Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2025; 31(29): 109090
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.109090
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.109090
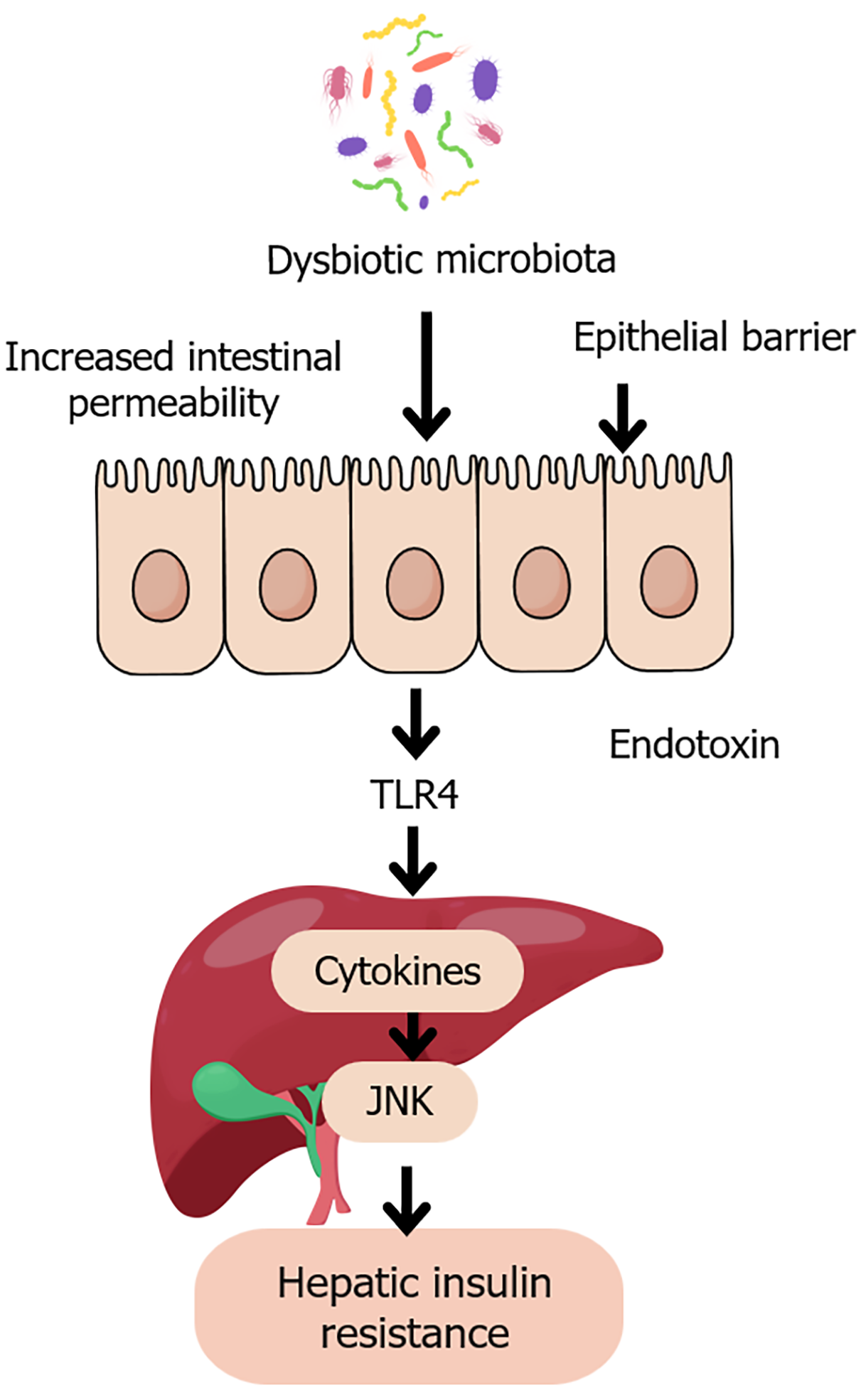
Figure 2 Gut dysbiosis and hepatic insulin resistance.
This figure is a schematic illustration of the pathological pathway linking dysbiotic gut microbiota to hepatic insulin resistance. Disruption of microbial balance leads to increased intestinal permeability and epithelial barrier dysfunction, allowing the translocation of endotoxins such as lipopolysaccharide into the portal circulation. These endotoxins activate toll-like receptor 4 on hepatic Kupffer cells, triggering pro-inflammatory cytokine release and activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling. This inflammatory cascade impairs insulin receptor signaling, contributing to hepatic insulin resistance, a key feature of type 2 diabetes. JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4.
- Citation: Abdalla MMI. Gut-liver axis in diabetes: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(29): 109090
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i29/109090.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.109090