Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2024; 16(4): 353-374
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.353
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.353
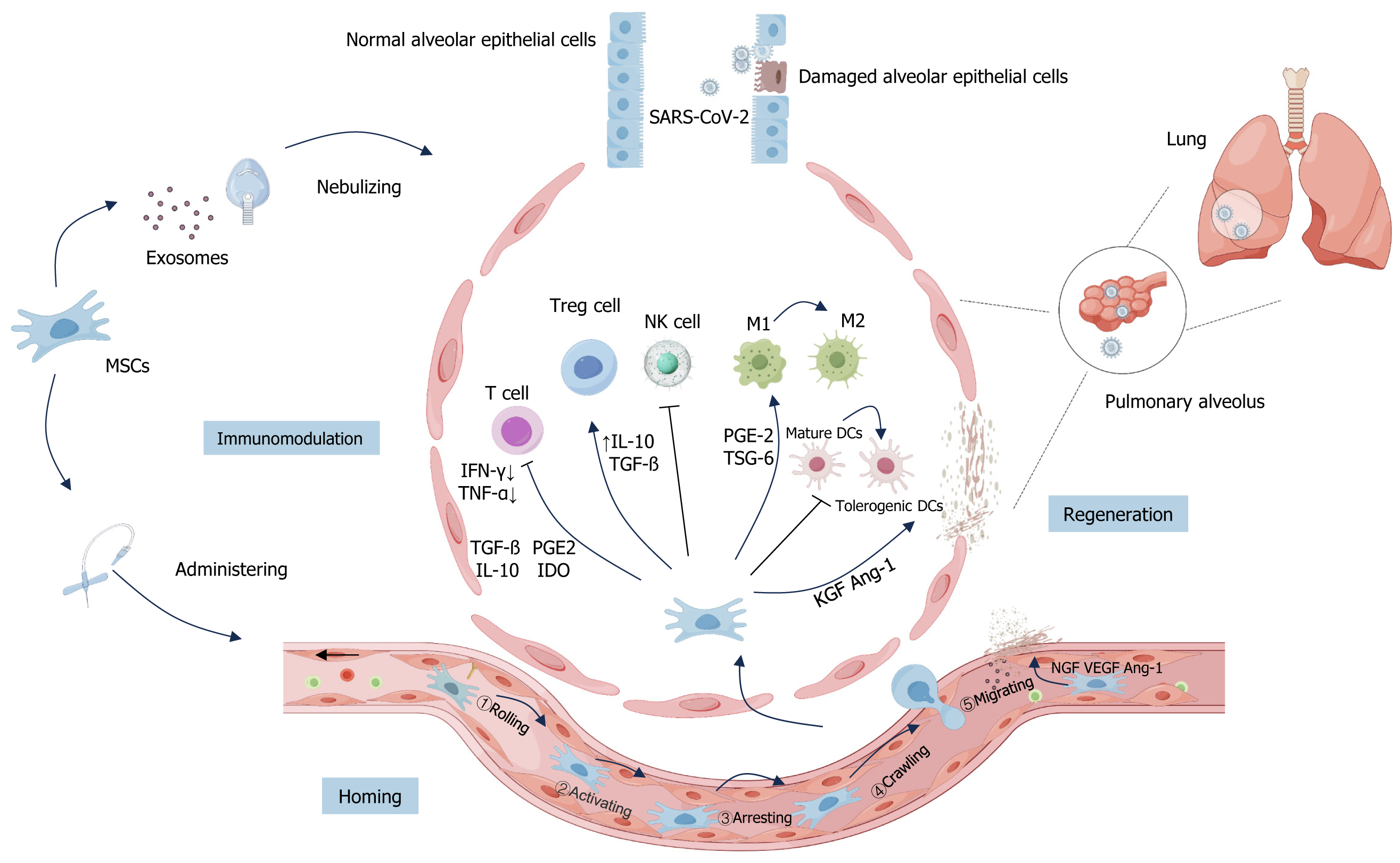
Figure 2 Main mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes for coronavirus disease 2019 treatment.
By Figdraw, https://www.figdraw.com. Currently, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and their derived exosomes (MSCs-Exo) used for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are administered by intravenous infusion or nebulized inhalation. The main mechanisms of MSCs and MSCs-Exo for COVID-19 include: (1) Homing: Non-systemic homing: MSCs are locally transplanted and directed to the site of injury by a chemokine gradient; systemic homing process of MSCs in the inflammatory microenvironment: Rolling; activating; arresting; crawling; migrating; (2) Immunomodulation: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 invasion into alveoli and other tissues leads to the activation of T cells. At the same time, MSCs coordinate local and systemic innate and adaptive immune responses, promote macrophage polarization from M1 to M2 subtypes, inhibit T cell activation and proliferation, promote the proliferation of regulatory T cells (Tregs), inhibit the killing function of natural killer cells and the maturation of dendritic cell (including mature dendritic cells and tolerogenic dendritic cells). T cells produce interferon (IFN)-γ and IFN-α. MSCs may produce anti-inflammatory mediators such as transforming growth factor β, prostaglandin E2 (PGE 2), indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, and interleukin-10, which regulate T-cell and Treg-cell-mediated immune responses. On the other hand, MSCs can promote macrophage polarization from the M1 to M2 subtype by secreting PGE 2 and tumor necrosis factor α stimulated gene 6; and (3) Regenerative repair: Growth factors such as keratinocyte growth factor and angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) promote the restoration of the alveolar-capillary barrier, while nerve growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and Ang-1 promote neovascularization in healing tissues, activate the coagulation pathway, and promote blood coagulation, which contributes to repair and regeneration. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; NK cells: Natural killer cells; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-α: Interferon-α; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; IL: Interleukin; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; TSG-6: Tumor necrosis factor α stimulated gene 6; Ang-1: Angiopoietin-1; DCs: Dendritic cells; KGF: Keratinocyte growth factor; NGF: Nerve growth factor; Tregs: Regulatory T cells; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Hou XY, Danzeng LM, Wu YL, Ma QH, Yu Z, Li MY, Li LS. Mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes for the treatment of COVID-19. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(4): 353-374
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i4/353.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.353