Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2013; 5(4): 163-171
Published online Oct 26, 2013. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.163
Published online Oct 26, 2013. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.163
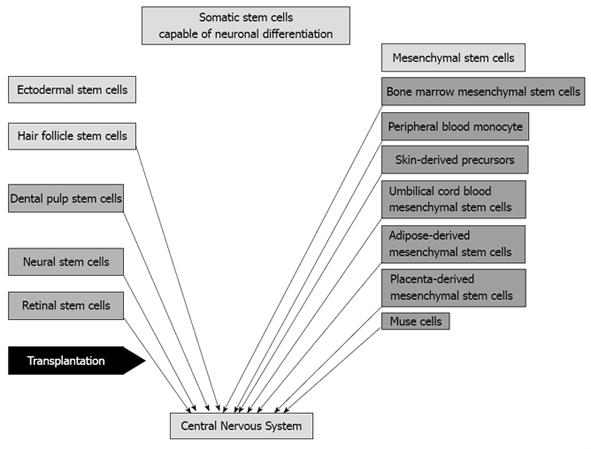
Figure 1 Somatic stem cells capable of neuronal differentiation.
These cells are classified into two groups, ectodermal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells. Ectodermal stem cells include hair follicle stem cells, dental pulp stem cells, neural stem cells and retinal stem cells, while mesenchymal stem cells include bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, peripheral blood monocytes, skin-derived precursors, umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells, placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and Muse cells. These cells are candidates for donor cells for cell transplantation therapy for intractable neuronal diseases.
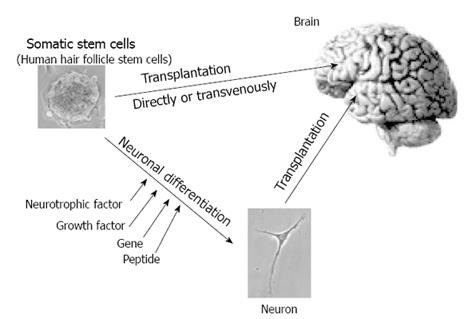
Figure 2 Transplantation of somatic stem cells into the central nervous system.
Somatic stem cells (human hair follicle cell cells) forming a neurosphere, non-treated or neuronally differentiated by various methods, are directly or transvenously transplanted to brain.
- Citation: Kanno H. Regenerative therapy for neuronal diseases with transplantation of somatic stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2013; 5(4): 163-171
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v5/i4/163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v5.i4.163