Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2025; 17(5): 105266
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105266
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105266
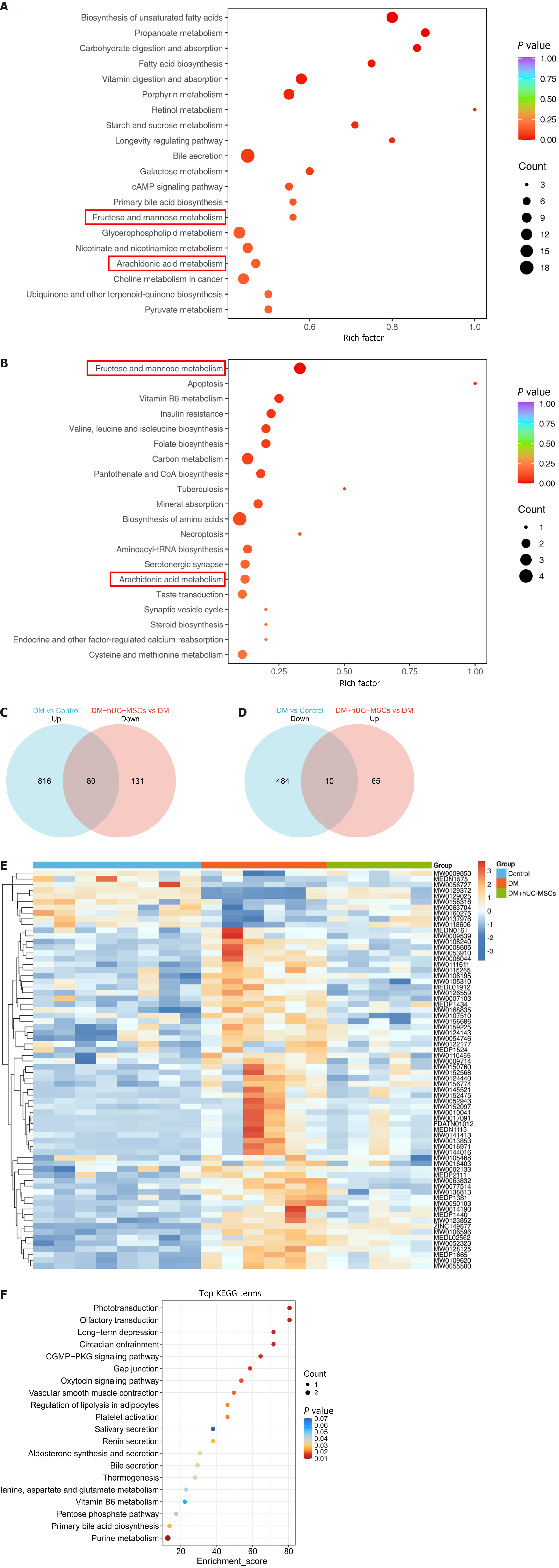
Figure 3 The effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on liver metabolic pathways and metabolites in rats with concurrent diabetes mellitus and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.
A and B: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment bubble plot for the differential metabolites between the diabetes mellitus (DM) group and the control group (A) and between the DM group and the DM + human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells group (B); C and D: Venn diagram showing the upregulated and downregulated differential metabolites in the different comparison groups; E: Heatmap of the intersecting differential metabolites; F: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis bubble plot for the intersecting differential metabolites. Control group, n = 8; diabetes mellitus group, n = 6; diabetes mellitus + human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells group, n = 5. hUC-MSCs: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; DM: Diabetes mellitus; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
- Citation: Zhou KB, Nie L, Wang ML, Xiao DH, Zhang HY, Yang X, Liao DF, Yang XF. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate liver metabolism in diabetic rats with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(5): 105266
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i5/105266.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.105266