Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2025; 31(32): 104277
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.104277
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.104277
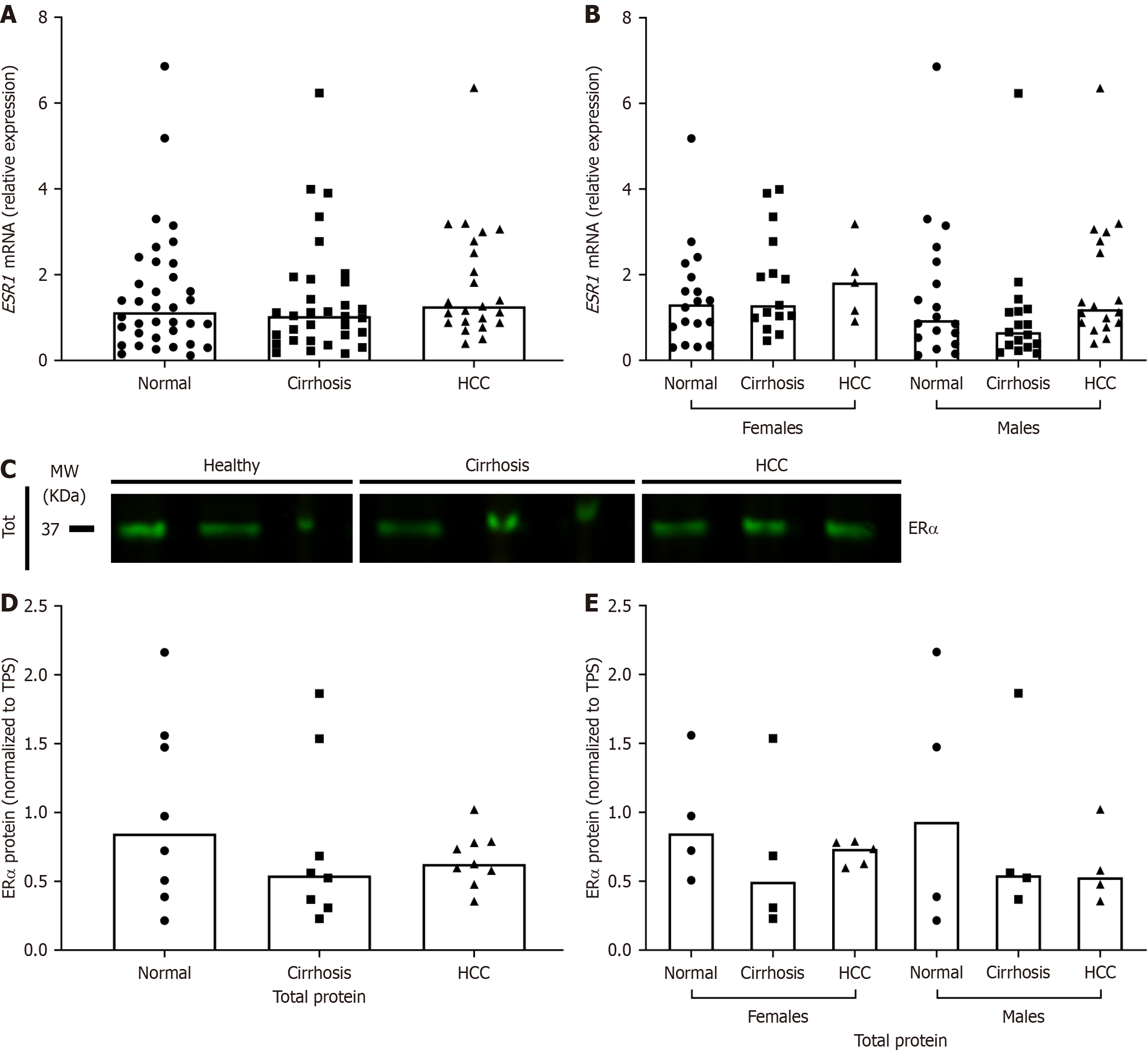
Figure 2 Expression of estrogen receptor α in human liver tissues with hepatitis C virus-related diseases.
Estrogen receptor (ER) α message RNA and protein expressions were analyzed in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-related cirrhosis and HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma liver tissues and compared to normals. A: ESR1 transcript levels by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction normalized to GUSB and SRSF4 expression and compared using the ΔΔCt method; B: Stratification of A by sex; C: ERα protein expression by Western blot using whole liver tissue lysates (tot); D: Quantification of C by densitometry from multiple blots and normalized to total protein; E: ERα protein expression in human liver tissues stratified by sex. Column bars represent the median. Each symbol represents one individual. Data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s Multiple Comparisons posttest where P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. mRNA: Message RNA; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ER: Estrogen receptor; TPS: Total protein stain.
- Citation: Groover S, Addison S, Nicks S, Mwangi M, Brooks A, Kaul A, Kaul R. Sex based relative expression of estrogen receptors and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in liver affects hepatitis C virus viral pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(32): 104277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i32/104277.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.104277