Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2025; 31(32): 109897
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.109897
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.109897
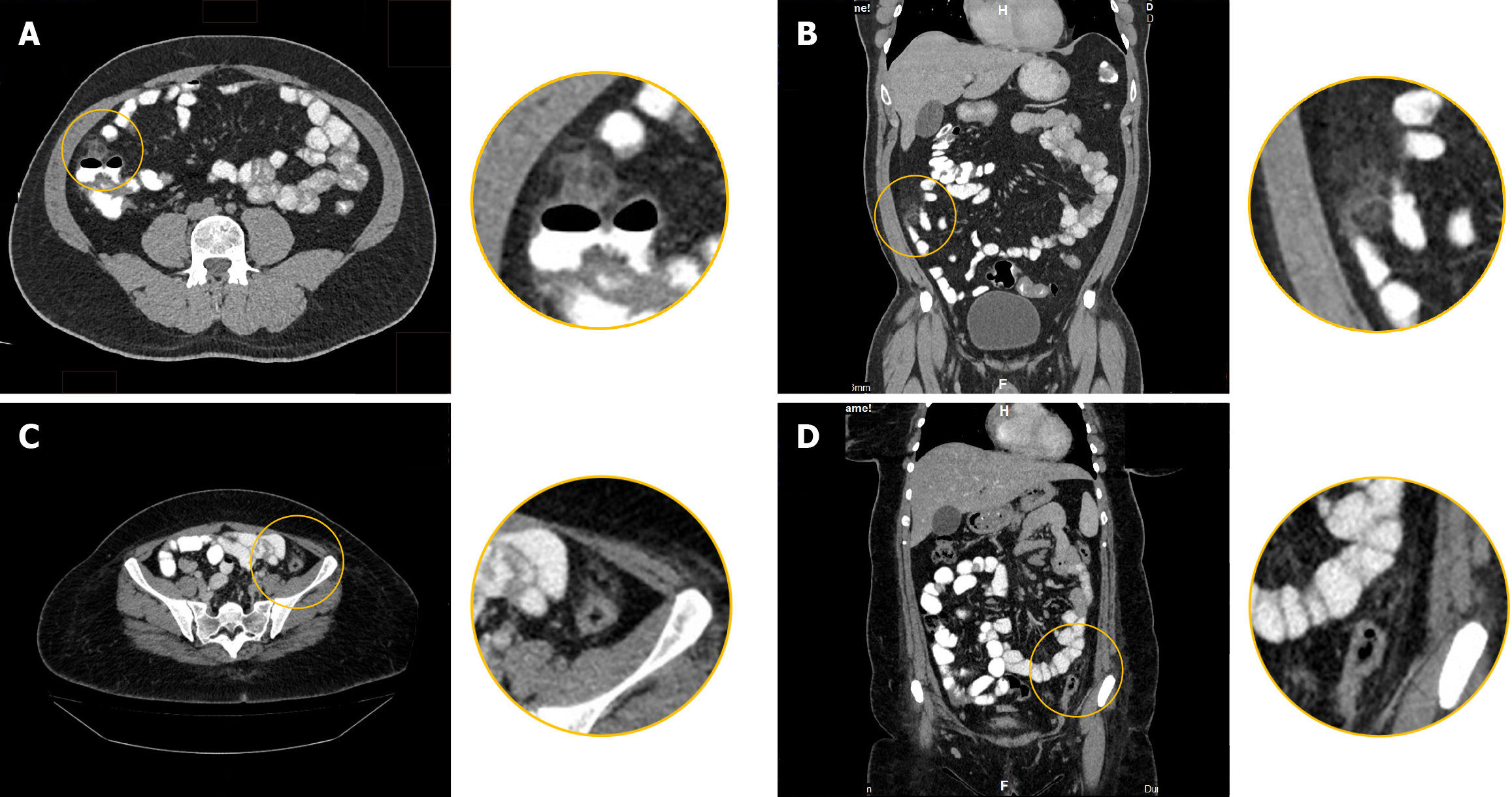
Figure 2 Computed tomography-scan findings of acute epiploic appendagitis.
A and B: In a 43-year-old woman: Axial (A); Coronal contrast-enhanced computed tomography-scan (B). Acute epiploic appendagitis in a 43-year-old man. A well-defined, oval-shaped fat density nodule is seen adherent to the anterior wall of the cecum, measuring 24 cm × 1.6 cm. It has a thick rim and is surrounded by mild fat stranding. This is in keeping with epiploic appendagitis; C and D: In a 35-year-old woman: Axial (C); Coronal contrast-enhanced computed tomography-scan (D). Acute epiploic appendagitis in a 35-year-old woman. An oval-shaped fat-density nodule is noted in the left lower abdomen abutting the anterior wall of the distal descending colon with mild surrounding fat stranding.
- Citation: El-Sawaf Y, Alzayani S, Saeed NK, Bediwy AS, Elbeltagi R, Al-Roomi K, Al-Beltagi M. Epiploic appendagitis: An overlooked cause of acute abdominal pain. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(32): 109897
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i32/109897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.109897