Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2025; 31(28): 107361
Published online Jul 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361
Published online Jul 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361
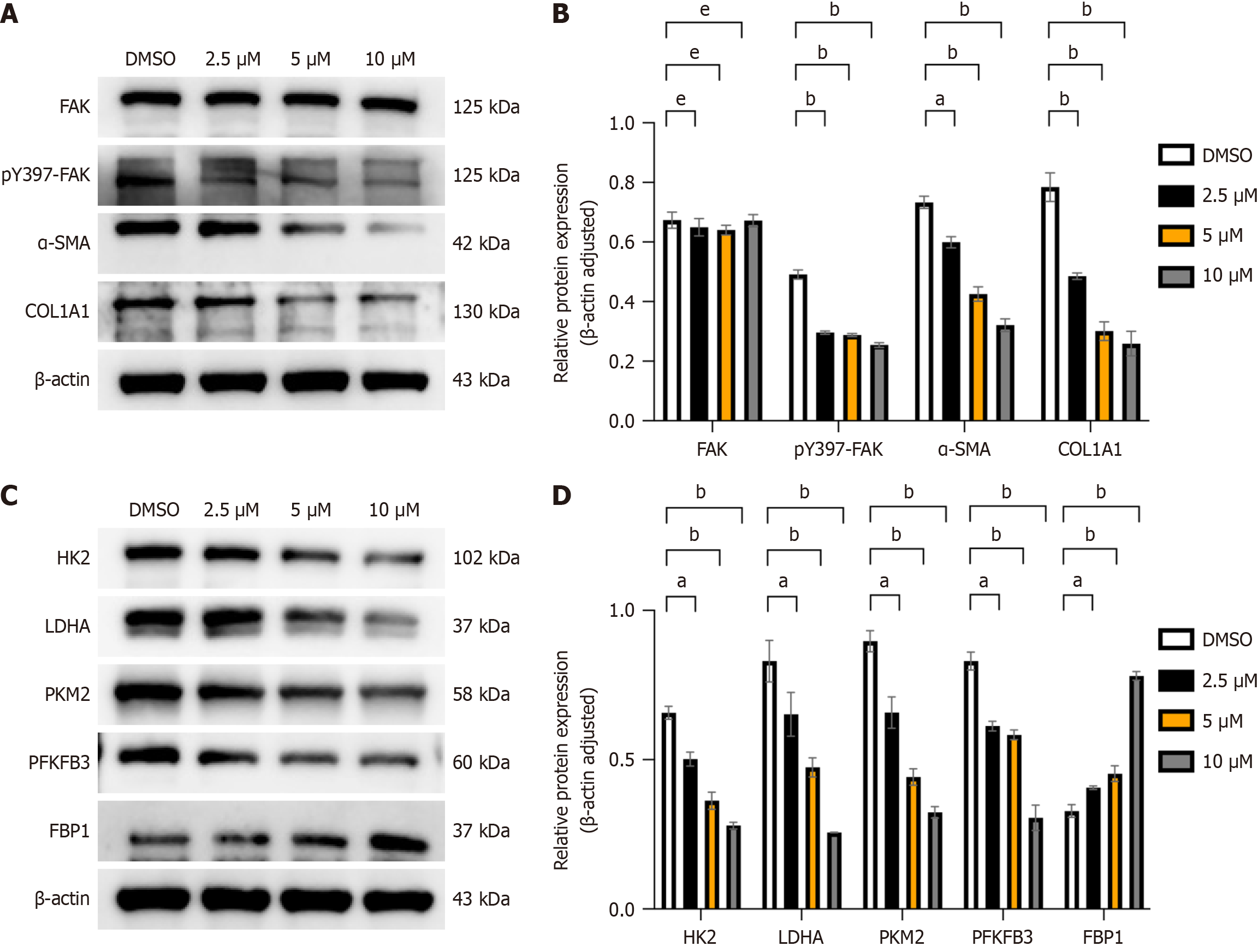
Figure 5 Focal adhesion kinase inhibitors can modulate the activation, migration, and aerobic glycolysis of hepatic stellate cells.
A: After adding focal adhesion kinase (FAK) inhibitor at different concentrations (2.5 μM, 5 μM, 10 μM), proteins were extracted, and Western blot (WB) analysis was performed to detect the expression of liver fibrosis markers collagen type 1, alpha 1 (COL1A1) and alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), as well as FAK and phosphorylated FAK (p-FAK) proteins, with β-actin serving as the internal control; B: Grayscale value analysis was conducted, and statistical significance relative to the control (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]) group was assessed; C: WB analysis was employed to detect the protein expression of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), hexokinase 2 (HK2), phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3), pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1) in each group; D: Grayscale value analysis was performed for each proteome, and statistical significance relative to the control (DMSO) group was evaluated. All data are from three independent samples. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001; dP < 0.0001; eNot significant.
- Citation: Wu HY, Han L, Ran T, Sun Y, Zhang QX, Huang T, Zou GL, Zhang Y, Zhou YM, Lin GY, Chen SJ, Wang JL, Pan C, Lu F, Pu HF, Zhao XK. FBP1 as a key regulator of focal adhesion kinase-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation: Multi-omics and experimental validation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(28): 107361
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i28/107361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361