Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2024; 16(4): 353-374
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.353
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.353
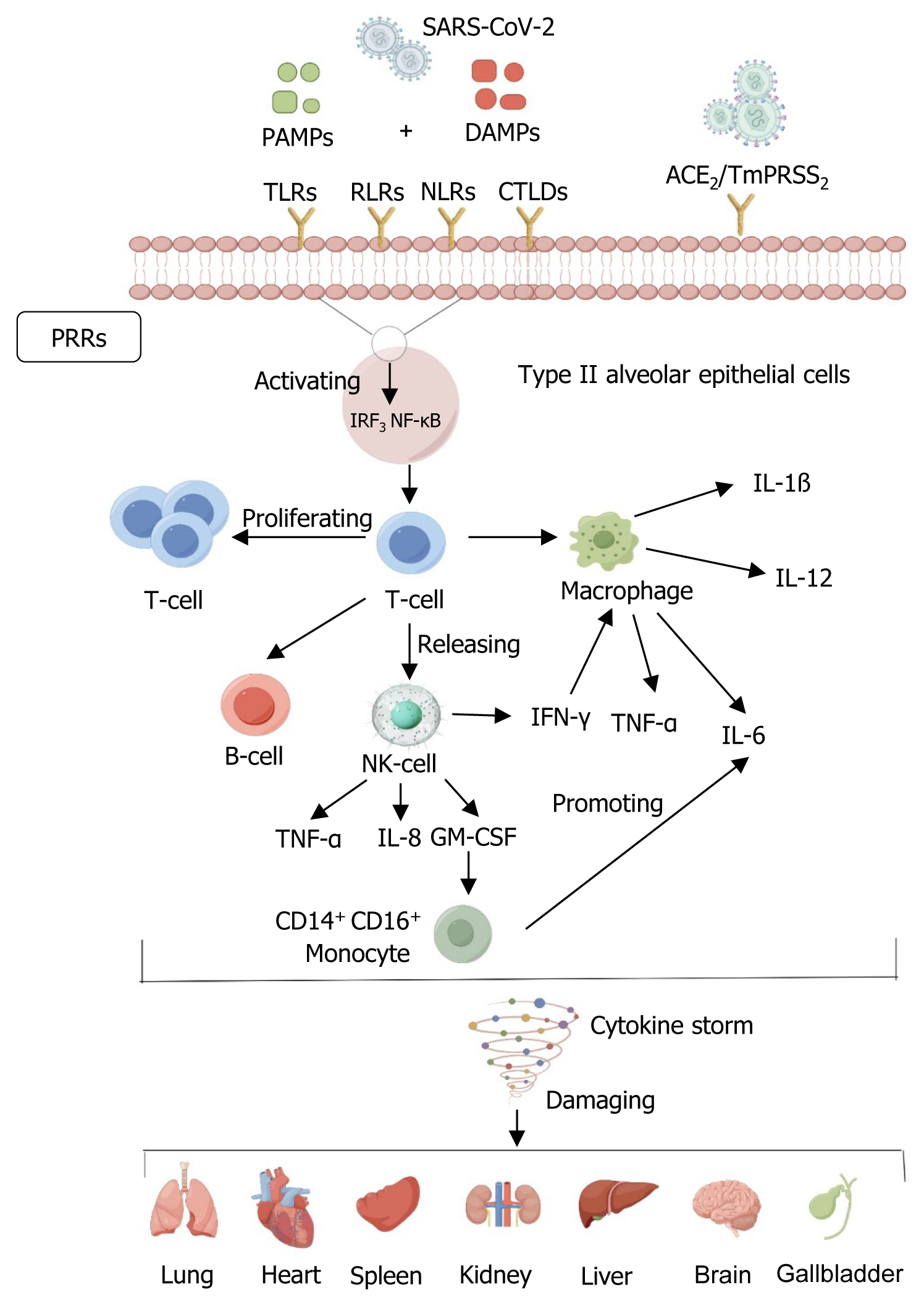
Figure 1 Mechanisms of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 damage.
By Figdraw, https://www.figdraw.com. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) binds to host receptors, mediates membrane fusion and viral penetration, and predominantly infects type II alveolar epithelial cells expressing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors in the alveoli. Rapid replication of SARS-CoV-2 after the invasion of the body subsequently triggers a potent immune system response, with heat shock proteins or other damage-associated molecular patterns released by injured lung parenchymal cells, and inhaled pathogen-associated molecular patterns initiating the immune response through the activation of classical pattern recognition receptors, which include not only toll-like receptors, but also multiple lineage-encoded receptors, such as Rig-I like receptor, Nod-like receptors, and C-type lectin-like domains, which further activate interferon regulatory factor 3 and nuclear factor kappa-B pathways and enhance T-cell secretion. Pathogenic T helper cell 1 releases signals to B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and macrophages, whereas NK cells release tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-8, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and interferon (IFN)-γ. GM-CSF further activates CD14+ CD16+ inflammatory monocytes and enhances the secretion of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, IL-1β) from alveolar macrophages, thereby further elevating the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, thus further elevating the level of inflammation in damaged lung tissues and causing a cytokine storm that results in multi-organ dysfunction and even failure of the lung, heart, spleen, kidneys, liver, brain, and gall bladder. ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; CTLD: C-type lectin-like domain; DAMPs: Damage associated molecular patterns; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; IL: Interleukin; IRF3: Interferon regulatory factor 3; NK cells: Natural killer cells; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; NLRs: Nod-like receptors; PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PRRs: Pattern recognition receptors; RLRs: Rig-I like receptors; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TLRs: Toll-like receptors; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Hou XY, Danzeng LM, Wu YL, Ma QH, Yu Z, Li MY, Li LS. Mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes for the treatment of COVID-19. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(4): 353-374
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i4/353.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i4.353