Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2025; 31(27): 109105
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109105
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109105
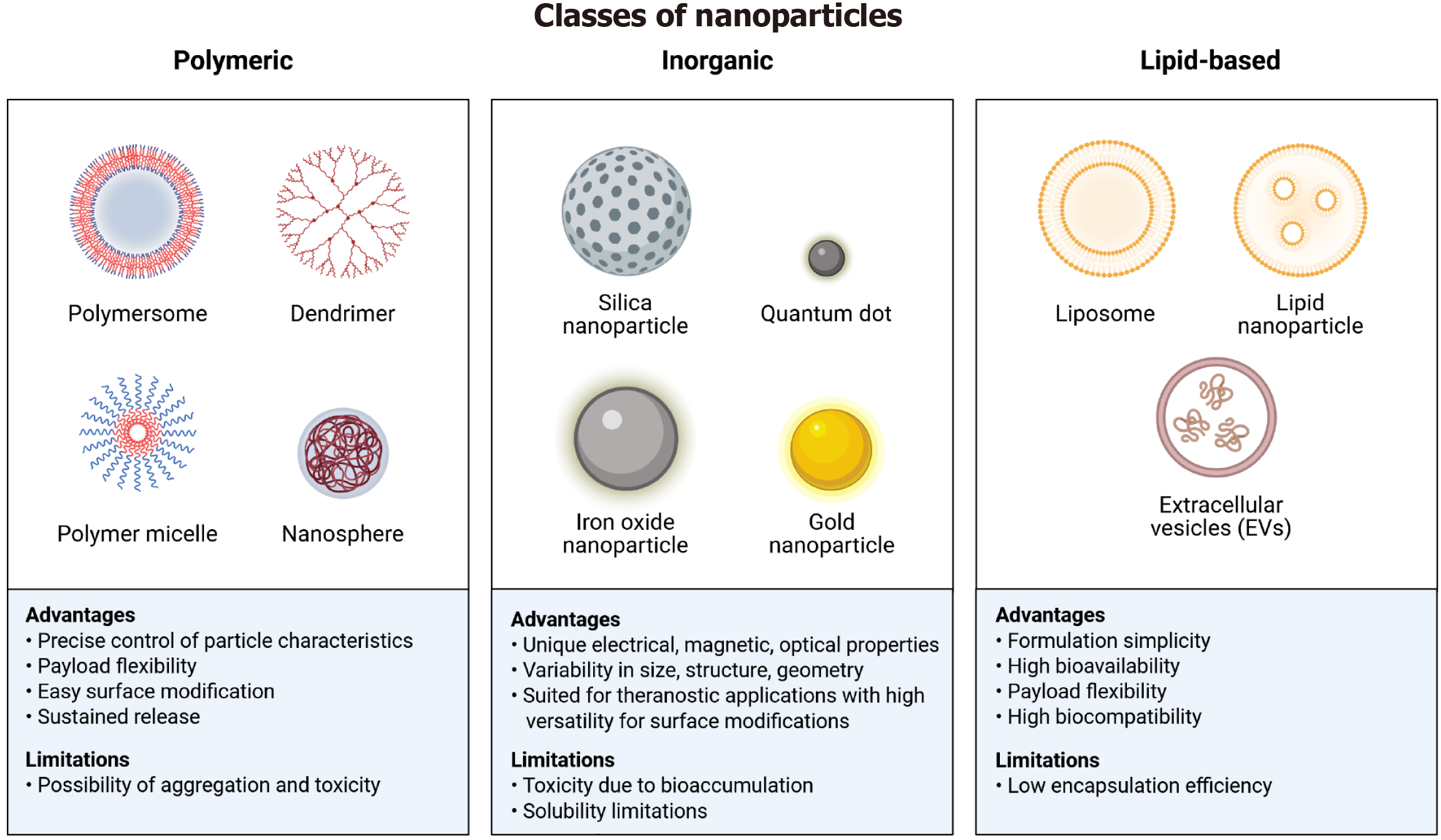
Figure 2 Classification of different types of nanoparticles with their specific advantages and disadvantages.
The figures enlist three major types of nanoparticles: Polymeric, inorganic, and lipid-based. The polymeric nanoparticles include polymersomes, dendrimers, polymer micelles, and nanospheres. Advantages of polymeric nanoparticles are precise control, flexibility, surface modification, and sustained release; while the limitations include risk of toxicity and aggregation. The inorganic nanoparticles comprise silica nanoparticles, quantum dots, iron oxide nanoparticles, and gold nanoparticles. Their advantages are the unique physicochemical properties, tailored design, and versatility. Their solubility and toxicity might pose challenges in delivery. The lipid-nanoparticles can be subdivided into liposomes, lipid nanoparticles, and extracellular vesicles. They offer advantages such as simplicity, high bioavailability, payload flexibility, and high biocompatibility, whereas the low encapsulation remains a limitation. Created with a license from BioRender.com.
- Citation: Khurana A, Hartmann P. Gut microbiome-specific nanoparticle-based therapeutics for liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(27): 109105
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i27/109105.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.109105