Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2025; 31(31): 109605
Published online Aug 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.109605
Published online Aug 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.109605
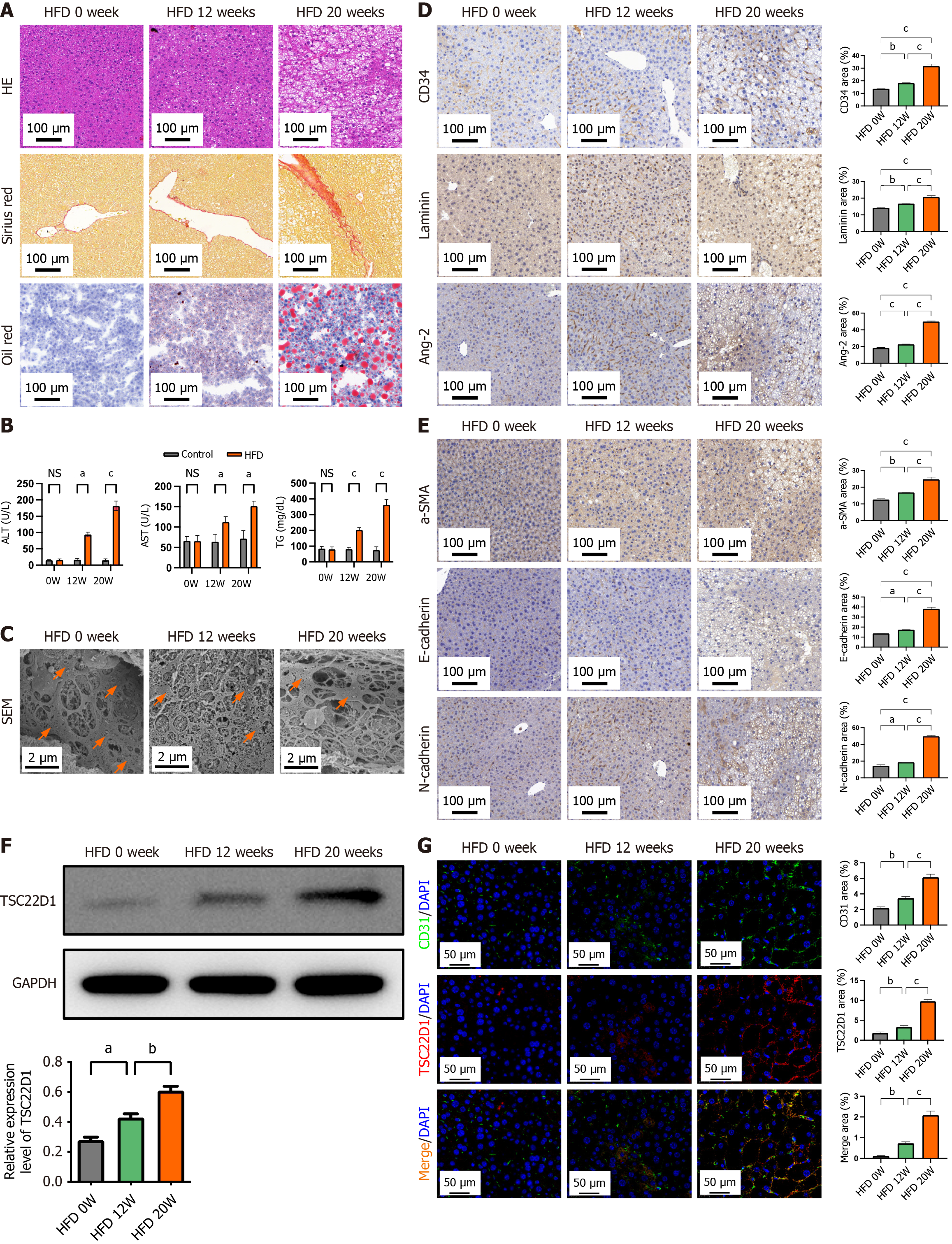
Figure 3 High-fat diet upregulates TSC22D1 expression and promotes liver sinusoidal endothelial cell dysfunction.
A: Hematoxylin eosin, Sirius red, and Oil red O staining of liver tissues from three groups of mice; B: Biochemical indices of the three groups of mice; C: Electron microscopy showing fenestrae in liver tissues with orange arrows; D: Immunohistochemical staining for cluster of differentiation (CD) 34, laminin, and angiotensin-2; E: Immunohistochemical staining for α-smooth muscle actin, E-cadherin, and N-cadherin; F: Western blot analysis for TSC22D1 expression; G: Immunofluorescence staining for CD31 and TSC22D1. Scale bar 100 μm, 100 × magnification. Scale bar 50 μm, 200 × magnification. Scale bar 2 μm, 5000 × magnification. n = 6 mice each group. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. One-way analysis of variance. HE: Hematoxylin eosin; HFD: High-fat diet; CD: Cluster of differentiation; Ang-2: Angiotensin-2; NS: No significant; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TG: Triglyceride; SEM: Scanning electron microscopy; SMA: Smooth muscle actin; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Ding W, Xu XQ, Wu LL, Wang Q, Wang YQ, Chen WW, Tan YL, Wang YB, Jiang HJ, Dong J, Yan YM, Xu XZ. TSC22D1 promotes liver sinusoidal endothelial cell dysfunction and induces macrophage M1 polarization in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(31): 109605
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i31/109605.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i31.109605