Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2025; 31(27): 108483
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.108483
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.108483
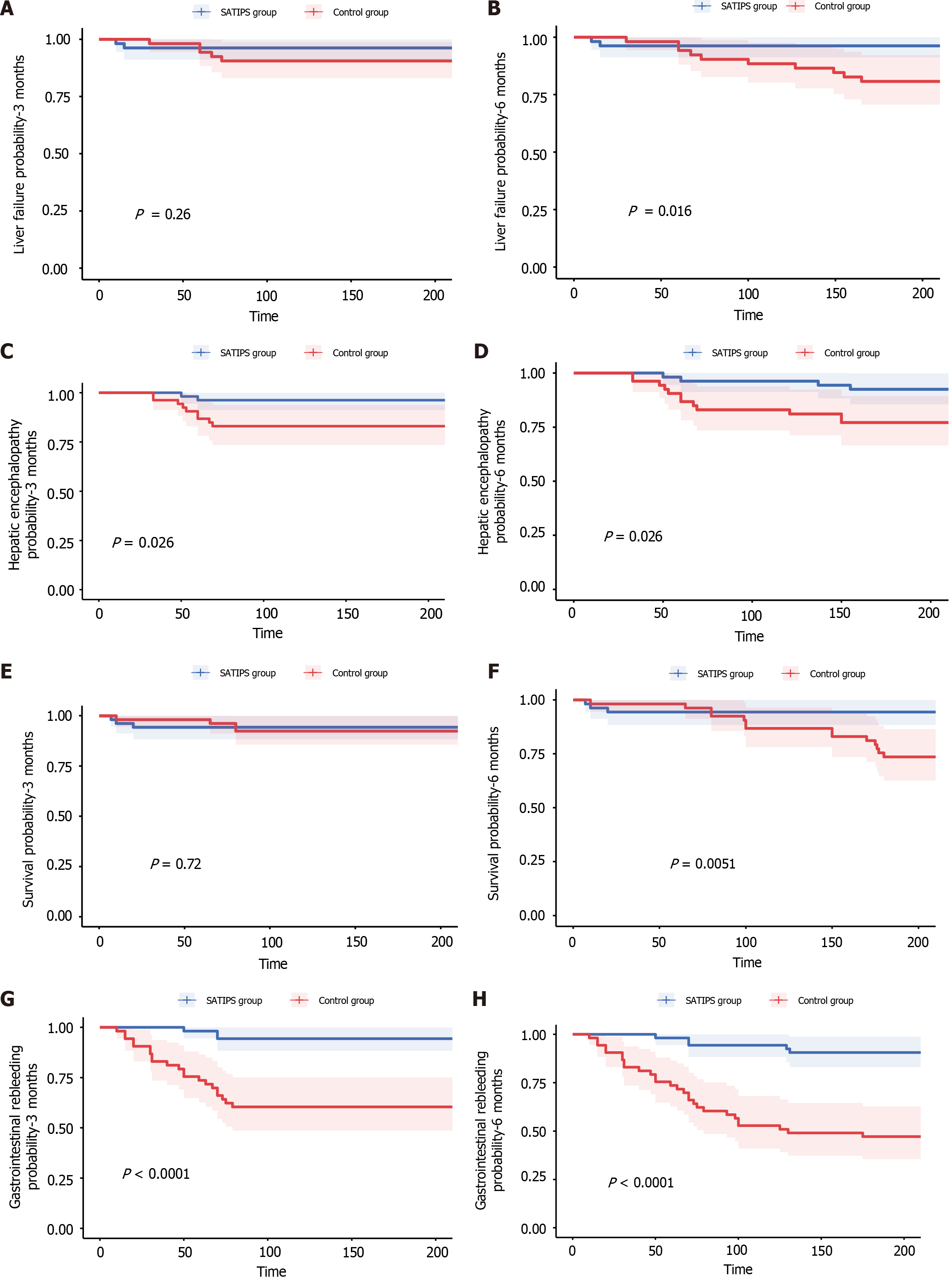
Figure 2 Survival, hepatic encephalopathy, gastrointestinal rebleeding and liver failure incidence curves between the surgically assisted transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt group and control group.
A and B: Incidence curves of liver failure at three and six months in the two groups; C and D: Incidence curves of hepatic encephalopathy at three and six months in the two groups; E and F: Survival curves at three and six months in the two groups; G and H: Incidence curves of gastrointestinal rebleeding at three and six months in the two groups. SATIPS: Surgically assisted transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
- Citation: Wu YF, Yue ZD, Fan ZH, Dong CB, Zhang Y, Li QM, Liu DF, Xu GZ, Wang DZ, Zhao HM, Wu ZP, Wang L. Clinical efficacy of surgically assisted transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for cavernous transformation of portal vein. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(27): 108483
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i27/108483.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.108483