Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2025; 31(27): 109239
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109239
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109239
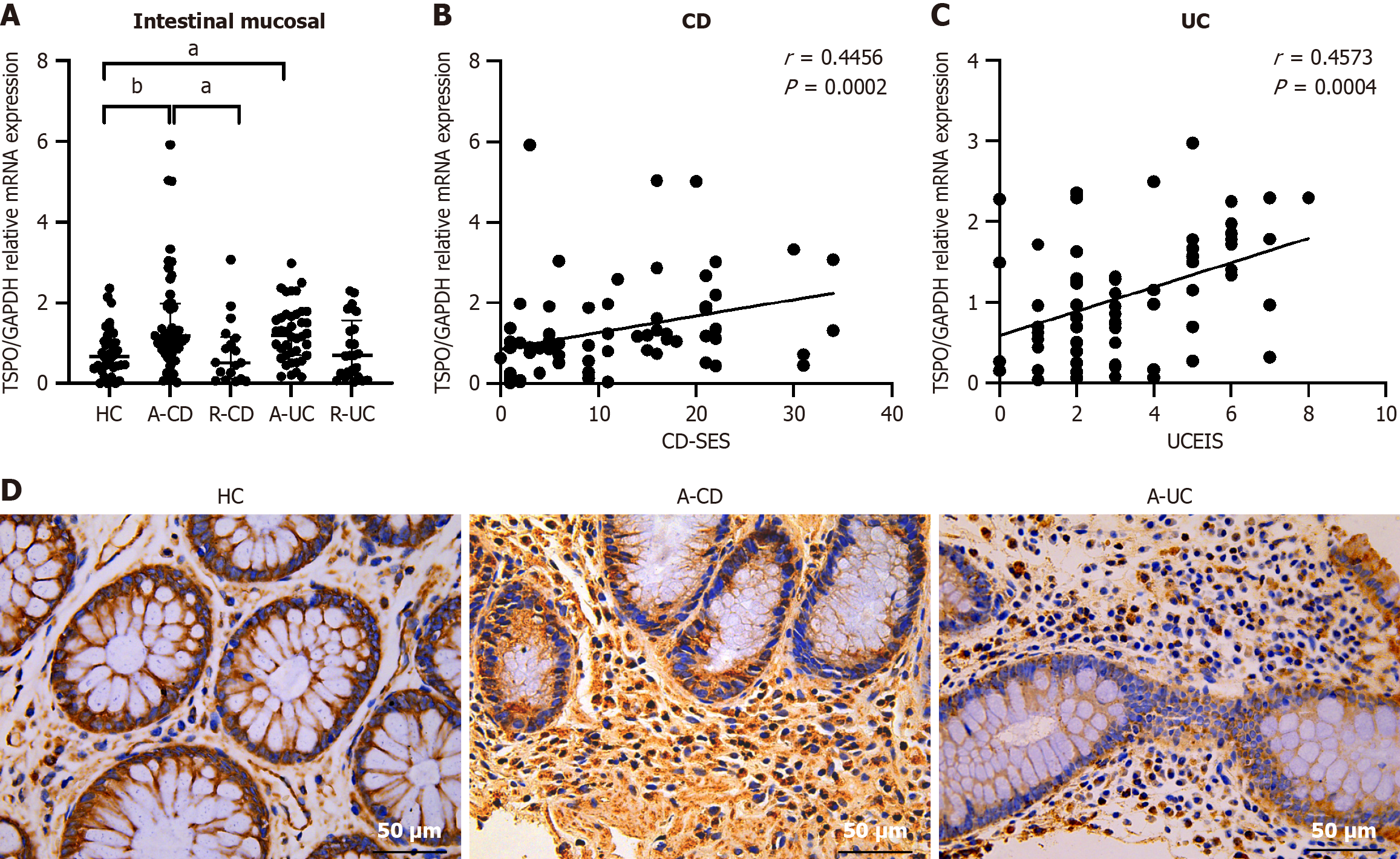
Figure 2 Expression of translocator protein in the intestinal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases.
A: Intestinal mucosa samples are collected from healthy controls (n = 35), patients with active Crohn's disease (CD) (n = 47), those with CD in remission (n = 18), those with active ulcerative colitis (UC) (n = 40), and those with UC in remission (n = 25). Total RNA is extracted and translocator protein (TSPO) mRNA expression is analyzed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; B and C: Correlation analysis of TSPO intestinal mucosa expression with endoscopic scores for inflammatory bowel diseases (Simple Endoscopic Score for CD/Ulcerative Colitis Endoscopic Index of Severity); D: Immunohistochemical assessment of TSPO expression in the intestinal mucosa. Original magnification 400 ×. n: The biologically independent replicates used in the statistical analyses. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. A-CD: Active Crohn's disease; A-UC: Active ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn's disease; CD-SES: Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's disease; HC: Healthy controls; R-CD: Crohn's disease in remission; R-UC: Ulcerative colitis in remission; TSPO: Translocator protein; UC: Ulcerative colitis; UCEIS: Ulcerative Colitis Endoscopic Index of Severity.
- Citation: He Q, Wu XH, Jiang DL, Lin RT, Xie F, Guan YH, Fei AH. Translocator protein facilitates neutrophil-mediated mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(27): 109239
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i27/109239.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109239