Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2025; 31(29): 109090
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.109090
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.109090
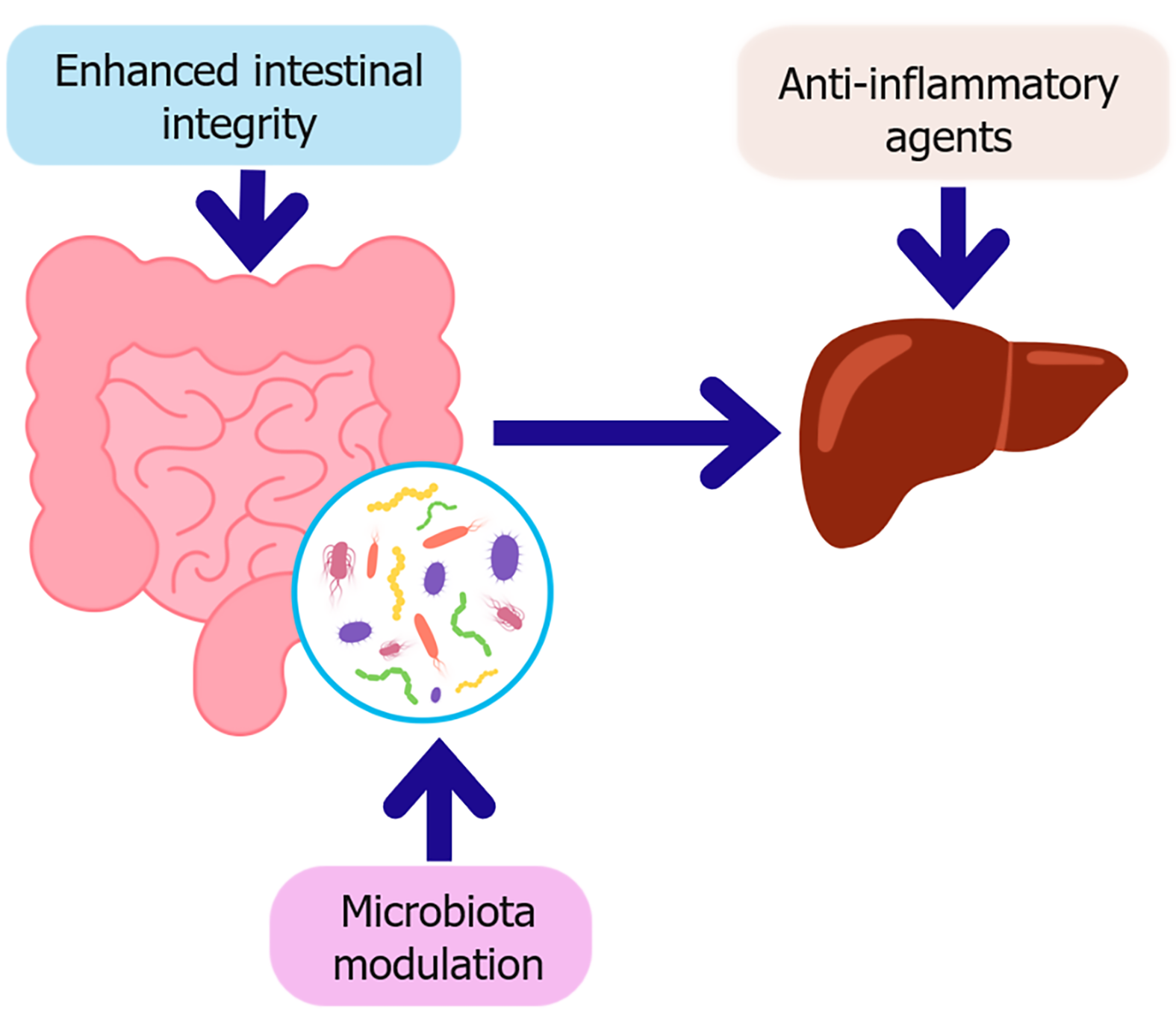
Figure 4 Key therapeutic strategies targeting the gut-liver axis in diabetes.
This schematic illustrates therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring gut-liver axis homeostasis in the context of type 2 diabetes. Microbiota modulation, through probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, or fecal microbiota transplantation which enhances intestinal integrity by strengthening the epithelial barrier and promoting beneficial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids. Improved barrier function reduces microbial translocation, subsequently decreasing hepatic inflammation. In parallel, anti-inflammatory agents directly target hepatic immune activation, contributing to improved insulin sensitivity and metabolic regulation.
- Citation: Abdalla MMI. Gut-liver axis in diabetes: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(29): 109090
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i29/109090.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.109090