Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2025; 31(29): 107066
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066
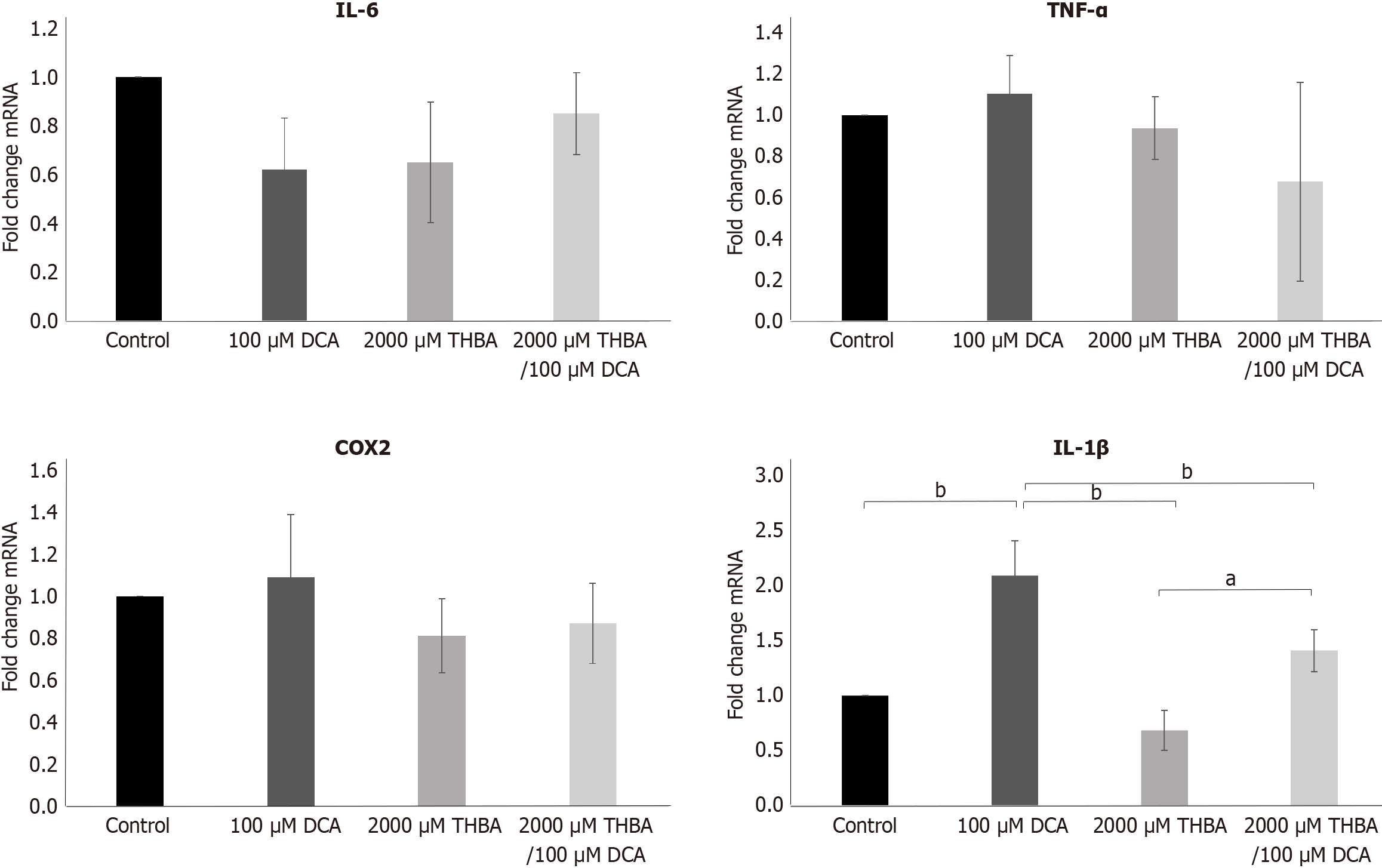
Figure 6 Effects of deoxycholic acid and tetrahydroxylated bile acids co-exposure on proinflammatory (interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, cyclooxygenase-2) genes expression in adult tissue-resident stem cells isolated from Barrett esophagus clinical biopsies.
Barrett esophagus clinical biopsies treated with deoxycholic acid, tetrahydroxylated bile acids, their combination did not demonstrate significant difference in the gene expression interleukin-6, cyclooxygenase-2, and tumor necrosis factor-α. At the same time, these cells demonstrated significant 2-fold increase in interleukin-1β gene expression after cultivation with 100 μM deoxycholic acid. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; COX2: Cyclooxygenase-2; DCA: Deoxycholic acid; THBA: Tetrahydroxylated bile acids.
- Citation: Mamchur A, Duggan S, Xue H, Niu XJ, Wang YZ, Ma ZW, Kelleher D, Ling V, Gao ZH. Tetrahydroxylated bile acids prevents malignant progression of Barret esophagus in vitro by inhibiting the interleukin-1β-nuclear factor kappa-B pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(29): 107066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i29/107066.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066