Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2025; 31(31): 109605
Published online Aug 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.109605
Published online Aug 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.109605
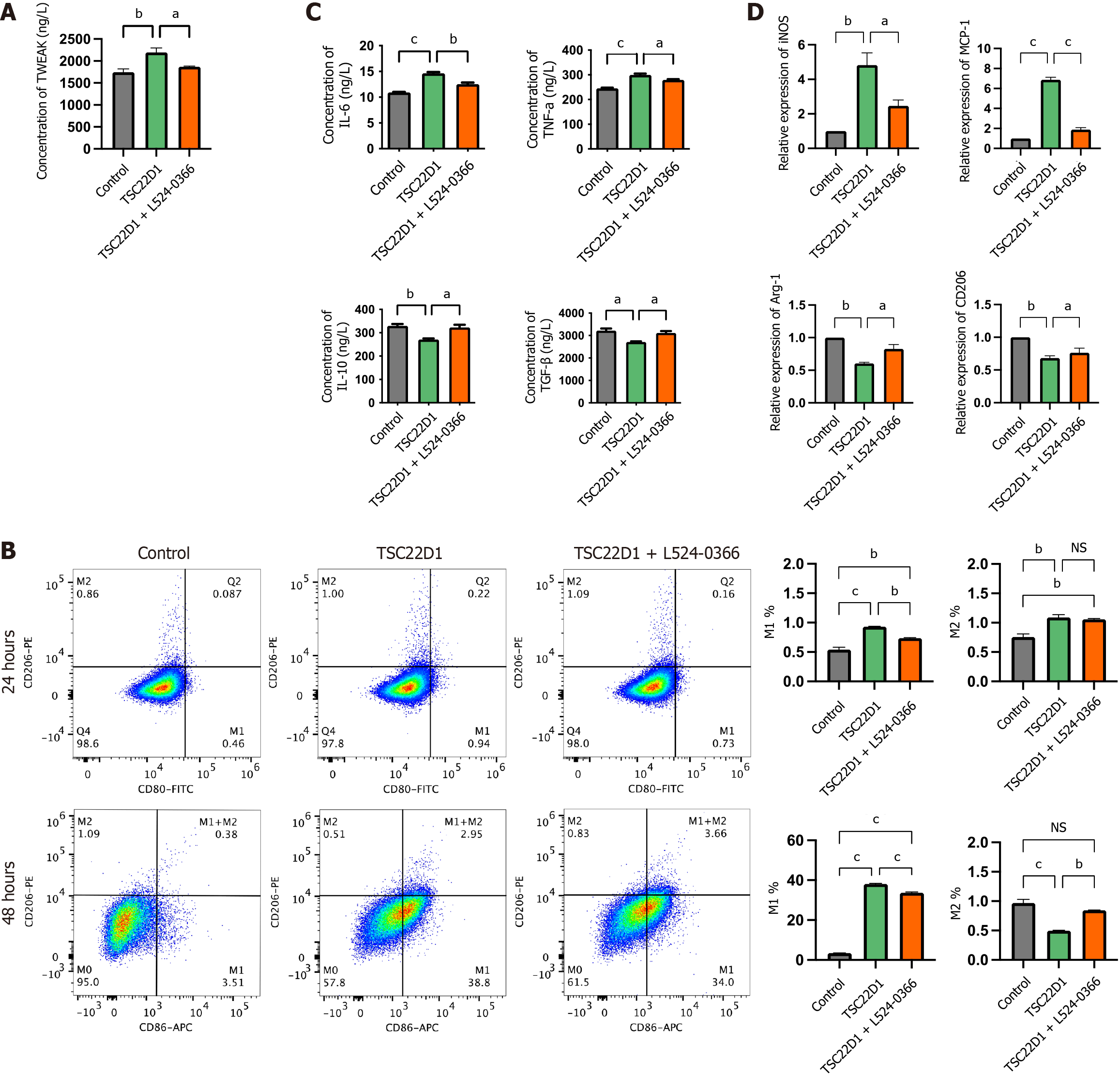
Figure 6 Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis promotes macrophage M1 polarization secreted by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells overexpressing TSC22D1 via the tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis/fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 pathway.
A: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis in the supernatants of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs); B: Flow cytometry analysis detecting the expression levels of M1 and M2 macrophages; C: ELISA analysis of interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-10, and transforming growth factor-β in the supernatants of macrophages cultured in conditioned media from LSECs; D: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of inducible nitric oxide synthase, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, arginase-1 and cluster of differentiation 206 in macrophages. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. One-way analysis of variance. TWEAK: Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis; CD: Cluster of differentiation; FITC: Fluorescein Isothiocyanate; APC: Antigen-presenting cell; NS: No significant; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; MCP: Monocyte chemoattractant protein; Arg-1: Arginase-1.
- Citation: Ding W, Xu XQ, Wu LL, Wang Q, Wang YQ, Chen WW, Tan YL, Wang YB, Jiang HJ, Dong J, Yan YM, Xu XZ. TSC22D1 promotes liver sinusoidal endothelial cell dysfunction and induces macrophage M1 polarization in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(31): 109605
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i31/109605.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.109605