Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2025; 31(27): 109239
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109239
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109239
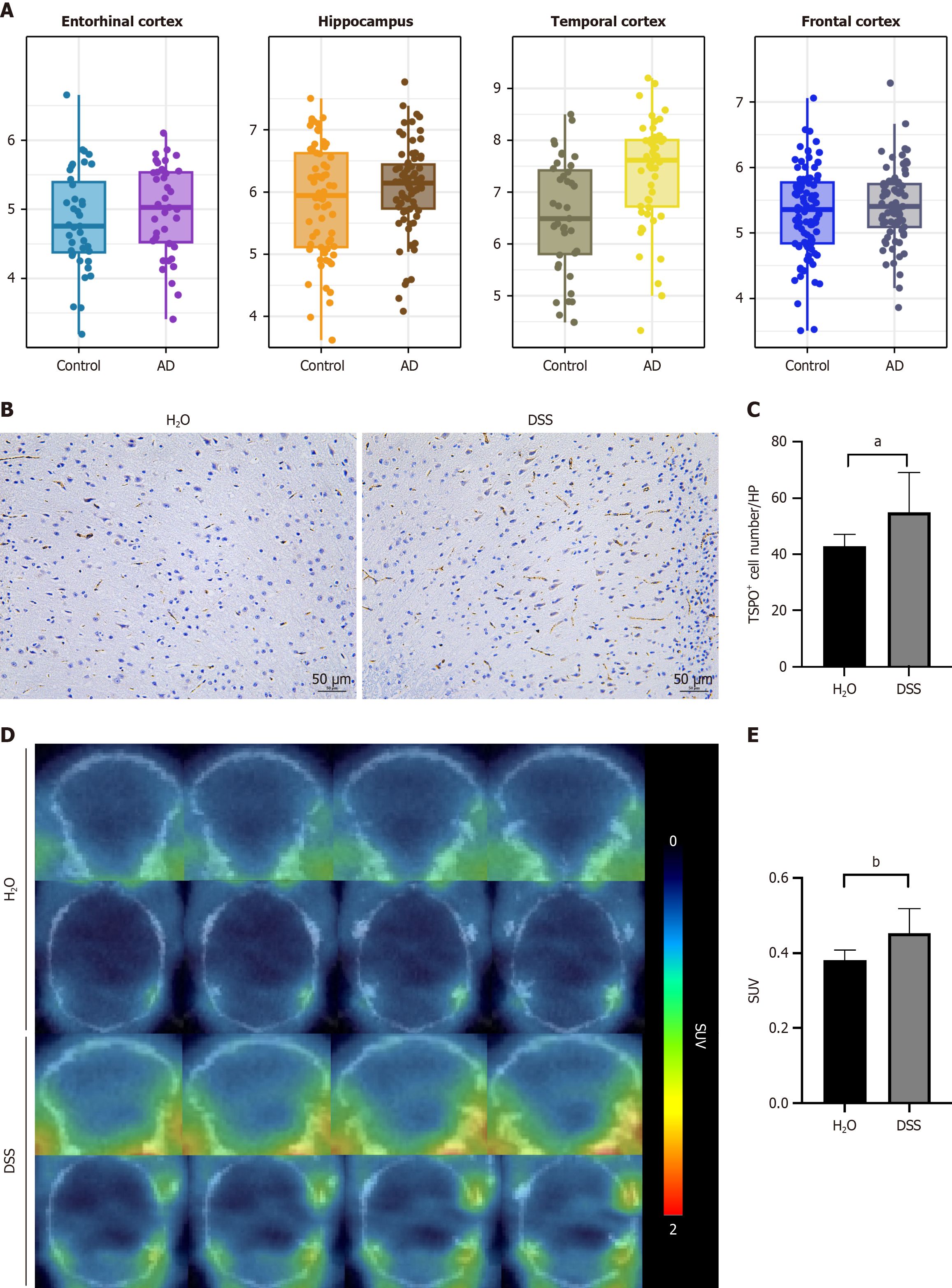
Figure 6 Translocator protein expression is significantly increased in the mouse brain after dextran sodium sulfate treatment.
A: For patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), the AlzData database is utilized, which includes integrated analysis of gene expression profiles from 684 patients with AD and 562 control brain tissues. This analysis generates a comprehensive gene expression profile of brain tissues and a catalog of susceptibility genes associated with AD. Separate analyses are conducted for four distinct brain regions affected by AD, including the entorhinal cortex, hippocampus, temporal cortex, and frontal cortex. The results reveal a significant increase in translocator protein (TSPO) expression in the temporal cortex of patients with AD compared with healthy controls. In other brain regions, TSPO expression in patients with AD shows an increasing trend, although the differences do not reach statistical significance; B and C: Immu
- Citation: He Q, Wu XH, Jiang DL, Lin RT, Xie F, Guan YH, Fei AH. Translocator protein facilitates neutrophil-mediated mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(27): 109239
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i27/109239.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109239