Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2025; 31(28): 107361
Published online Jul 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361
Published online Jul 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361
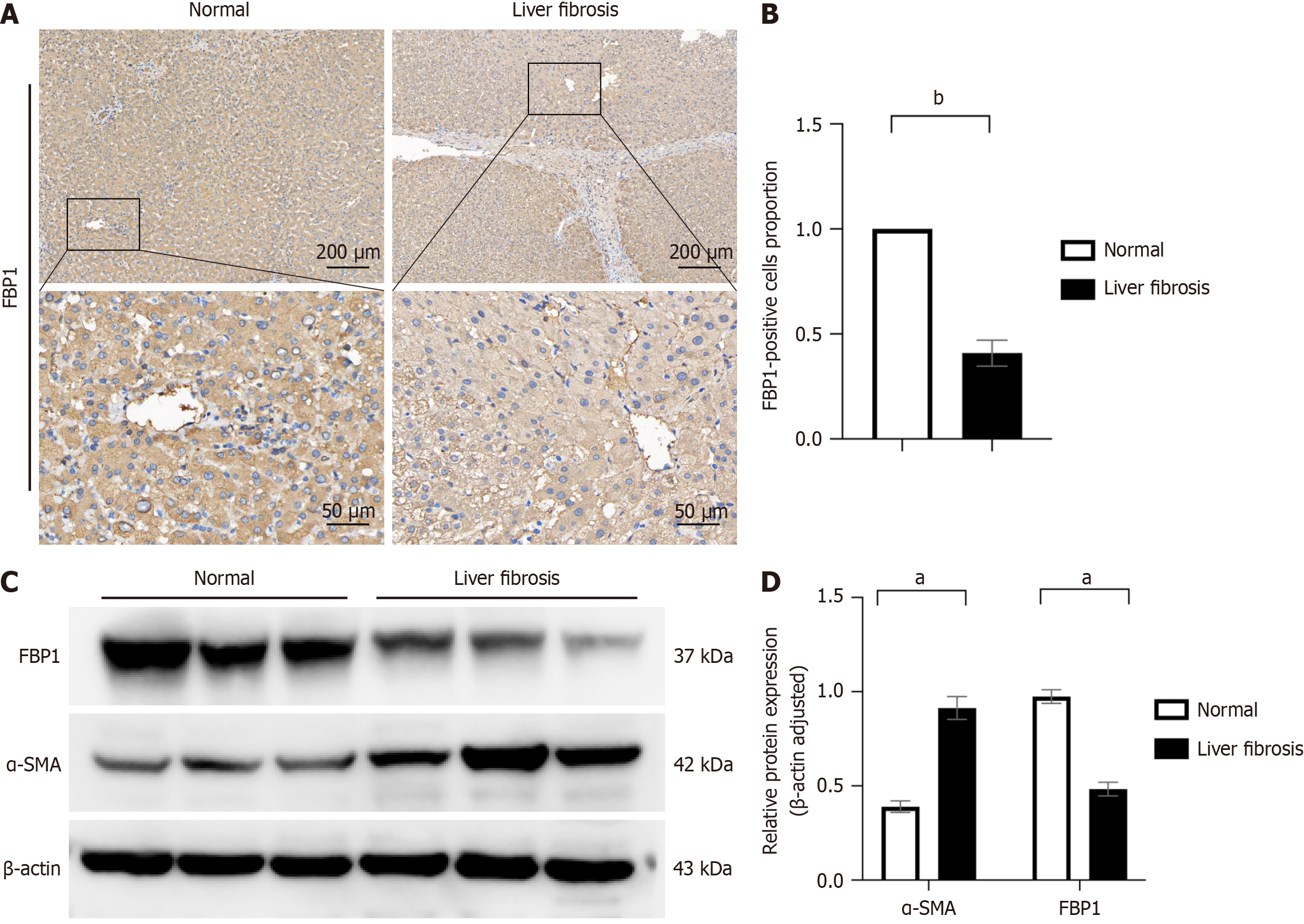
Figure 7 Decreased expression of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 in patients with liver fibrosis.
A: Hepatic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1) expression was examined by immunohistochemistry in patients with liver fibrosis and controls; B: Immunohistochemical staining was statistically analyzed to quantify the number of positive cells in each group; C: Expression of hepatic fibrosis marker alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and FBP1 was detected by Western blot analysis in patients with liver fibrosis and controls; D: Grayscale values of the respective protein bands were analyzed, and statistical significance relative to the normal group was assessed. All data are from three independent samples. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.001.
- Citation: Wu HY, Han L, Ran T, Sun Y, Zhang QX, Huang T, Zou GL, Zhang Y, Zhou YM, Lin GY, Chen SJ, Wang JL, Pan C, Lu F, Pu HF, Zhao XK. FBP1 as a key regulator of focal adhesion kinase-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation: Multi-omics and experimental validation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(28): 107361
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i28/107361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361