Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2025; 31(28): 107361
Published online Jul 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361
Published online Jul 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361
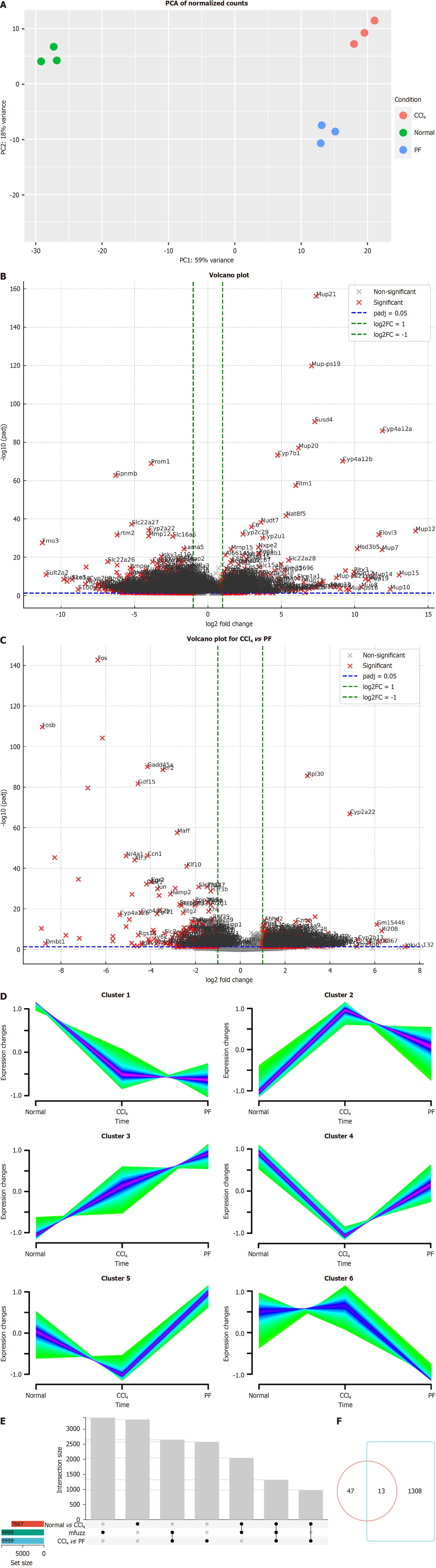
Figure 1 Transcriptomics analysis of differential gene expression.
A: Principal component analysis (PCA) of normalized counts PCA showing gene expression variance among normal, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), and PF562271 (PF) conditions. The first principal component (PC1) explains 59% of the variance, and PC2 explains 8%; B: Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the normal and CCl4 groups. Significant genes (log2 fold change > 1 or < -1, P < 0.05) are highlighted; C: Volcano plot comparing gene expression between the CCl4 and PF groups. Significant genes are marked similarly; D: Mfuzz clustering of gene expression. Six gene clusters showing expression changes across the normal, CCl4, and PF groups, highlighting condition-specific gene regulation; E: UpSet plot showing the overlap of DEGs between comparisons; F: Venn diagram showing unique and shared DEGs between the normal vs CCl4 and CCl4vs PF groups.
- Citation: Wu HY, Han L, Ran T, Sun Y, Zhang QX, Huang T, Zou GL, Zhang Y, Zhou YM, Lin GY, Chen SJ, Wang JL, Pan C, Lu F, Pu HF, Zhao XK. FBP1 as a key regulator of focal adhesion kinase-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation: Multi-omics and experimental validation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(28): 107361
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i28/107361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.107361