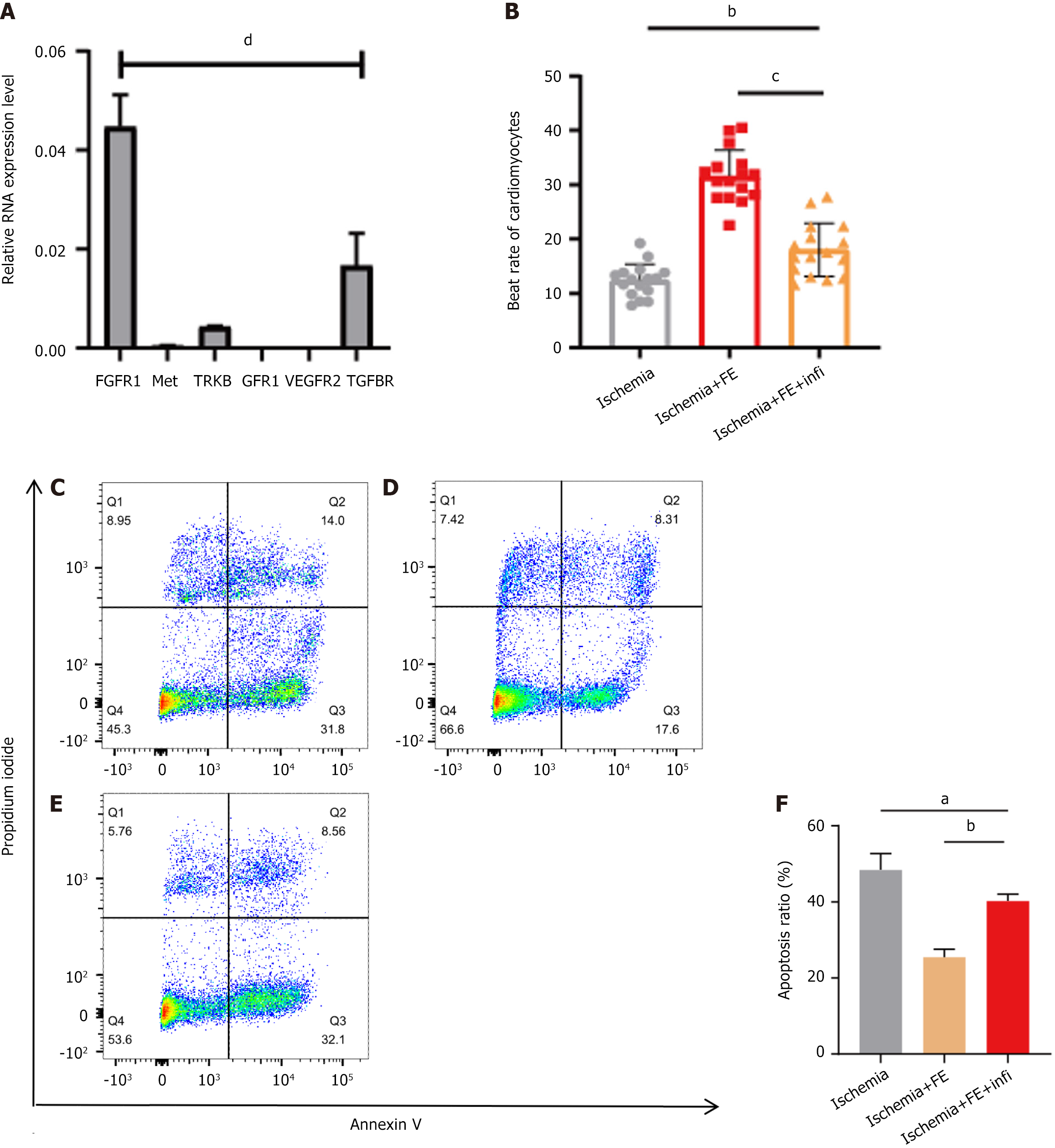
Figure 4 Fibroblast growth factor receptor family inhibitor partly blocked the therapeutic effect of fat extract at the cellular level after ischaemia injury.
A: Relative mRNA expression levels of tropomyosin receptor kinase B, transforming growth factor-beta receptor, Met, fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, GFR1 in cardiomyocytes; B Quantification of beat rate of cardiomyocytes; C-E: The level of cell apoptosis were calculated using flow cytometry (n = 3); F: Quantification of cell apoptosis. Values indicate mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. TRKB: Tropomyosin receptor kinase B; TGFBR: Transforming growth factor-beta receptor; FGFR1: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; VEGFR2: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; FE: Fat extract; Infi: Infigratinib.
- Citation: Yang TY, Sun Y, Zhang WJ, Wang CQ, Zhou J. Cell-free extracts from human fat tissue attenuate ischemic injury in cardiomyocytes in a murine model. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(5): 105394
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i5/105394.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105394