Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2025; 31(29): 107066
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066
Published online Aug 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066
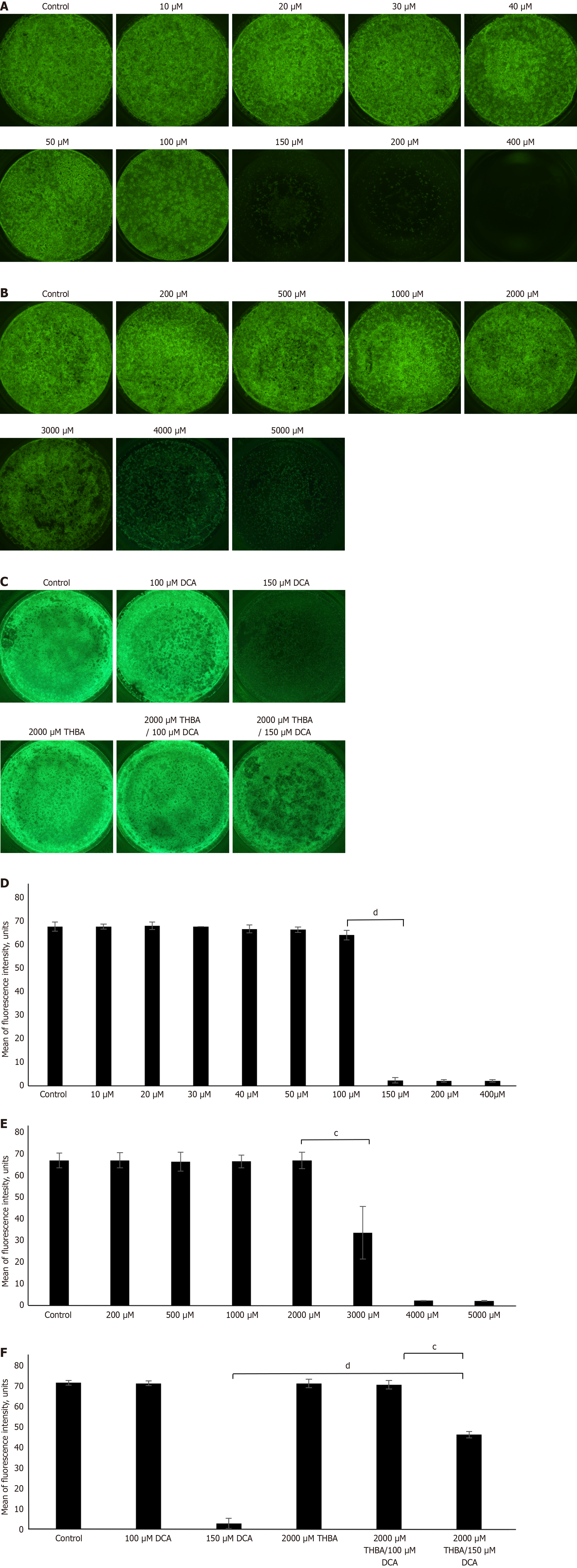
Figure 2 Effect of deoxycholic acid, tetrahydroxylated bile acids and their combination on adult tissue-resident stem cells isolated from Barrett esophagus clinical biopsies cytotoxicity.
Representative green fluorescent protein-labeled (GFP) fluorescent images of Barrett esophagus clinical biopsies (BE-ASCs) in transwell inserts after 15 days in culture with various deoxycholic acid (DCA) and hydrophilic tetrahydroxylated bile acids (THBA) concentrations. 1 × 106 BE-ASCs were plated in 12 Matrigel coated transwell inserts on the feeder layer of irradiated 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts (1 × 105 fibroblasts per transwell). A: BE-ASCs cultured with 100 μM DCA showed slight cytotoxicity and significant decreasing of viability (22-fold) after treatment with 150 μM DCA or higher; B: BE-ASCs treated with 3000 μM THBA or higher demonstrated significant decreases in viability; C: BE-ASCs co-treated with 2000 μM THBA/150 μM DCA showed 17-fold higher viability in comparison to cells treated with DCA alone; D-F: Viability levels of BE-ASCs treated with DCA (D), THBA (E), their combination (F), were correlated with GFP fluorescence intensity measured using ImageJ software. Averages from triplicates are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. DCA: Deoxycholic acid; THBA: Tetrahydroxylated bile acids.
- Citation: Mamchur A, Duggan S, Xue H, Niu XJ, Wang YZ, Ma ZW, Kelleher D, Ling V, Gao ZH. Tetrahydroxylated bile acids prevents malignant progression of Barret esophagus in vitro by inhibiting the interleukin-1β-nuclear factor kappa-B pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(29): 107066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i29/107066.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.107066