Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2025; 31(29): 107066
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066
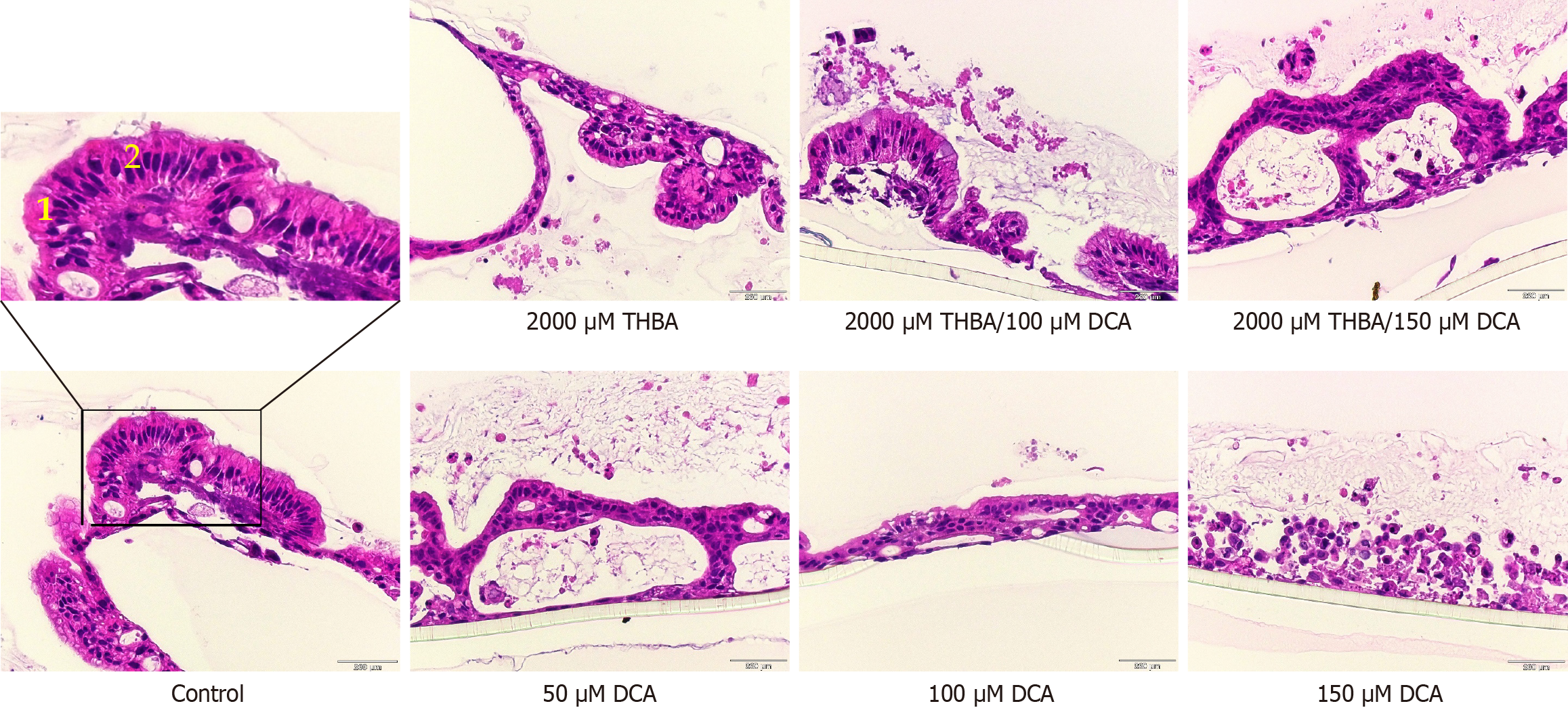
Figure 4 Effects of deoxycholic acid and tetrahydroxylated bile acids co-exposure on adult tissue-resident stem cells isolated from Barrett esophagus clinical biopsies intestinal differentiation.
Representative pictures of hematoxylin and eosin stained air liquid interface Barrett esophagus clinical biopsies tissue sections (× 20 magnification). Samples treated with 2000 μM tetrahydroxylated bile acids (THBA), co-treated with THBA and deoxycholic acid (DCA) (2000 μM THBA/150 μM DCA, 2000 μM THBA/100 μM DCA) and control demonstrated high level intestinal differentiation with distinct interspersed goblet-like cells between well polarized columnar intestine-like cells resembling mature intestinal mucosa. Samples treated with DCA alone showed attenuation of the cell layer, reduced number of goblet dells and nuclear atypia. (1goblet-like cells, 2columnar polarized intestine-like cells). DCA: Deoxycholic acid; THBA: Tetrahydroxylated bile acids; Scale bar = 250 μm.
- Citation: Mamchur A, Duggan S, Xue H, Niu XJ, Wang YZ, Ma ZW, Kelleher D, Ling V, Gao ZH. Tetrahydroxylated bile acids prevents malignant progression of Barret esophagus in vitro by inhibiting the interleukin-1β-nuclear factor kappa-B pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(29): 107066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i29/107066.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066