Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2025; 31(32): 104277
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.104277
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.104277
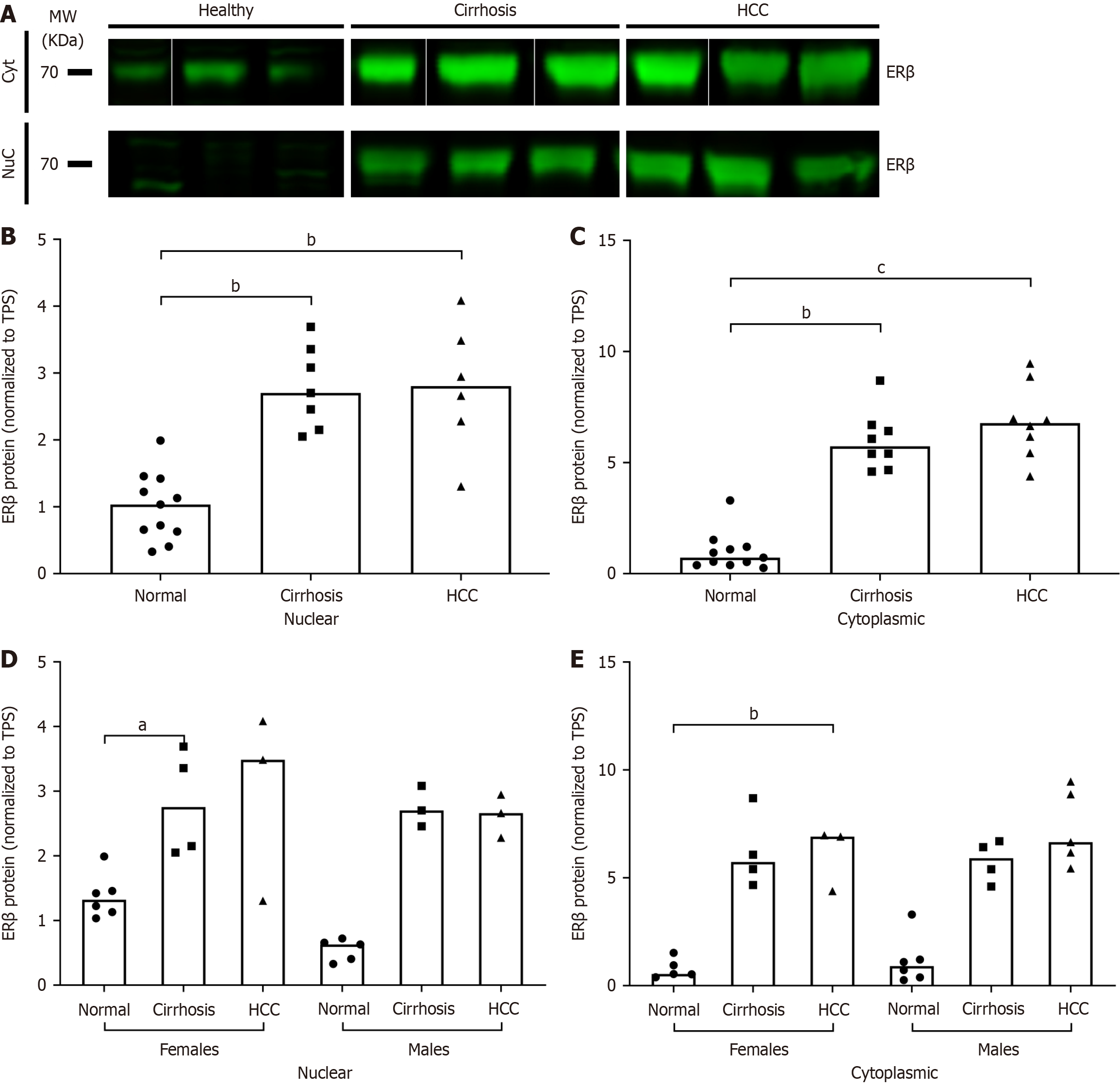
Figure 4 Protein expression of estrogen receptor β in human liver tissues with hepatitis C virus-related diseases.
Estrogen receptor (ER) β protein expression was analyzed in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-related cirrhosis and HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma liver tissues and compared to normals. A: ERβ protein expression by Western blot in human liver tissues fractionated by nuclear and cytoplasmic protein; B and C: Quantification of A by densitometry from multiple blots and normalized to total protein; D and E: ERβ protein expression in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of human liver tissues and stratified by sex. Column bars represent the median. Each symbol represents one individual. Data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s Multiple Comparisons posttest where aP ≤ 0.05. bP ≤ 0.01. cP ≤ 0.001. Nuc: Nuclear; Cyt: Cytoplasmic; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ER: Estrogen receptor; TPS: Total protein stain.
- Citation: Groover S, Addison S, Nicks S, Mwangi M, Brooks A, Kaul A, Kaul R. Sex based relative expression of estrogen receptors and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in liver affects hepatitis C virus viral pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(32): 104277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i32/104277.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.104277